Maximum Speed
advertisement

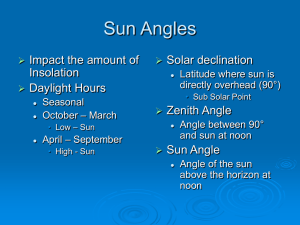
Pressure and Speed Limits Transmission Design Elements Sauer-Danfoss Hydraulic Unit Design Fluid Quality Pressure and Speed Ratings Transmission Design Component Sizing Circuit Design Customer Machine Design Pressure & Speed Limits BULLETIN PURPOSE • Provide understanding of ratings and their relationship to expected life. BLN-9884 Key Concepts • Maximum and Rated pressure • Expected life • Maximum and Rated speed • Duty cycle Low PRESSURE Hi Load Vs Life Short LIFE Long Unit Life • Upper life limit – Rotating group – Bearings • Actual life – Heat – Contamination – Viscosity and lubricity of fluid Max vs Rated Pressure PRESSURE MAXIMUM CONTINUOUS TIME Pressure • Maximum Pressure – Highest intermittent pressure allowed – Determined by max. machine load demand – Less than 2% of total operating time • Continuous Pressure – Pressure expected when performing normal function – Normal input power, max. pump displacement – Weighted average Speed Limits Consider Operating Conditions • Normal driving • High idle/no load • Overrunning load – Must know something about the frictional characteristics of engine Speed Ratings Swashplate Units If Above Continuous, Contact Sauer- Bent Axis (Series 51) Danfoss Not always block lift first Rated Speed • Life inversely proportional to speed • Highest speed recommended at full power • Highest speed for normal life • Varies with angle • Must always check Maximum speed limit Maximum Speed • • • • • Highest operating speed permitted Risk immediate failure if exceeded May loose driveline power if exceeded Highest negative power (downhill braking) Catalog ratings…: – pumps: always reflect maximum swashplate angle – fixed motors: always reflect maximum swashplate angle – variable motors: both maximum and minimum angle are published Cavitation damage Over speed Over speed Design Speed Considerations • • • • • • • Full power Full braking Prime mover speed change Pump drive ratios Tolerance and drift of engine governors Hydraulic unit volumetric losses Tolerance in hydraulic unit displacement Maximum Speed Considerations • Maximum motor operating speeds must be determined and compared to Maximum speed limits. • For vehicle propel drives this usually occurs during down-hill braking conditions. • Another severe condition is zero delta pressure at high engine idle speed. Drive Design Finalization • Operating parameter check • Pressures < recommended limit • Speeds < recommended limit • Expected life achieved Secondary Braking Insist that your customers provide a secondary means of braking on ALL vehicle propulsion systems! Check Speed Limits • Check max angle limits of base units in catalog • Check charge pump limits • Check reduced displacement variable motor limits Reduced Angle Speed Calculation • Swashplate Units: Speed at Tan Max Angle Speed at = reduced angle maximum angle Tan Reduced Angle • Bent Axis Units: Speed at Speed at Sin Max Angle = reduced angle maximum angle Sin Reduced Angle Do not use speeds greater than the "Reduced Angle" speeds shown in the tables! Series 51 Speed Limits • Maximum Speed is the highest speed permitted. Rated Speed rpm Maximum Speed rpm Frame Size (Full Displ.) (Min. Displ.) (Full Displ.) (Min. Displ.) 080 3100 5000 4000 6250 110 2800 4500 3600 5600 160 2500 4000 3200 5000 250 2200 3400 2700 4250 Reduced Angle Motor Example • What is Rated speed limit of 51V110 at 22 deg speed @ 22 deg = speed @ 32 deg * (sin 32) (sin 22) = 2800 * (sin 32) (sin 22) = 3960 rpm • catalog reduced angle displacement max = 4500 rpm • use lesser of calculated vs. catalog, i.e. 3960 rpm The Million Dollar Question D T U Y C C Y L E Duty Cycle Definition • What is a Duty Cycle? DUTY CYCLE 1 Condition % Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1.0% 2.0% 5.0% 16.0% 30.0% 34.0% 9.0% 3.0% SUM: 100.0% Delta Pressure Speed (bar) (rpm) 450 350 250 200 180 150 100 50 1700 1750 1840 1900 1950 2000 2100 2200 Cumulative Damage • Cumulative damage, or more precisely, cumulative fatigue damage, is the total damage to a component as a result of repeated cyclic loading. – Stress levels are not great enough to cause the component to fail under static loading. – Related to crack initiation within the material. Duty Cycle Calculations • Calculation procedures vary. • Procedure has dramatic effect on predictions. • Sauer-Danfoss uses conservative procedures. • Competition: Compare calculation procedures. What is Weighted Pressure? • Weighted pressure serves as a general indication of a duty cycle’s severity – The greater the weighted pressure, the lower the predicted life. – Of the three criteria for weighted pressure, this one is the least demanding. Calculating Weighted Pressure • Weighted pressure equation: Pw = %Time1 P1 exp + %Time2 P2 exp + ... %Time j Pj exp 1 exp • Equation does not include any information concerning the shaft speed at each condition. • For duty cycles with equal weighted pressures, the life will be the same only if the speed at every condition is the same for both duty cycles. Weighted Speed • Every duty cycle also has a weighted speed: Weighted Pressure = Root Mean Octic Pressure = (SUM(Column G))^(1/ EXP) Weighted Speed = SUM(Column H)/ (Weighted Pressure)^EXP Predicted L20 Kit Life Using Load-Life Equation & Weighted Values 263 2206 4875 bar rpm hours Predicted L20 Kit Life Using %Time/Life Method 4875 hours Weighted Speed • Equation for weighted speed is RPMw = %Time1 RPM1 P1 exp + %Time 2 RPM2 P2 exp ...%Time j RPM j Pj Pw exp • Weighted Speed is not calculated using the traditional “weighted average” formula: RPMw %Time1RPM1 + %Time2 RPM2 + ...%Time j RPMj exp Duty Cycle Reduction • Knowing how to calculate the predicted life or the weighted pressure for a customer’s duty cycle is good thing to know, but… • How do I measure a duty cycle? – Usually too many conditions – Can’t test everything at once Hi Typical Pressure Distribution MAX LOAD PRESSURE HILL CLIMB NORMAL POWER LEVEL GROUND Lo IDLE % Time Combining duty cycles Max load 2% Hill climbing 20% Normal power 40% 25% Level ground Idle 13% Life estimate Thank You • Questions?