Presbyopia
advertisement

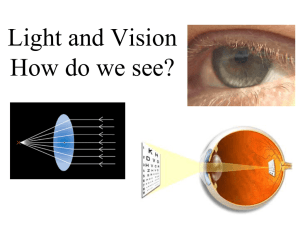
Presbyopia Walter Huang, OD Yuanpei University Department of Optometry Definition Latin definition Presbyopia = “old man’s eye” Definition Decrease in the amplitude of accommodation or loss of accommodative ability with age Etiology Natural part of the aging process Onset at approximately 40 years of age and over though may be earlier in low hyperopes Progression Once presbyopia occurs, it increases over a period of 10 to 12 years, after which it stabilizes Symptoms Blurry vision at near Difficult or impossible to accommodate sufficiently for near work Increasing Near Point of Accommodation with Age Age (years) Distance (cm) 10 7 20 10 30 14 40 20 50 40 Amplitude of Accommodation and Age (Donder’s Table) Age (years) Amplitude (D) Age (years) Amplitude (D) 10 14.00 45 3.50 15 12.00 50 2.50 20 10.00 55 1.75 25 8.50 60 1.00 30 7.00 65 0.50 35 5.50 70 0.25 40 5.00 75 0.00 Near Work Comfortable vision at near uses less than or equal to half of the available amplitude of accommodation Near work becomes difficult when the amplitude of accommodation is less than 5.00D Example Working distance at 40 cm requires 2.50D of accommodation Patient A has 5.00D of accommodation He can use up to 2.50D of accommodation comfortably Therefore, he has just enough accommodative power for reading at 40 cm, and no reading glasses are required Patient B has 3.00D of accommodation He can use up to 1.50D of accommodation comfortably Therefore, he needs an additional 1.00D of accommodative power for reading at 40 cm, and +1.00D reading glasses are required Management Converging or plus lenses for near work only in spectacles or contact lenses Changes in prescriptions are required every two to three years for presbyopia Surgery Management Spectacles Single vision reading glasses Multifocal lenses containing near Add Bifocal lenses Trifocal lenses Progressive addition lenses Management Contact lenses Single vision contact lenses with glasses Monovision contact lenses Bifocal and multifocal contact lenses Modified monovision contact lenses Management Surgery Laser in-situ keratomileusis (LASIK) More for presbyopic hyperopia than presbyopia myopia at the moment Multifocal intraocular lens (IOL) Conductive keratoplasty (monovision) Scleral expansion