Probability of Compound Events PowerPoint
advertisement
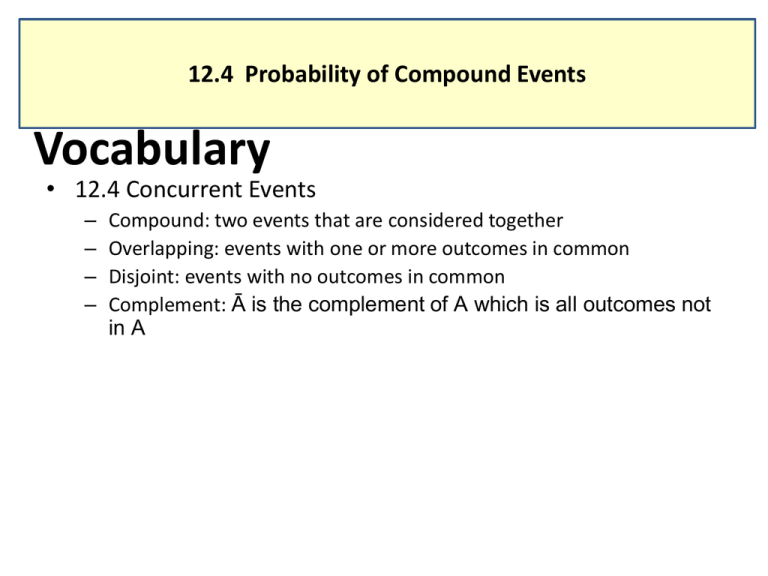
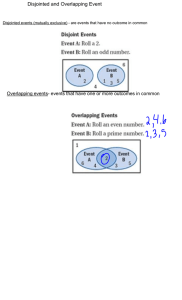
12.4 Probability of Compound Events Vocabulary • 12.4 Concurrent Events – – – – Compound: two events that are considered together Overlapping: events with one or more outcomes in common Disjoint: events with no outcomes in common Complement: Ā is the complement of A which is all outcomes not in A Compound Events • Compound: two events that are considered together on one trial – Overlapping events have one or more outcomes in common – Disjoint events have no outcomes in common (often called mutually exclusive) • Compound events will generally use the word ‘or’. (What is the probability of this or that happening when I …) Overlapping Events • Overlapping events have one or more outcomes in common – Ex: a number thrown on a fair 6-sided die is < 4 or it is odd (1 and 3 satisfy both conditions) – Ex: A card is drawn and it is a number (like 4) or a suit (like hearts) Probability of Overlapping Events • If A and B are two overlapping events, then the probability of A or B is: P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A and B) A B = A + B A&B (Each possibility must be accounted for once and only once) SAT Test Practice • A card is randomly selected from a standard deck of 52 cards. What is the probability that it is a face card or a spade? Deck of Cards Face card Spade Deck of Cards = Face card Deck of Cards + Spade Deck of Cards Both A. ³/₅₂ B. ¹⅟₂₆ C. ²⁵/₅₂ D. ⁷/₁₂ Disjoint Events • Disjoint events have no outcomes in common (often called mutually exclusive) – Ex: A fair 12-sided die is rolled. What is the probability it will land with a 5 or a 9 up? – Ex: a disk is drawn from a cup of 5 red, 6 blue, 4 green, and 5 yellow. What is the probability that the disk is yellow or green? Probability of Disjoint Events • If A and B are two disjoint events, then the probability of A or B is: P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) A B = A + B (Each possibility must be accounted for once and only once) Find Probability of Disjoint Events • A card is randomly selected from a standard deck of 52 cards, What is the probability that it is a 10 or a face card? Deck of Cards 10 Face card = Deck of Cards Deck of Cards 10 Face card + Use a formula to find P(A and B) • Out of 200 students in a senior class, 113 students are either varsity athletes or on the honor roll. There are 74 seniors who are varsity athletes and 51 seniors who are on the honor roll. – What is the probability that a randomly selected senior is both a varsity athlete and on the honor roll? Seniors Honor Role Varsity Athlete = Honor Role + Varsity Athlete Both Try these: A card is randomly drawn from a standard deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of the given event. •Selecting an ace or an eight •Selecting a 10 or a diamond •In the senior class example, suppose 32 seniors are in band and 64 seniors are in the band or on the honor roll. What is the probability that a randomly selected senior is both in the band and on the honor roll? Compliments • Ā is the compliment of A, which is all outcomes not in A. Ā A A is everything in the pink circle. Ā is everything in the blue region • The probability of Ā is: P(Ā) = 1 – P(A) Find Probabilities of compliments When two six sided dice are rolled, there are 36 possible outcomes. Find the probability of: a. The sum is not 6 P(sum not 6) = 1 – P(sum is 6) b. The sum is less than or equal to 9 P(sum ≤ 9) = 1 –[P(sum is 10)+P(sum is 11)+P(sum is 12)] Use a Compliment in real life • A restaurant gives a free fortune cookie to every guest. The restaurant claims there are 500 different messages hidden inside the fortune cookies. – What is the probability that a group of 5 people receive at least 2 fortune cookies with the same message? P(at least 2 fortunes match) = 1 – P(0 matches) • HW 48: pg 727, 17-27 odd, 28-41 all