Alternative Algorithms
advertisement

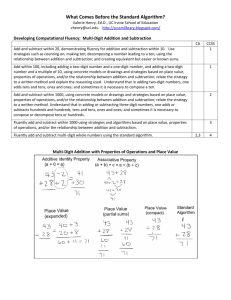
Alternative Algorithms Presented at SAG 2009 Presented by: Marlene Letkeman David Milley Agenda We will be going through all 4 operations and showing some alternative algorithms. 59 + 16 • How many ways can you add these two numbers? Why Alternatives? • Research shows that once the traditional algorithm is taught, thinking stops. • “The traditional algorithm limits our thought process. As teachers we have been taught, and we teach this way. As a result, we as teachers have our own limits imposed upon us. We can’t think ‘outside the box.’ ” (Trevor Brown) Addition Alternative Algorithms for Addition • • • • • • horizontal addition base-ten blocks Kagan method partial sums empty number line compensation Horizontal Addition • 264 + 397 = 200 + 60 + 4 + 300 + 90 + 7 = 200 + 300 + 60 + 90 + 4 + 7 = 500 + 150 + 11 = 500 + 100 + 50 + 10 + 1 = 600 + 60 + 1 = 661 Base Ten Blocks this uses the traditional algorithm but it is modeled concretely Hundreds 346 + 233 579 Tens Ones Kagan Method (1) (1) 23 (1) 18 15 (3) 17 11 ______ 84 Finding Partial Sums 345 345 +138 +138 400 (add the hundreds) 13 (add the ones) 70 (add the tens) 70 (add the tens) +13 (add the ones) +400 (add the hundreds) 483 (add the partial sums) 483 (add the partial sums) Empty Number Line 47 + 25 (Jump method) +10 47 +10 57 +3 67 +2 70 72 Compensation • 497 + 235 (500 + 232) Subtraction Alternative Algorithms for Subtraction • • • • base-ten blocks empty number line horizontal subtraction (not as friendly) “Add-up-to” Base Ten Blocks – this uses the traditional algorithm but it is modeled concretely Hundreds 346 - 233 113 Tens Ones Those *%^#$@ Zero’s! Yes Virginia! There is an easier way! 1000 – 763 999 + 1 - 763 236 + 1 = 237 Empty Number Line 47 – 25 (jump method) -5 22 -10 27 -10 37 47 Horizontal Subtraction (Split-to-fit Method) 528 - 192 400 + 120 + 8 - 100 + 90 + 2 300 + 30 + 6 = 336 “Add-up-to” 852 - 268 + 2 270 + 30 300 + 500 800 + 52 584 6391 - 4729 4730 4800 5000 6000 + 1 + 70 + 200 + 1000 + 391 1662 Multiplication Multiplication Problem • Make up a word problem for the following: 14 x 12 Alternative Algorithms for Multiplication • • • • • Distributive property area model lattice Grid Straight line Area Model 32 x 24 10 10 10 1 1 10 100 100 100 10 10 10 100 100 100 10 10 1 10 10 10 1 1 1 10 10 10 1 1 1 10 10 10 1 1 1 10 10 10 1 1 7x8 5 +2 5 25 10 +2 10 4 32 x 24 30 +2 20 600 40 +4 120 8 x 100 +4 100 10 000 + 400 -7 -700 - 28 Lattice Multiplication 3 2 6 4 1 2 7 6 8 8 2 4 Straight Line Multiplication 32 x 24 6 16 8 32 x 24 = 768 Chart Multiplication 3 2 2 4 8 4x2 2 0 4 x 30 4 0 20 x 2 6 0 0 20 x 30 7 6 8 1 Division Symbols • 9~ 3 • 3w9 • 9# means 9 “divided by” 3 means 3 “divided into” 9 means 9 “divided by” 3 The “Gozinta” Method 51 5e255 25 05 5 0 Alternative Algorithms for Division • • • • curriculum sheets base-ten blocks repeated subtraction Trevor Brown method **in WNCP curriculum, anything beyond a 1 digit divisor, use a calculator Base Ten Blocks: 342 ~ 6 Hundreds Tens 5 Ones 7 Repeated Subtraction Algorithm 7r 126 -7 119 -7 112 -7 105 -7 98 Trevor Brown’s Method 7 1 2 5 10 7 14 35 70 7r126 70 56 35 21 14 7 7 0 (10 groups of 7) (5 groups of 7) (2 groups of 7) (1 group of 7) (18 groups of 7) Conclusion