Data Classification
advertisement

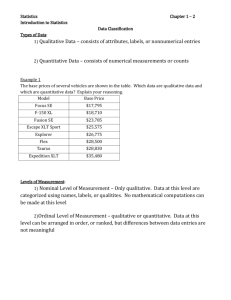
Data Classification DATA classification Qualitative Data: consists of attributes, labels, or nonnumerical entries. Examples: red, Mr. Smith, Dogs Quantitative Data: consists of numerical measurements or counts. Examples: 5.5 inches, 10, $23,290 Qualitative VS Quantitative Telephone number Qualitative Length of a song Quantitative Responses in an opinion poll Qualitative Inherent zero An inherent zero represents the position on the number line. Not an inherent zero implies that there are none. 4 levels of Measurement Nominal Are Qualitative only Can be categorized by names, labels, or qualities Can’t do mathematical calculations Example: Colors, Music Ordinal Are Qualitative and Quantitative Can be put in order or ranked, but difference between them are meaningless. Examples: Top 5 teachers, movies 4 levels of Measurement Interval Can be ordered and you can calculate meaningful differences. Zero is not an inherent zero. Examples: 1999, 2001, 2004, 2008, 2009, 2010 Temperature Ratio Is similar to interval but 0 is an inherent zero. Find ratios of values Can’t go below zero. Examples: Red Sox: 128 homeruns, Pirates: 78 homeruns Precipitation Examples Body temperature in Fahrenheit of a swimmer interval Collection of phone numbers nominal Final standings for football Northeaster Conference ordinal Heart rate (beats per minute) of an athlete. Ratio Chart Levels of Measurement Put data in categories Arrange data in order Subtract data values Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio Yes Yes Yes Yes No yes yes Yes No No Yes Yes Homework: pg 15: 8- 24 Even Determine if one data valuse is a multiple of another No No No Yes