How CDMA works? - K.f.u.p.m. OCW
advertisement

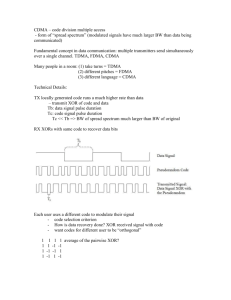
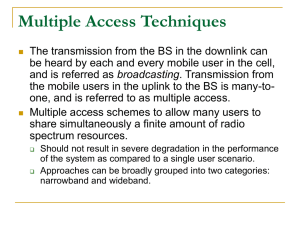
King Fahd University of Petroleum &Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE-400 presentation CDMA systems Done By: Ibrahim Al-Dosari 221416 Mohammad Al-Doraibi 202647 Outline 1. Multiple Access Techniques 2. Introduction. 3. How CDMA works? 4. Types of CDMA 5. Spreading Codes 6. Multiple Access Interference 7. Detection in the CDMA system 8. Commercial usage of CDMA 9. Advantages and Disadvantages of CDMA 10. Conclusion Multiple Access Techniques In many wireless systems, multiple transmitters attempt to communicate with the same receiver. There are three widely-used policies: 1. FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) 2. TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) 3. CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access Multiple Access Techniques FDMA TDMA C C BOnly possibleBin A A f2 B f1 CBA C B for A CGSM B ACB A Used f0 analog system A f0 C Time Time Introduction Definition: CDMA is a technology that allows multiple users to share the whole spectrum at all the time unlike TDMA and FDMA. CDMA has wider bandwidth compared to TDMA & FDMA. Requires digital transmission How CDMA works? CDMA transmitter: The voice has to be digitalize (Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) then compressed) Each user is given a unique PN code. The Codes must have low cross-correlation The transmitter multiplies the code by the data to get the coded massage (bit) How CDMA works? CDMA transmitter: Ck R bps bk (t) RJ bps X Sk (t) How CDMA works? Spectrum of the CDMA: 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 noise massege After Spreding Chip Duration is 0.4 ms. Bit Duration is 6.4 ms. Processing Gain is 16 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 -5000 -4000 -3000 -2000 -1000 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 How CDMA works? CDMA Receiver: The received signal is multiplied again by the same code that used in the transmitter. Integrate over bit duration and, then using a hard decision to get the transmitted massage (bit) How CDMA works? CDMA Receiver: Hard Decision C1 Sum over J chips ∑ RJ bps R bps R bps R bps R bps y(t) Ck Sum over J chips ∑ RJ bps Matched Filter How CDMA works? Types of CDMA 1. Frequency Hopping fixed sequence of frequency values & Time is divided into slots . In the first time slot, a given user transmit to the base station using the first frequency in its frequency hopping sequence. In the next time interval, it transmits using the second frequency value in its frequency hopping sequence, and so on. This way, the transmit frequency keeps changing in time. Types of CDMA 2. Direct Sequence each user transmits its message to the base station using the same frequency, at the same time. Here signals from different users interfere with each other. But the user distinguishes its message by using a special, unique code. This code serves as a special language that only the transmitter and receiver understand. Spreading Codes There are two types of PN codes orthogonal codes and shift register codes: Orthogonal Codes: have zero cross-correlation Walsh Shift Register Codes: have low cross-correlation and they are produced from shift register M-sequence Gold (produced from two different m-sequence ) kassami (produced from Gold and m-sequence ) Multiple Access Interference: Result from the lack of perfect orthogonally between the spreading codes, that is, the cross-correlation does not equal to zero As the number of the users increases, the more interference will be. Because, each user consider the other users as a noise. Detection in the CDMA system: Multi-Users Detection (MUD) The capacity and the performance of the CDMA system increase when MUD is implemented. The basic principle of MUD is the elimination of the negative effect of each user on the other. MUD is also known as joint detection and interference cancellation . Multi-user detection considers all users as signals for each other. Detection in the CDMA system: Multi-Users Detection (MUD) The ultimate technique for the MUD is the optimum receiver. Optimum Receiver: Very complex. So, it is unpractical solution to reduce the multiple access interference. Sup-optimum detector will be implemented. Detection in the CDMA system: Multi-Users Detection (MUD) Sup-optimum solution: Serial Interference cancellation (SIC): SIC is preferred in the absence of power control. Serial canceling the interference generated from the other users. Cancel the strongest signal first (most negative effect ) Detection in the CDMA system: Multi-Users Detection (MUD) Parallel Interference Cancellation (PIC): PIC would be preferred when the amount of interference from each user is similar. In the initial detection stage, all active users are detected in parallel by a SUD technique. Then, the obtained interference is subtracted from the received signal and data detection is performed again with reduced MAI Commercial usage of CDMA CDMA was introduced in the 2nd Generation (early of the 1990s). E.g. IS-95 standard, also known as cdmaOne which support up to 64 users that are orthogonally coded and at the same time transmitted over 1.25 MHz channel Used for Cellular Communication System (824-894 MHz in US Cellular) 3rd Generation: cdma2000 Allow high rate of packet transmitting in addition of voice transmitting. Advantages and Disadvantages of CDMA Advantages: CDMA provides : 1. better cost effective. 2. high voice quality. 3. Increased cellular communications security. 4. system capacity is higher than TDMA and FDMA 5. operate at very low power levels. Advantages and Disadvantages of CDMA Disadvantages: 1. Multiple Access Interference: Require multi-user detection (MUD) algorithms to solve. Advantages and Disadvantages of CDMA Disadvantages: 2. Near-far problem. Where stronger (near to the Base Station) user masks the weaker user (far from the Base Station) 3. Requires wideband channel. Conclusion The CDMA will allow many signals to be transmitted at the same channel at the same time. This done by giving each user a Pseudo-Noise code which is a binary sequence. This code should have low cross-correlation between each other. Multiple access interference has bad effect on the CDMA system so the multiple user detection is used to reduce the MAI. References http://www.cellular.co.za/technologies/cdma/cdm a_w_paper.htm http://www.arcx.com/sites/CDMAvsTDMA.htm Questions