inherent zero
advertisement

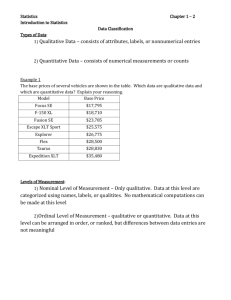
1.2 Stuff Qualitative data consists of attributes, labels, or nonnumeric entries. Quantitative data consists of numerical measurements or counts. 1.2: Qualitative or Quantitative? telephone numbers in a directory (#7) heights of hot air balloons (#8) player numbers for a soccer team (#13) 1.2 Stuff Data at the nominal level of measurement are qualitative only. Data at this level are categorized using names, labels, or qualities. No mathematical computations can be made at this level. Data at the ordinal level of measurement are qualitative or quantitative. Data at this level can be arranged in order, or ranked, but differences between data entries are not meaningful. 1.2 Stuff An inherent zero is a zero that implies “none” Examples: $0 0 inches NOT examples: 0 degrees Year 0 1.2 Stuff Data at the interval level of measurement can be ordered, and meaningful differences between data entries can be calculated. At this level, a zero entry simply represents a position on a scale (the entry is not an inherent zero). Data at the ratio level of measurement are similar to data at the interval level, with the added property that a zero entry is an inherent zero. A ratio of two data values can be formed so one data value can be expressed as a multiple of another. 1.2 Stuff Put data in categories Arrange data in order Subtract data values Determine if one data value is a multiple of another Nominal Yes No No No Ordinal Yes Yes No No Interval Yes Yes Yes No Ratio Yes Yes Yes Yes Level of Measurement 1.2: Case Study answers 6) “Rating”, “Share”, “Audience” … inherent zero and “twice as much” 5) “Day, Time” 4) “Rank”, “Rank last week” 3) “Program name”, “Network” 2) divide 20,000 by 114.5 million = .009% 8) shows to consider cancelling … price of advertising minutes …