Globalization and inequality
advertisement

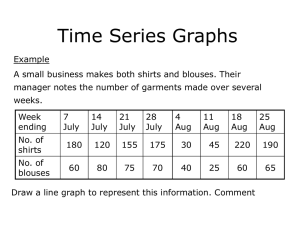
Figure 14.1 Income levels, growth rates and population, 1980–2010 a. Initial income and economic growth, 1980-2010 10 annual growth, 1980-2010 (%) 8 6 Other countries 4 2 0 100 -2 -4 1,000 African countries 10,000 100,000 GDP per capita in 1980 (log scale) -6 Data source: World Development Indicators online; GDP per capita in constant 2000 US $; size of bubble in panel b is proportional to population size in 1980; information for 143 countries depicted, 131 with 1980-2010 information plus 12 countries above 10 million people in 1980 with different time frame (as long as possible); together these countries account for 96 percent of the world population in 1980. Figure 14.1 Income levels, growth rates and population, 1980–2010 b. Initial income, population, and economic growth, 1980-2010 12 annual growth, 1980-2010 (%) 10 8 China Other countries 6 4 India 2 0 100 -2 -4 1,000 African countries 10,000 100,000 GDP per capita in 1980 (log scale) -6 Data source: World Development Indicators online; GDP per capita in constant 2000 US $; size of bubble in panel b is proportional to population size in 1980; information for 143 countries depicted, 131 with 1980-2010 information plus 12 countries above 10 million people in 1980 with different time frame (as long as possible); together these countries account for 96 percent of the world population in 1980. Figure 14.2 Total factor productivity index; 1989 = 100, 1989-2011 Total Factor Productivity index; 1989 = 100, 1989-2011 TFP index 170 166 China 140 Germany 123 USA 110 112 105 Japan 80 1989 1995 2001 2007 Source: author’s calculations based on Conference Board Total Economy Database year 2013 Figure 14.3 Changes in US real income; working adults, by education, 19912010 Bachelor’s degree 20 15 Advanced degree 10 High school 5 Some college 2010 2008 2006 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 -5 1992 0 Source: based on Haskel et al. (2012); cumulative percentage changes relative to 1991 in mean real money earnings for working adults (aged 25 and above) by educational cohort in terms of the highest level of education attained (adjusted for price inflation and smoothed to three-year averages) Figure 14.4 Worker’s remittances received; per cent of GDP, 2010 40 Tajikistan remittances Worker's remittances received (% of GDP) and per cent rank, 2010 Lesotho 30 Kyrgyz Rep Haiti 20 Jamaica Philippines 10 Morocco average 0 0 China Uruguay Chile 10 20 30 Belgium India 40 50 60 Ukraine 70 80 rank 90 Source: based on data from World Development Indicators online; worker’s remittances and compensation of employees received (% of GDP), based on 155 countries 100 Figure 14.5 Labour reallocation between Home and Foreign VMPLhome VMPLforeign wF0 C Ohome wF1 A wH1 wH0 B LH E1 E0 LF Oforeign Figure 14.6 Number of poor people in the developing world, 1981-2008 3,500 a. Number of poor people in developing world; headcount index, million 70 2,901 3,000 2,453 1,906 70.5 60 $2 per day 2,500 2,000 80 b. Number of poor people in developing world; headcount index, % of population 50 $2 per day 52.9 43.6 40 1,500 $1.25 per day 1,281 1,000 $1.25 per day 22.8 20 500 0 1980 30 10 0 1990 2000 2010 1980 1990 2000 2010 Source: author’s calculations based on World Development Indicators online; the developing world consists of developing countries in EAP, ECA, LAC, MENA, SSA, and SA, see the main text. Figure 14.7 Poverty headcount ratio at $ 1.25 a day (PPP), % of population, 1981-2008 Poverty headcount ratio at $1.25 a day (PPP), % of population 80 EAP SSA 60 SA 40 Developing world total 20 LAC MENA ECA 0 1981 1984 1987 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 Source: author’s calculations based on World Development Indicators online; see the main text for regional abbreviations EAP, ECA, LAC, MENA, SSA, and SA 2008 Figure 14.8 Global income distribution, 1970 and 2006 density a. 1970 poverty line 60,000 World 40,000 EA 20,000 SA OECD SSA 0 $50 $500 $5,000 $50,000 Income level; constant 2000 international $, log scale Source: based on Pinkovskiy and Sala-i-Martin (2009); the poverty line corresponds to $312 a year, or $1 a day in 2006 prices; see the main text for abbreviations; note: not all regions are identified in the figures Figure 14.8 Global income distribution, 1970 and 2006 density 120,000 b. 2006 poverty line World 80,000 40,000 EA SA OECD SSA 0 $50 $500 $5,000 $50,000 Income level; constant 2000 international $, log scale Source: based on Pinkovskiy and Sala-i-Martin (2009); the poverty line corresponds to $312 a year, or $1 a day in 2006 prices; see the main text for abbreviations; note: not all regions are identified in the figures Note for publisher: make sure the scales line up correctly horizontally for panels a and b Figure 14.9 The Lorenz curve and the Gini coefficient 1 cumulative income Gini coefficient = A/(A+B) A B 0 0 cumulative population 1 Figure 14.10 Income inequality; Gini coefficient, selected countries, 1981-2010 Gini coefficients for selected countries; per cent 1981-2010 80 maximum 70 60 South Africa Brazil 50 Nigeria 40 Russia India 30 China 20 minimum 10 0 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Source: author’s calculations based on World Development Indicators online; minimum is 19.4 for Czech Republic in 1988; maximum is 74.3 for Namibia in 1993 Figure 14.11 Global income inequality; Gini coefficient, 1970-2006 Global income inequality; Gini coefficient, 1970-2006 0.75 0.70 0.679 0.65 0.612 0.60 0.55 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 Source: based on data from Pinkovskiy and Sala-i-Martin (2009); note: scale does not start at zero 2005 Figure 14.12 Income inequality decomposition; across and within countries, 1970-2000 a. Global income inequality; mean logarithmic deviation, 1970-2000 1.0 b. Global income inequality; Theil index, 1970-2000 1.0 0.8 0.8 within countries within countries 0.6 0.6 0.4 0.4 Source: based on data from Sala-i-Martin (2006). 2000 1997 1994 1991 1988 1985 1982 1976 1973 1970 2000 1997 1994 1991 1988 1985 1982 1979 0.0 1976 0.0 1973 0.2 1970 0.2 1979 across countries across countries Figure 14.13 Development and income inequality, some historical examples Coefficient of variation of regional income 0.6 Sweden, 1920-1961 0.5 Spain, 18601975 0.4 USA, 1840-1960 0.3 0.2 Japan, 1955-1983 0.1 0 2 Source: based on World Bank (2009). 4 6 8 10 12 14 Income per capita (PPP, thousands)