Independent Component Analysis.
advertisement

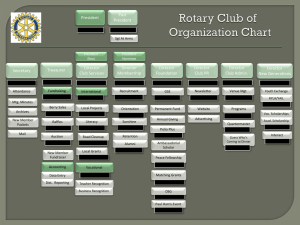
Independent components analysis of starch deficient pgm mutants GCB 2004 M. Scholz, Y. Gibon, M. Stitt, J. Selbig Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Overview Introduction Methods – Principal Component Analysis ICA – Independent Component Analysis Kurtosis PCA Results Summary Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Introduction – techniques visualization techniques supervised biological background information unsupervised present major global information General questions about the underlying data structure. Detect relevant components independent from background knowledge. Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Introduction – techniques PCA dimensionality reduction extracts relevant information related to the highest variance ICA Optimizes independence condition Components represent different nonoverlapping information Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Introduction - experiments Micro plate assays of enzymes form Arabidopsis thaliana. data j Samples i Enzymes pgm mutant vs. wild type continuous night Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Introduction – workflow Data PCA ICA ICs 1st IC j Samples Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 j Samples ICs PC’s j Samples i Enzymes Kurtosis 2nd IC PCA – principal component analysis 4 3 2 Enzyme 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 Enzyme 1 Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 1 2 3 4 PCA – principal component analysis 4 3 2 1. Principal Component Enzyme 2 1 0 -1 -2 2. Principal Component -3 -4 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 Enzyme 1 Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 1 2 3 4 PCA – principal component analysis 4 3 2 2. PC 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1. PC Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 1 2 3 4 PCA – calculation Eigenvalues λ1 Cov-Matrix - mean - mean i Enzymes i Enzymes - mean ... i Enzymes j Samples ... Data-Matrix λi Eigenvectors - mean x1 ... ... xi Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 PCA – dimensionality reduction Selected Components Data Matrix Reduced Data Matrix j Samples Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 j Samples = PCs i Enzymes PCs i Enzymes PCA – principal component analysis 4 3 2 1. Principal Component Enzyme 2 1 0 -1 -2 2. Principal Component -3 -4 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 Enzyme 1 Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 1 2 3 4 PCA – principal component analysis 4 3 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1. PC Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 1 2 3 4 PCA – principal component analysis Minimizes correlation between components. Components are orthogonal to each other. Delivers transformation matrix, that gives the influence of the enzymes on the principal components. PCs ordered by size of eigenvalues of cov-matrix Reduced Data Matrix Selected Components Data Matrix j Samples PCs PCs = Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 i Enzymes i Enzymes j Samples ICA – independent component analysis Mike 1 Person 1 Person 2 microphone signals are mixed speech signals x1 (t ) a11 s1 (t ) a12 s 2 (t ) a13 s3 (t ) x2 (t ) a 21 s1 (t ) a 22 s 2 (t ) a 23 s3 (t ) Mike 2 x3 (t ) a31 s1 (t ) a32 s 2 (t ) a33 s3 (t ) Person 3 Mike 3 Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 ICA – independent component analysis Microphone Signals X Mixing Matrix A mixing speech Microphone signals X Speech signals S time t time t microphone signals demixing speech Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 = speech signals Demixing matrix A-1 speech signals = time t microphone microphone signals time t speaker Speech Signals S ICA – independent component analysis 35 The sum of distribution of the same time is more Gaussian. 30 25 20 15 60 10 35 5 30 50 0 0 0.1 0.2 25 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 20 40 15 10 35 5 30 30 25 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 20 20 15 10 10 5 0 0 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 ICA – independent component analysis ICs ICs Demixing Matrix Data Matrix j Samples PCs j Samples = Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 PCs Maximizes independence (non Gaussianity) between components. ICA doesn’t work with purely Gaussian distributed data. Components are not orthogonal to each other. Delivers transformation matrix, that gives the influence of the PCs on the independent components. ICs are unordered ICs Kurtosis – significant components measure of non Gaussianity n 4 – random variable (IC) ( z ) i μ – mean kurtosis( z ) i 1 3 4 (n 1) σ – standard deviation z positive kurtosis super Gaussian negative kurtosis sub Gaussian Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Kurtosis – significant components Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Influence Values Which enzymes have most influence on ICs? Reduced Data Matrix Selected Components Data Matrix j Samples i Enzymes i Enzymes PCs = Demixing Matrix Data Matrix j Samples PCs j Samples = Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 PCs ICs ICs ICs PCs j Samples Influence Values Influence Matrix Demixing Matrix i Enzymes Selected Components ICs i Enzymes PCs = ICs ICs PCs Influence Matrix Data Matrix i Enzymes = Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 ICs ICs j Samples i Enzymes j Samples Results pgm mutant compares wild type and pgm mutant 17 enzymes,125 samples wild type, pgm mutant continuous night response to carbon starvation 17 enzymes, 55 samples +0, +2, +4, +8, +24, +48, +72, +148 h Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Results – pgm mutant Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Results – continuous night Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Results – combined Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Results – combined Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Results – combined Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 Summary ICA in combination with PCA has higher discriminating power than only PCA. Kurtosis is used for selection optimal PCA dimension and ordering of ICs. pgm experiment, 1st IC discriminates between mutant and wild type. Continuous night, 2nd IC represents time component. The two most strongly implicated enzymes are identical. Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05 References Scholz M., Gibon Y., Stitt M., Selbig J.: Independent components analysis of starch deficient pgm mutants. Scholz M., Gatzek S., Sterling A., Fiehn O., Selbig J.: Metabolite fingerprinting: an ICA approach. Blaschke, T., Wiskott, L.: CuBICA: Independent Component Analysis by Simultaneous Third- and FourthOrder Cumulant Diagonalization. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 52(5):1250-1256. http://itb.biologie.hu-berlin.de/~blaschke/ Hyvärinen A., Karhunen J., Oja E.: Independent Component Analysis. J. Wiley. 2001. Matthias Maneck - Journal Club WS 04/05