Presentation One
advertisement

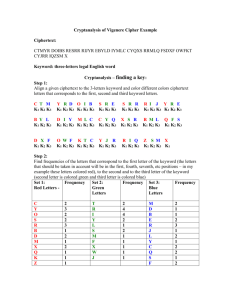
Vigenére Cipher Kimberly Chiffens & Maria Jannelli Progress Report •Implementation of Vigenere encryption and decryption •Applet design •Implementation of Friedman attack to find key length •Apply cryptanalysis algorithms Friedman Attack Key Length • Uses frequencies to count the amount of each letter in the ciphertext • We multiply the count of each letter by count minus 1 and then add up the sum. • It computes the sum of the frequencies as follows: • for(int k = 0; k < 26; k++) • sum = sum + Fcount[k]*(Fcount[k]-1); • } Friedman Attack Index of Coincidence • To find this we divide the entire sum of the frequencies withThe the length of the cipher probability of choosing an 1. identical The probability thatlength a times the minus The probability that pair of letters from a letter selected at two randomly selected pool in which there random is an “A” sum/(length*(length-1)); • index= letter in the English are equal numbers of alphabet letters are the respective letters • Then we must calculate the key length. identical To do so we use this equation: • keyword= ((0.0265*length)/((0.065index)+(length*(index-0.0385)))); Friedman Example Ciphertext: KSMEHZBBL KSMEMPOGA JXSEJCSFL ZSY Frequencies: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 1 2 1 0 3 1 1 1 0 2 2 2 3 0 1 1 0 0 5 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 Length = 30 letters ((0.0265*length)/((0.065keyword= index)+(length*(index Key: RELATIONS -0.0385)))); Plaintext: TOBEORNOT TOBETHATIST HEQUEST ION Cryptanalysis Step One: Find the key length Step Two: Generate possible keys C T M K1 K2 K3 Y R D O I B K1 K2 K3 K1 K2 K3 S R E K1 K2 K3 S R R R I J Y R E K1 K2 K3 K1 K2 K3 K1 K2 K3 B Y L K1 K2 K3 D I Y M L C K1 K2 K3 K1 K2 K3 C Y Q K1 K2 K3 X S R R M L Q F S K1 K2 K3 K1 K2 K3 K1 K2 K3 D X F K1 K2 K3 O W F K T C K1 K2 K3 K1 K2 K3 Y J R K1 K2 K3 R I Q Z S M X K1 K2 K3 K1 K2 K3 K1 Cryptanalysis Set 1: Frequency Set 2: Red Letters Green Letters C 2 T Y 3 R O 2 I S 2 Y R 3 L B 1 S D 2 M M 1 F X 2 X Q 1 W K 1 J Z 1 Frequency Set 3: Blue Letters 2 M 4 D 4 B 2 E 1 R 2 J 1 L 1 Y 1 C 1 Q 1 S F Frequency 2 1 1 2 3 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 Cryptanalysis Most frequent letters of the English alphabet: E, T, N, O, R, I, A, S Ciphertext letter Possible plaintext Corresponded keyletter word letter Possible first letter of the keyword Y E U Y T F Y N L Y O K Y R H Y I Q Y A Y Y S G Cryptanalysis Ciphertext letter Possible plaintext letter Corresponded key-word letter Possible second letter of the keyword R R R R R R R R E T N O R I A S N Y E D A J R Z Cryptanalysis Corresponded keyword letter Possible first letter of the keyword U F L K H Q Y G Corresponded key-word letter Possible second letter of the keyword N Y E D A J R Z Corresponded keyword letter Possible third letter of the keyword N Y E D A J R Z Create all possible three-letter words by choosing first letter from the first column, second from second column and third from third column. Possible keywords: FED, FEE, FEN, LEA, KEN, KEY, HER…. Cryptanalysis The answer: Deciphering the ciphertext with keyword KEY will give a plaintext: SPOON FEEDING IN THE LONG RUN TEACHES US NOTHING BUT THE SHAPE OF SPOON. References •Principles of Operating Systems: Design and Application, Brian L. Stuart. Course Technology. 2009. •Invitation to Cryptology, Thomas H. Barr. Prentice Hall. 2002.