Earned Value Management
advertisement

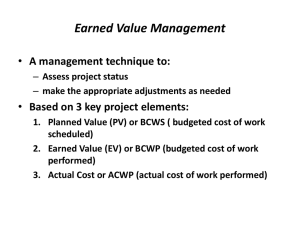
Earned Value Management
How to apply Earned Value Management to
measure the Performance of your Project
alphaPM Inc.
www.alphaPM.com
Project Performance Tracking (Project Dashboard)
PROJECT MILESTONES
Develop Strategy and Vision
Establish Readiness and Blueprint
Identify Business and User Goals
Document Project Scope
Prepare Detailed Requirements
Build and Test
Launch
2
Planned
Date
Planned
Date
Notes
Project Issues/Risks
Mitigating Actions To Be Taken
How To
Earned Value Management Overview
Earned Value Management (EVM) is a management methodology for integrating scope,
schedule and resources, and for objectively measuring project performance and progress.
Performance is measured by determining the budgeted cost of work performed (i.e. earned
value) and comparing it to the actual cost of work performed (i.e. actual cost).
Progress is measured by comparing the earned value to the planned value.
Source: A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) Third Edition 2004
Example:
Project Budget: $400K
Project Schedule: 4 months
(= Baseline Duration)
At the 3 month checkpoint:
Spent:
$200K
Work completed: $100K
Earned Value Management helps you to report how the
project is doing in terms of cost and schedule?
Earned Value Management
Terms and Formulas
Terms and Formulas
Alternative Definition
Example:
Project Budget: $400K
Project Schedule: 4 months
At the 3 month checkpoint:
Spent:
$200K
Work completed: $100K
Example
Earned Value (EV)
Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP)
i.e. the budgeted cost to date x % complete
$100K
Actual Cost (AC)
Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP)
i.e. actual cost of work performed to date
$200K
Planned Value (PV)
Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS)
i.e. the estimated value of work to be performed
$300K
Cost Variance (CV)
= EV - AC
Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP)
- Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP)
$100K – $200K
= ($100K)
Schedule Variance (SV)
= EV - PV
Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP)
- Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS)
$100K - $300K
= ($200K)
Cost Performance Index
(CPI) = EV/AC
Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP)/ Actual Cost
of Work Performed (ACWP)
$100K/$200K
= 0.5 i.e. 50%
Schedule Performance
Index (SPI) = EV/PV
Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP)/
Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS)
$100K/$300K
= 0.33 i.e 33%
Revised Total Duration
Baseline Duration/Schedule Performance Index
4/0.33
= 12 months
Example:
Project Budget: $400K
Project Schedule: 4 months
At the 3 month checkpoint:
Spent:
$200K
Work completed: $100K
Earned Value Management
Chart for project example
800
3 Month
Checkpoint
700
CV = EV – AC = (100K)
SV = EV – PV = (200K)
CPI = EV/AC = (50%)
SPI = EV/PV = (33%)
600
500
400
Budget PV
300
200
Actual Cost
100
Earned Value
0
J
F
M
A
M
J
J
A
S
O
Revised Total Duration = Baseline Duration/SPI = 4/0.33 = 12 months
N
D
How To
Activities
Prepare Plan
Exercise
Owner
Planned Effort
(Days)
Budget
Actual
Effort
Actual Cost
(Planned Value)
$
(As of Day 10)
$
(As of Day 10)
Status
(As of Day 10)
John
2
$2,000
4
$4,000
Completed
Design Solution
Susan
4
$4,000
3
$3,000
Completed
Code Programs
Jim
10
$10,000
5
$5,000
30% of all work
completed
Test Programs
Debbie
2
$2,000
Not started
Brad
2
$2,000
Not started
20
$20,000
Deploy into Production
Total
Report the Performance for the Project at the 10 day point. (Assume a labour rate of $1,000/day)
Step 1: Determine the value of the three variables needed to measure the project
performance at the 10 day point (all activities are sequential)
Planned Value:
Planned Value:
Earned Value:
Earned Value:
Actual Cost
Actual Cost:
PV =
Click+ here
when
yousince Jim should have
PV = $10,000 {2,000
4,000+
4,000
have
your
answer
completed 4 days of coding at the 10 day point}
EV =
EV = $9,000 {2,000 + 4,000 + 3,000 since Jim is only 30%
complete}
AC =
AC = $12,000 (4,000 + 3,000 + 5,000 since that is the actual
amount that all have spent}
How To
Activities
Prepare Plan
Exercise (continued)
Owner
Planned Effort
(Days)
Budget
Actual
Effort
Actual Cost
(Planned Value)
$
(As of Day 10)
$
(As of Day 10)
Status
(As of Day 10)
John
2
$2,000
4
$4,000
Completed
Design Solution
Susan
4
$4,000
3
$3,000
Completed
Code Programs
Jim
10
$10,000
5
$5,000
30% of all work
completed
Test Programs
Debbie
2
$2,000
Not started
Brad
2
$2,000
Not started
20
$20,000
Deploy into Production
Total
Report the Performance for the Project at the 10 day point. (Assume a labour rate of $1,000/day)
We now know that
Planned Value (PV) = $10,000
Earned Value (EV) = $ 9,000
Actual Cost (AC)
= $12,000
Step 2: Calculate the Earned Value Performance Indices
Cost Performance Index (CPI):
Cost Performance Index (CPI):
Schedule Performance Index (SPI):
CPI = EV/AC
Click here when you
CPI = EV/AC = $9.000/$12,000
0.75 or 75%
have your=answer
SPI = EV/PV
Schedule Performance Index (SPI):
SPI = EV/PV = $9,000/10,000 = 0.90 or 90%
Project Performance Tracking (Project Dashboard)
PROJECT MILESTONES
Develop Strategy and Vision
Establish Readiness and Blueprint
Identify Business and User Goals
Document Project Scope
Prepare Detailed Requirements
Build and Test
Launch
8
Planned
Date
Planned
Date
Notes
Project Issues/Risks
Mitigating Actions To Be Taken
An Easy Way to Remember the Formulas
Four Formulas
Three Variables: EV PV AC
S
C
S
C
An Easy Way to Remember the Formulas
Four Formulas
Three Variables: EV PV AC
SV
=
EV -
P
CV
=
EV -
A
SPI
=
EV /
P
CPI
=
EV /
A
An Easy Way to Remember the Formulas
Four Formulas
Three Variables: EV PV AC
SV
=
EV -
PV
CV
=
EV -
AC
SPI
=
EV /
PV
CPI
=
EV /
AC
Earned Value Management
How to apply Earned Value Management to
measure the Performance of your Project
alphaPM Inc.
www.alphaPM.com