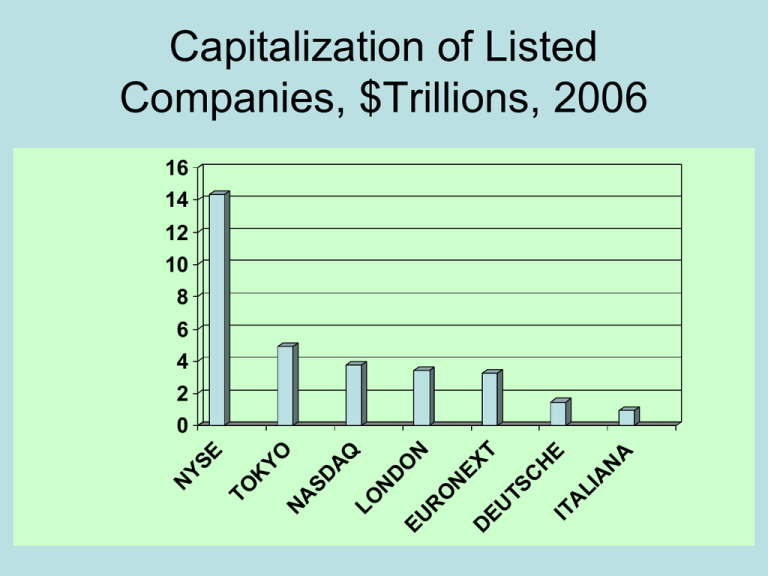
Capitalization of Listed
Companies, $Trillions, 2006
16
14
12
10
8
6
A
LI
A
N
IT
A
H
E
TS
C
D
EU
O
N
EX
T
N
EU
R
D
O
LO
N
SD
A
Q
N
A
YO
TO
K
N
YS
E
4
2
0
1
Annual Stock Market Returns, 1926-2010
Chapter
5
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
The Stock
Market
Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learning Objectives
Take stock in yourself. Make sure you
have a good understanding of:
1. The difference between private and public equity and primary and
secondary stock markets.
2. The workings of the New York Stock Exchange.
3. How NASDAQ operates.
4. How to calculate index returns.
5-4
The Stock Market
• Our goal in this chapter is to provide a “big picture”
overview of:
– Who owns stocks,
– How a stock exchange works, and
– How to read and understand the stock market
information reported in the financial press.
5-5
Private Equity
• Private Equity is used in the rapidly growing area of equity financing
for nonpublic companies.
• Banks are generally not interested in making loans to start-up
companies, especially ones :
– with no assets (other than an idea).
– run by fledgling entrepreneurs with no track record.
– Firms with this profile search for venture capital (VC),
an important part of the private equity markets.
• Firms other than start-ups might also need financing.
• Private equity also includes:
– middle-market firms
– large leveraged buyouts
5-6
The Structure of Private Equity Funds
• Private equity funds and hedge funds are two types of investment
companies. Both
–
–
–
–
are set up as limited partnerships.
pool money from investors.
invest this money on behalf of these investors.
use, typically, a 2/20 fee structure (i.e., a 2 percent
annual management fee and 20 percent of profits).
– have built-in constraints to prevent managers from
taking excessive compensation.
• Private equity funds generally have:
– a high-water-mark provision
– a “clawback” provision
5-7
Types of Private Equity Funds:
Venture Capital
• Venture Capital refers to financing new, often high-risk, start-ups.
• Individual venture capitalists invest their own money.
• Venture capital firms pool funds from various sources, like
–
–
–
–
–
Individuals
Pension funds
Insurance companies
Large corporations
University endowments
• Venture capitalists know that many new companies will fail.
• The companies that succeed can provide enormous profits.
5-8
Venture Capital, II
• To limit their risk:
– Venture capitalists generally provide financing in
stages.
– Venture capitalists actively help run the company.
• At each stage, enough money is invested to reach the next stage.
– Ground-floor financing
– Mezzanine Level financing
• At each stage of financing, the value of the founder’s stake grows
and the probability of success rises.
• If goals are not met, the venture capitalists withhold further financing.
• If a start-up succeeds:
– The big payoff frequently comes when the company is sold to
another company or goes public.
– Either way, investment bankers are often involved in the process.
5-9
Types of Private Equity Funds:
Middle Market
• Many small, regional private equity funds concentrate
their investments in “middle market” companies.
– ongoing concerns (i.e., not start-ups)
– known performance history
– typically, small and family owned and operated.
• Reasons middle market companies seek more capital
– Expansion beyond their existing region
– Founder wants to “cash out”
• A private equity fund might purchase a portion of the
business so that others can now manage the company.
5-10
Types of Private Equity Funds:
Leveraged Buyouts
• Suppose a company (or someone else) purchases all the shares
of the company held by the public at large?
• This process is called “taking the company private.”
• The cost of going private is often high.
– A manager or investor who wants to take a company private
probably needs to borrow a significant amount of money.
– Taking a company private is called a leveraged buyout (LBO).
• LBO market activity levels depend on credit markets.
– Around 2005, the LBO market was quite active.
– Activity in the LBO market came to a standstill after the crash
of 2008.
5-11
Selling Securities to the Public
• The primary market is the market where investors purchase newly
issued securities.
– Initial public offering (IPO): An IPO occurs when a
company offers stock for sale to the public for the first time.
– Seasoned equity offering (SEO): If a company already
has public shares, an SEO occurs when a company raises
more equity.
• The secondary market is the market where investors trade
previously issued securities. An investor can trade:
– Directly with other investors.
– Indirectly through a broker who arranges transactions for
others.
– Directly with a dealer who buys and sells securities from
inventory.
5-12
The Primary Market for Common Stock
• An IPO (and an SEO) involves several steps.
– Company appoints an investment banking firm to arrange
financing.
– Investment banker designs the stock issue and arranges
for fixed commitment or best effort underwriting.
– Company prepares a prospectus (usually with outside
help) and submits it to the Securities and Exchange
Commission (SEC) for approval. Investment banker
circulates preliminary prospectus (red herring).
• Upon obtaining SEC approval, company finalizes prospectus.
• Underwriters place announcements (tombstones) in newspapers
and begin selling shares.
5-13
IPO Tombstone
5-14
The Secondary Market for Common Stock
• The goal of a secondary market is to match investors wishing to buy
stocks with investors wishing to sell stocks.
• Common stock trading typically occurs on either an organized stock
exchange or a trading network.
• Important concepts:
– The bid price:
•
•
The price dealers pay investors.
The price investors receive from dealers.
– The ask price:
•
•
The price dealers receive from investors.
The price investors pay dealers.
– The difference between the bid and ask prices is called the bidask spread, or simply the spread.
5-15
The New York Stock Exchange
•
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), popularly known as the Big Board,
celebrated its bicentennial in 1992.
•
The NYSE has occupied its current building on Wall Street since the early
1900’s.
•
For 200 years, the NYSE was a not-for-profit New York State corporation.
•
The NYSE went public in 2006
– NYSE Group, Inc., ticker: NYX
– Naturally, NYX stock is listed on the NYSE
•
In 2007, NYSE Group merged with Euronext to form NYSE Euronext, the
world’s largest exchange.
5-16
NYSE Seats and Trading Licenses
•
Historically, the NYSE had 1,366 exchange members. These members:
– Were said to own “seats” on the exchange.
– Collectively owned the exchange, although professionals
managed the exchange.
– Regularly bought and sold seats (Record seat price: $3 million in
2005)
– Seat holders could buy and sell securities on the exchange floor
without paying commissions.
•
In 2006, all of this changed when the NYSE went public.
– Instead of purchasing seats, exchange members purchase
trading licenses:
•
•
number limited to 1,500
In 2010, a license would set you back a cool $40,000—per year.
– Having a license entitles the holder to buy and sell securities on
the floor of the exchange.
5-17
Farewell, Specialists
•
For a long time, most securities listed at the NYSE were divided among
specialists—an exclusive dealer, or intermediary, for a set of securities.
•
Specialists:
– posted bid prices and ask prices for each security assigned to them.
– were obligated to make and maintain a fair, orderly market
– Specialists stood ready to buy at bid prices and sell at ask prices when
outside sell and buy order flows were unequal
•
Specialists had an exclusive, advance look at incoming orders flowing to the
display book.
– Because of this advance look, specialists had an information advantage
when they were making quotes and matching orders.
– Under this system, specialists, however, could “work” orders, that is, try
to improve trading prices for customers.
5-18
Designated Market Makers
• In 2009, aiming to stay competitive, the NYSE replaced the role of
specialists with two classes of market makers:
– designated market makers (DMMs)
– and supplemental liquidity providers (SLPs).
• What were specialists are now the DMMs.
– The DMMs are assigned a set of securities and are
– obligated to maintain a fair and orderly market in these stocks
• Differences between the Specialist Role and the DMM Role
– DDMs can compete against other exchange members for trades.
– Specialists had to step back from a trade if a floor broker order had the
same price.
– Unlike the former specialist system, however, DMMs do not receive an
advance look at incoming orders.
• DMMs do not have an exclusive right to make markets in their
5-19
DMMs and Supplemental
Liquidity Providers (SLP)
• A newly created class of market maker is called the
supplemental liquidity provider (SLP).
• SLPs can trade the same stocks as the DMMs.
– SLPs can trade only from offices outside the exchange.
– DMMs are located on the floor of the exchange.
• Quoting Requirements:
– DMMs must quote bid and ask prices for at least 5% of the trading
day.
– SLPs are required to quote bid or ask prices for at least 5% of the
trading day.
•
Incentives. For 100 shares traded, the NYSE pays:
– DMMs 30 cents.
– SLPs 15 cents (lower quoting requirements).
– Floor brokers 4 cents (no quoting requirements).
5-20
Other NYSE Participants
• The largest number of NYSE members are registered as
commission brokers.
• Commission brokers execute customer orders to buy and
sell stocks.
• When commission brokers are too busy, they may
delegate some orders to floor brokers, or two-dollar
brokers, for execution.
• A small number of NYSE members are floor traders,
who independently trade for their own accounts.
5-21
Super Display Book System (SDBK)
•
A substitute for floor brokers: the efficient Super Display Book system
(SDBK)
•
The SDBK has recently replaced the well-known SuperDOT system (the
DOT stands for designated order turnaround).
•
Based on the NYSE’s electronic trading engine, Arca, the NYSE SDBK is a
server-based system.
•
Trading via the SDBK is remarkably fast. NYSE customers can have their
trades executed within 5 milliseconds (down from a relatively sluggish 350
milliseconds in 2007).
•
How fast is this trading? For comparison, when Danica Patrick is running her
Number 7 JR Motorsports Go Daddy Chevrolet at 200 miles per hour, she
races only about 1.5 feet in 5 milliseconds.
5-22
The NYSE Hybrid Market
•
The NYSE rolled out a faster automated execution system called the Hybrid
platform beginning in late 2006 and continues to refine the system.
•
Hybrid trading combines the exchange’s automated technology with the
advantages of an auction market.
•
In the Hybrid market, DMMs, SLPs, and floor brokers have the choice to
interact with the market electronically as well as in person.
•
Hybrid trading has evolved because human judgment is valuable:
– in less liquid stocks.
– during the opening and closing of trading sessions.
– during times of market duress.
•
In normal times, for the average stock, the automated platform is an efficient
trading option.
5-23
NYSE-Listed Stocks
• In 2008, the total number of companies listed on the NYSE
represented a total global market value of about $16.7 trillion.
• Initial and annual listing fees are charged based on the number of
shares.
• To apply for listing, companies have to meet certain minimum
requirements with respect to:
–
–
–
–
The number of shareholders
Trading activity
The number and value of shares held in public hands
Annual earnings
5-24
Operation of the New York Stock
Exchange
• The fundamental business of the NYSE is to attract and process
order flow.
• In 2010, the average trading volume on the NYSE was over
2 billion shares a day.
• Volume breakdown:
– About one-third from individual investors.
– Almost half from institutional investors.
– The remainder represents NYSE-member trading,
mostly from specialists acting as market makers.
5-25
NYSE Floor Activity
• There are a number of DDM posts, each with a roughly figure-eight
shape, on the floor of the exchange.
• At the telephone booths, commission brokers:
– Receive customer orders.
– Walk out to DMM posts where the orders can be
executed,
– Return to confirm order executions and receive new
customer orders.
• Coat colors indicate the person’s job or position.
5-26
Stock Market Order Types
5-27
Trading on the Web
5-28
NASDAQ, I.
• The name “NASDAQ” is derived from the acronym NASDAQ, which
stands for National Association of Securities Dealers Automated
Quotations system.
• NASDAQ is now a proper name in its own right.
• Introduced in 1971, the NASDAQ market is a computer network of
securities dealers who disseminate timely security price quotes to
NASDAQ subscribers.
• The NASDAQ has more companies listed than the NYSE.
• On most days, volume on the NASDAQ exceeds the NYSE volume.
5-29
NASDAQ, II.
• NASDAQ trading is almost exclusively done through dealers who buy
and sell securities for their own inventories.
• Like NYSE specialists, NASDAQ dealers use their inventory as a
buffer to absorb buy and sell order imbalances.
• NASDAQ is actually made up of three separate markets:
– The Global Select Market
– The Global Market
– The Capital Market
• In the late 1990s, the NASDAQ system opened to electronic
communications networks (ECNs)
• ECNs are basically websites that allow investors to trade directly with
one another.
5-30
NASDAQ Quotes
• The NASDAQ network provides bid and ask prices as
well as recent transaction information.
• The bid and ask prices for the NASDAQ represent inside
quotes.
– The highest bid
– The lowest ask
• For a small fee, you can have access to “Level II” quotes.
– Displays all bids and asks
– Frequently displays the market maker identity
5-31
NYSE and NASDAQ Competitors
• The third market is an off-exchange market for securities listed on
an organized exchange.
• The fourth market is for exchange-listed securities in which
investors trade directly with one another, usually through a computer
network.
• For dually listed stocks, regional exchanges also attract substantial
trading volume.
5-32
Stock Market Information
• The most widely followed barometer of day-to-day stock
market activity is the Dow Jones Industrial Average
(DJIA), or “Dow” for short.
• The DJIA is an index of the stock prices of 30 large
companies representative of American industry.
5-33
The Dow Jones Industrial Average
5-34
Yields on DJIA Component Stocks
5-35
Stock Market Indexes, I.
• Indexes can be distinguished in four ways:
– The market covered,
– The types of stocks included,
– How many stocks are included, and
– How the index is calculated (price-weighted,
e.g. DJIA, versus value-weighted, e.g. S&P
500).
• Stocks that do not trade during a time period cause index
staleness over that time period.
– That is, we do not know the "true" index level if
all the stock prices are not updated, i.e., fresh.
5-36
Stock Market Indexes, II.
• For a value-weighted index (i.e., the S&P 500),
companies with larger market values have higher
weights.
• For a price-weighted index (i.e., the DJIA), higher priced
stocks receive higher weights.
– This means stock splits cause issues.
– But, stock splits can be addressed by
adjusting the index divisor.
– Note: As of April 12, 2010, the DJIA divisor
was a nice “round” 0.132319125!
5-37
Stock Market Indexes, III.
5-38
Example I: $1,000,000 to Invest,
Price-Weighted Portfolio
Company
Price
Price
Weight
Shares
to Buy
Boeing
67.50 0.5148
7,626
Nordstrom
41.93 0.3198
7,626
Lowe's
21.70 0.1655
7,626
131.130
1.000
7,626
Note: Shares = $1,000,000 / 131.130 = 7,626
5-39
Example II: Changing the Divisor
Day 1 of Index:
Company
Boeing
Nordstrom
Lowe's
Sum:
Index:
Price
67.50
41.93
21.70
131.13
43.71 (Divisor = 3)
Before Day 2 starts, you want to replace Lowe's with Home Depot, selling at $32.90.
To keep the value of the Index the same, i.e., 43.71:
Boeing
Nordstrom
Home Depot
Sum:
67.50
41.93
32.90
142.33
142.33 / Divisor = 43.71, if Divisor is: 3.256234271
What would have happened to the divisor if Home Depot
shares were selling at $65.72 per share instead of $32.90?
5-40
Example III: $1,000,000 to Invest,
Value-Weighted Portfolio
Company
Price
Shares Capitalization Value Shares
(millions)
(millions)
Weight to Buy
Boeing
67.50
732.74
49,460.0
0.5550
8,223
Nordstrom
41.93
219.65
9,210.0
0.1034
2,465
Lowe's
21.70
1,402.76
30,440.0
0.3416
15,742
Total: 131.130
Total:
89,110.0
1.0000
26,430
Note: Shares to Buy = $1,000,000*Weight / Price
5-41
Example IV: How Does the
Value-Weighted Index Change?
Using the Portfolio from Example III:
Lowe's
Day 2:
Company
Boeing
Nordstrom
Lowe's
21.70
1402.76
Total MV(1):
30,440
89,110
Divisor (Set by Vendor):
89.11
Day 1 Index Level:
1,000.00
Price
69.00
41.93
21.70
Total Shares
Market Capitalization
(millions)
(millions)
732.74
50,559
219.65
9,210
1402.76
30,440
Total MV(2):
90,209
Day 2 Index Level:
1,012.33
5-42
The Day 3 Index Can be Calculated in
Two Ways:
Day 3:
Company
Boeing
Nordstrom
Lowe's
Price
71.10
41.93
21.70
Day 3 Index
Total Shares
Market Capitalization
(millions)
(millions)
732.740
52,098
219.650
9,210
1,402.760
30,440
Total MV(3):
91,748
Total MV(2):
90,209
Day 2 Index Level:
1,012.33
Day 3 Index Level:
1,029.60
Total MV(1):
89,110
Day 3 Index Level:
1,029.60
Market Value Day 3
Index Level Day 2
Market Value Day 2
or
Day 3 Index
Market Value Day 3
Index Level Day 1
Market Value Day 1
5-43
Useful Internet Sites
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
www.hoovers.com (information on Initial Public Offerings, or IPOs)
www.nyse.com (website for the New York Stock Exchange)
www.nasdaq.com (website for the NASDAQ)
averages.dowjones.com (The Dow Jones Industrial Average)
www.russell.com (the Russell Indexes)
www.barra.com (reference for “value” and “growth” indexes)
www.djindexes.com (reference for current divisor for the DIJA)
www.standardandpoors.com (website for S&P 500)
www.nni.nikkei.co.jp (website for Japan’s Nikkei 225 index)
5-44
Chapter Review, I.
• Private and Public Equity
– Private Equity Funds
• The Primary and Secondary Stock Markets
– The Primary Market for Common Stock
– The Secondary Market for Common Stock
– Dealers and Brokers
• The New York Stock Exchange
– Designated Market Makers, DDMs
– Types of Members
– NYSE-Listed Stocks
5-45
Chapter Review, II.
• Operation of the New York Stock Exchange
– NYSE Floor Activity
– Special Order Types
• NASDAQ
– NASDAQ Operations
– NASDAQ Participants
– The NASDAQ System
• NYSE and NASDAQ Competitors
5-46
Chapter Review, III.
• Stock Market Information
– The Dow Jones Industrial Average
– Stock Market Indexes
– More on Price-Weighted Indexes
– Value-Weighted Indexes
5-47