Prevention of hemorrohid?
advertisement

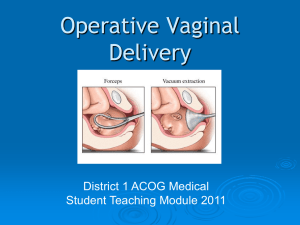
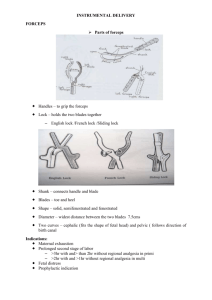
Instrumental Delivery Forceps Delivery indications A. Indicated : 1. Anesthesia 2. Heart disease 3. Pulmonary disease 4. Fetal distress 5. After coming head 6. In cesarean section B. Selected : 1. Poor cintractions 2. Fatigue 3. Op position 4. Prevention of cystocele and rectocele ? 5. Prevention of hemorrohid? Contraindications • Extreme prematurity (< 34 weeks) • Suspected bleeding disorder • Macrosomia, suspected or USG established Prerequisitions for forceps 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Full dilatation Engagement Empty bladder Known position (of the fetal head) Ruptured membranes Adequate anesthesia Episiotomy R/O C.P.D Skilled operator Parts of Equipment 1. 2. Cup size 40, 50, 60 mm. Types of cup • • • • 3. 4. 5. Malestorm Bird Siliastic (Mety-vac) M-cup. Vacuum tubing. Traction chain. Suction apparatus—which has capacity to produce 0.8 kg/cm2 negative suction @ 550-600 mm Hg. 6. Traction force max @ 22.7 kg required before detachment or pop-off takes place. This is the safetyend point. 7. Application distance: is 3 cm from post edge of anterior fontanelle of fetal sclap till the anterior outer edge of traction cup. 8. Site of applications a- Flexing median b. Hexing paramedian Result in c. Deflexing median Asyncilitism d. Deflexing paramedian Failure for correct traction Parts of Forcep's • Has two crossing blade branches • Each branch blade has four components 1. The blade 2. Shank 3. Lock—English and/or sliding type 4. Handle • Each blade has two curves a. Cephalic-coniorms to shape of fetal head b. Pelvic-confoims to pelvic curvature Common Types of Forceps in Use 1. Wringly's outlet forceps 2. Simpson's 3. Tucker-McIane 4. Kielland forceps 5. Piper's forceps 6. Hay's forceps Classification of Forceps Delivery (Instrumental Delivery) (ACOG 2000) Procedure Criteria Outlet forceps 1. Sclap visible and at interoitus without separating labia 2. Fetal skull at pelvic floor 3. Sagittal suture in AF dia or LOA or ROA position 4. Fetal head is or at pelvic perineum (leading pole) 5. Rotation needed does not exceed 45° Low forceps • Leading point ^ +2 station and not on pelvic floor • Rotation is 45° or less. LOA/ ROA to occiput ant and/or LOP/POP with occiput posterior • Rotation is > 45° Mid forceps Station above +2 cm but head is Engaged (Abdomen palpable vertex is I/5th only) High forceps Not included in this classification Function of Forceps Used as traction, rotation or both, by and large used as a tractor Possible Max Force Used Upto 60 kg max after which fetal skull damage is assured. Generally with forceps at elbow along side body leads to force of 22-27 kgs per tractor pull. Preparation of Forcep Application 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Pudendal block or regional anesthesia Lithotomy position Bladder assured empty Perineum cleaned and draped Forceps are constructed outside as to be applied Precise knowledge of exact position of fetal head either by suture direction or by locating posterior ear Application as for biparital or bi malar position, is only safe application of forceps. Indications A. Maternal • Exhausation • Poor/absent maternal expulsive efforts • Need to avoid maternal expensive effort, cardiac disease/CVA • Lack of effort B. Fetal • Nonreassuring fetal CTG test C. Prolonged 2nd stage • Primi > 2 hr without regional anesthesia • Multi > 1 hr anesthesia (for with RA addl hr) • Desired selective shortening of 2nd stage Prerequisites A. Maternal • Lithotomy position • Reassurance • Consent • Adequate analgesia • Empty bladder • Adequate assessed pelvis. B. Fetal • Cephalic presentation • Membranes ruptured • Engaged fetal head • Position of head-known • Station +2 • Flexed attitude • Moulding of head +1 only. C. Others • Cervix fully dilated • No placenta praevia • Experienced operator • Ability to do less, with facilities existing prtoi to attempting. Indications Maternal • Heart disease • Pulmonary injury or severe COFD • Severe intrapartum infection • Neurological conditions such as cord injury or neuromuscular diseases • Prolonged 2nd stage. Fetal Indications • Prolapse of umbilical cord • Premature separation of placenta • Non-assuring CTG tracing, persistant. Others • Lack of maternal expulsive effort • Elective shortening of 2nd stage (prophylactive) or social need. Prerequisites 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Vertex presentation or face with chin out (mento-anterior) Head must be engaged Position of fetal head well known Cervix fully dilated Bladder completely empty Membranes ruptured No CPD assessed Informed mother's consent.