Chapter 4
advertisement

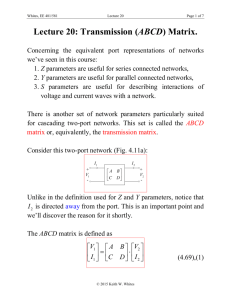
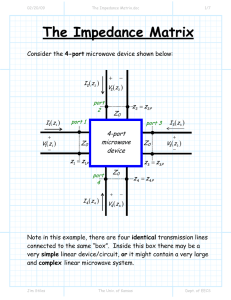
ELCT564 Spring 2013 Chapter 4: Microwave Network Analysis 4/13/2015 ELCT564 1 Equivalent Voltages and Currents Voltage is proportional to the transverse electric field Current is proportional to the transverse magnetic field The product of equivalent voltage and current is the power flow The ratio of the voltage to the current should be equal to the characteristic impedance of the line 4/13/2015 ELCT564 2 Impedance Matrices Reciprocal Networks Lossless Networks 4/13/2015 ELCT564 3 Example 4/13/2015 ELCT564 4 The Scattering Matrix 4/13/2015 ELCT564 5 The Scattering Matrix 4/13/2015 ELCT564 6 The Scattering Matrix Reciprocal Networks 4/13/2015 Lossless Networks ELCT564 7 Example: The Scattering Matrix A two port network is known to have the following scattering matrix: Determine if the network is reciprocal, and lossless. If port two is terminated with a matched load, what is the return loss seen at port 1? If port two is terminated with a short circuit, what is the return loss seen at port 1? -0.452 6.9dB 4/13/2015 ELCT564 8 Reference Plane 4/13/2015 ELCT564 9 The Transmission (ABCD) Matrix 4/13/2015 ELCT564 10 The ABCD Parameters Examples 4/13/2015 ELCT564 11 ABCD Parameters Relation to Impedance Matrix 4/13/2015 ELCT564 12 ABCD Parameters Relation 4/13/2015 ELCT564 13 Signal Flow Graph Nodes: Each port, I, of a microwave network has two nodes, ai and bi. Node ai is identified with a wave entering port I, while node bi is identified with a wave reflected from port i. The voltage at a node is equal to the sum of all signals entering that node. Branches: A branch is a directed path between two nodes, representing signal flow from one node to another. Every branch has an associated S parameter or reflection coefficient. 4/13/2015 ELCT564 14 Signal Flow Graph Representations 4/13/2015 ELCT564 15 Signal Flow Graph Rules Series rule Parallel rule Self-loop rule Splitting rule 4/13/2015 ELCT564 16 Signal Flow Graph Example Use signal flow graphs to derive expressions for Гin and Гout for the two-port network shown in the above Figure. 4/13/2015 ELCT564 17 Signal Flow Graph Example Use signal flow graphs to derive expressions for Гin and Гout for the two-port network shown in the above Figure. 4/13/2015 ELCT564 18 TRL Network Analyzer Calibration 4/13/2015 ELCT564 19 Microstrip Discontinuities 4/13/2015 ELCT564 20