Sales-Variance Analysis
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Customer Revenues
Price discounting is the reduction of
selling prices to encourage increases in
customer purchases
Lower sales price is a tradeoff for larger sales
volumes
Discounts should be tracked by customer
and salesperson
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
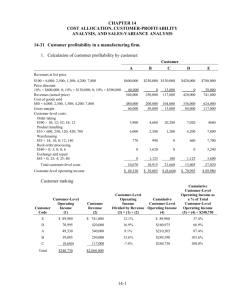
Customer Profitability Analysis Illustrated
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Sales Variances
Level 1: Static-budget variance – the
difference between an actual result
and the static-budgeted amount
Level 2: Flexible-budget variance –
the difference between an actual
result and the flexible-budgeted
amount
Level 2: Sales-volume variance
Level 3: Sales Quantity variance
Level 3: Sales Mix variance
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Sales-Mix Variance
Measures shifts between selling
more or less of higher or lower
profitable products
Sales-Mix
Variance =
Actual
Actual
Units of
X Sales-Mix
All
Percentage
Products
Sold
Budgeted
Sales-Mix X
Percentage
(c) 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Budgeted
Contribution
Margin per Unit
Sales-Quantity Variance
SalesQuantity =
Variance
Actual
Units of All
Products
Sold
Budgeted
Units of all
Products X
Sold
Budgeted
Sales-Mix
Percentage
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
X
Budgeted
Contribution
Margin per Unit
Flexible-Budget and Sales-Volume
Variances Illustrated
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Sales-Mix and –Quantity Variances
Illustrated
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Market-Share Variance
MarketShare
=
Variance
Actual
Actual
Market
X Market
Size in
Share
Units
Budgeted
Market X
Share
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Budgeted
Contribution
Margin per
Composite Unit
for Budgeted
Mix
Market-Size Variance
Market-Size
Variance =
Actual
Market
Size
Budgeted
Market X
Size
Budgeted
Market
Share
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
X
Budgeted
Contribution
Margin per
Composite Unit
for Budgeted
Mix
Market-Share and –Size Variances
Illustrated
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Market-Share and Market-Size Variances
Limitation: reliable information on
the actual size and share of various
markets is not always available
These are considered Level 4
variances (a decomposition of the
Sales-Quantity variance
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Sales Variances Summarized
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
Analysis of Profit Related
Variances
6
Sales price variance = (actual price – expected price)
X Quantity sold
Price Volume Variance = (Actual volume –
Expected volume) X expected price
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
18-14
Analysis of Profit Related
Variances
6
Contribution Margin Variance = Annual contribution
margin - Budgeted contribution margin
Contribution margin volume variance = (Actual
quantity sold – Budgeted quantity sold) X
Budgeted average unit contribution margin
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
18-15
Analysis of Profit Related
Variances
6
Sales Mix Variance = [(Product 1 actual units –
Product 1 budgeted units) X (Product 1 budgeted unit
contribution margin – Budgeted average unit
contribution margin] + [(Product 2 actual units –
Product 2 budgeted units) X (Product 2 budgeted unit
contribution margin – Budgeted average unit
contribution margin]
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
18-16
Analysis of Profit Related
Variances
6
Market Share Variance = [(Actual market share
percentage – Budgeted market share percentage) X
(Actual industry sales in units)] X ( Budgeted
average unit contribution margin)
Market Size Variance = [(Actual industry sales in
units – Budgeted industry sales in units) X
(Budgeted market share percentage)] (Budgeted
average unit contribution margin)
© 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.
18-17