以列為主
advertisement

Data Structure in C
─ 陣列與結構
大綱
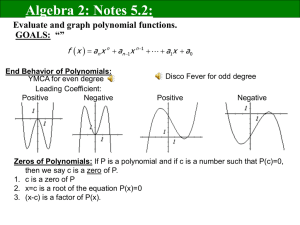
陣列
結構和聯結
多項式抽象資料型態
稀疏矩陣抽象資料型態
上三角和下三角表示法
1
陣列
陣列是一組序對,<index,value>,其中每一
個索引(index)定義了一個相關連的值(value)
陣列的宣告 int list[5], *plist[5];
記憶體配置 變數
記憶位址
(一維陣列) list[0]
base address = α
list[1]
α + size[int]
list[2]
α + 2 * size[int]
list[3]
α + 3 * size[int]
list[4]
α + 4 * size[int]
2
陣列的抽象資料型態(ADT:abstract data type)(是一
種資料型態,它的組織方式使得物件的規格與物
件上的運算之規格和該物件的內部表示法與運算
的實作法是獨立的)
structure Array is
objects: A set of pairs <index, value> where for each value of index there is a
value from the set item. Index is a finite ordered set of one or more dimensions,
for example, {0, …, n-1} for one dimension, {(0,0), (0,1), (0,2), (1,0), (1,1), (1,2),
(2,0), (2,1), (2,2)} for two dimensions, etc.
functions:
For all A
Array, i
Array Create(j, list)
index, x
::=
item, j, size
integer
return an array of j dimensions where list is a
j-tuple whose ith element is the size of the ith
dimension. Items are undefined.
Item Retrieve(A, i)
::=
if(i index) return the item associated with index
value i in array A else return error.
Array Store(A.i, x)
::=
if(i in index) return an array that is identical to
array A except the new pair<i,x> has been
inserted else return error.
end Array
二維陣列
若有一二維陣列是A[0:u1-1, 0:u2-1],表示此
陣列有u1列及u2行,也就是每一列是由u2個
元素組成。二維陣列化成一維陣列時,對
應方式有兩種:(1)以列為主,(2)以行為主
以列為主:視此陣列有u1個元素(0, 1, 2,…,u1-1),
每一元素有u2個單位,每個單位佔d個空間
A(i, j) = l0+i*u2d+j*d
以行為主:視此陣列有u2個元素(0, 1, 2,…,u2-1),
每一元素有u1個單位,每個單位佔d個空間
A(i, j) = l0+j*u1d+i*d
4
三維陣列
若有一三維陣列是A[0:u1-1, 0:u2-1, 0:u3-1]。
一般三維陣列皆先化為二維陣列後,再對應
到一維陣列,對應方式也有兩種:(1)以列為
主,(2)以行為主
u1
u2
u3
5
三維陣列 (續)
以列為主:視此陣列有u1個u2 * u3的二維陣列,
每一個二維陣列有u2個元素,每個u2皆有u3d個
空間A(i, j,k) = l0+i*u2u3d+j*u3d+k*d
i*u2u3
u3
u3
...
u2
A(0, u2, u3)
l0
...
u2
A(1, u2, u3)
A(i, u2, u3)
A(u1-1, u2, u3)
l0
6
三維陣列 (續)
以行為主:視此陣列有u3個u1 * u2的二維陣列,
每一個二維陣列有u2個元素,每個u2皆有u1d個
空間A(i, j,k) = l0+k*u1u2d+j*u1d+i*d
k*u1u2
u1
u1
...
u2
A(u1, u2,0)
l0
...
u2
A(u1, u2,1)
A(u1, u2,k)
A(u1, u2, u3-1)
l0
7
n維陣列
若有一n維陣列是A[0:u1-1, 0:u2-1, 0:u3-1, … ,
0:un-1]。同樣地,n維陣列亦有兩種表式方
法:(1)以列為主,(2)以行為主
參考課本pp.2-9~2-10
8
結構和聯結
結構是將不相同型態的資料群集在一起
Ex. struct {
char name[10];
int age;
float salary;
} person;
聯結的宣告與結構類似,但union中的欄位必須
共用記憶空間
Ex. Union {
int children;
int bread;
} u;
9
結構和聯結
自我參考結構(self-referential structure)是
一種結構,其中的一個或多個組成元素
是指向自身的指標
通常需要動態記憶管理程式(malloc和free)來
明確地取得或釋回記憶體
Ex. Type struct list {
char data;
list *link;
};
10
多項式抽象資料型態
何謂多項式?
Ex. A(x)=3x20+2x5+4與B(x)=x4+10x3+3x2+1
axe,其中x是變數,a是係數,而e是指數
多項式最大的指數指稱為次方(degree),等
於0的係數不必寫出,指數為0的項目不必寫
出數
多項式加法 A(x) + B(x) = (ai+bi)xi
多項式乘法 A(x) * B(x) = (aixi * (bjxj))
11
多項式的ADT
structure Polynomial is
objects: p(x) = a1xe1 + … + anxen; a set of ordered pairs of <ei, ai> where ai in
Coefficients and ei in Exponents, ei are integers >=0
functions:
For all poly, poly1, poly2
Polynomial Zero()
Boolean IsZero(poly)
Polynomial, coef
Coefficients, expon
Exponents
::=
::=
return the polynomial p(x)=0
if(poly)
return FALSE else return TRUE
Coefficient Coef(poly,expon) ::=
if(expon poly) return its coefficient else
return zero
Exponent Lead_Exp(poly)
::= return the largest
exponent in poly
Polynomial Attach(poly, coef, expon) ::= if(expon poly) return error else
return the polynomial poly with
the term<coef, expon> inserted
Polynomial Remove(poly, expon)
::=
if(expon poly) return the
polynomial poly with the term whose
exponent is expon deleted else return
error
Polynomial SingleMult(poly, coef, expon) ::= return the polynomial poly ×
coef × xexpon
Polynomial Add(poly1, poly2) ::= return the polynomial poly1+poly2
Polynomial Mult(poly1, poly2) ::= return the polynomial poly1 × poly2
end Polynomial
多項式抽象資料型態 (續)
在C中表示多項示的方法是使用typedef建立
polynomial型態
#define MAX_DEGREE 101 /*Max degree of polynomial+1*/
typedef struct{
int degree;
float coef[MAX_DEGREE];
} polynomial;
若a的型態是polynomial,且n<MAX_DEGREE,
則多項式A(x)= n
可表示為:
i
a
x
i
a.degree=n
i 0
a.coef[i]=an-i, 0 i n
13
多項式抽象資料型態 (續)
若多項式是稀疏的,係數不為0的項次個數
相對於係數為0的項次個數是很小時,會有
記憶體浪費的現象
#define MAX_TERMS 100 /*size of terms array*/
typedef struct{
float coef;
int expon;
} polynomial;
Polynomial terms[MAX_TERMS];
int avail=0;
14
多項式抽象資料型態 (續)
Ex. 將A(X)=2x1000+1和B(X)=x4+10x3+3x2+1相加
starta
finisha
startb
coef
2
1
1
10
3
1
exp
1000
0
4
3
2
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
finishb
avail
6
15
void padd (int starta, int finisha, int startb, int finishb, int *stard, int
*finishd)
{
/* add A(x) and B(x) to obtain D(x) */
float coefficient;
*startd=avail;
while (starta<= finisha && startb <= finishb)
switch(COMPARE(terms[starta].expon, terms[startb].expon))
{
case –1: /* a expon < b expon*/
attach(terms[startb].coef, terms[startb].expon);
startb++;
break;
case 0: /* equal exponents*/
coefficient = terms[starta].coef+terms[startb].coef;
if (coefficient)
attach(coefficient, terms[starta].expon);
starta++;
startb++;
break;
case –1: /* a expon > b expon*/
attach(terms[starta].coef, terms[starta].expon);
starta++;
break;
}
/* add in remaining terms of A(x)*/
for( ; starta<=finisha; starta++)
attach(terms[starta].coef, terms[starta].expon);
/* add in remaining terms of B(x)*/
for( ; startb<=finishb; startb++)
attach(terms[startb].coef, terms[startb].expon);
*finishd=avail-1;
}
void attach(float coefficient, int exponent)
{
/* add a new term to the polynomial*/
if(avail>=MAX_TERMS) {
fprintf(stderr,”Too many terms in the polynomial\n”);
exit(1);
}
terms[avail].conf = coefficient;
terms[avail].expon = exponent;
avail++;
}
稀疏矩陣抽象資料型態
在數學上,一個矩陣包含m列和n行的元素。
一般寫為m × n,表示矩陣有m列n行,共有
mn個元素。若m = n,矩陣為一方陣
在計算機科學上,一個矩陣的標準表示法為
二維陣列,定義為a[MAX_ROWS][MAX_COLS]
若矩陣中包含了許多的0,我們稱為“稀疏
矩陣”。而多少0少能算是稀疏?並沒有明
絶對的定對。一般而言,大於1/2個就可稱
之
19
稀疏矩陣抽象資料型態 (續)
稀疏矩陣表示法
#define MAX_TERMS 101 /*maximum number of terms +1*/
typedef struct{
int col;
int row;
int value;
} term;
term a[MAX_TERMS];
若將稀疏矩陣以陣列a表示,a[0].row為列數,
a[0].col為行數,而a[0].value為全部不為0之元素
個數。另外,a[1]~a[8]是儲存代表不為0的元素。
20
稀疏矩陣抽象資料型態 (續)
col0 col1 col2 col3 col4 col5
row
col
value
a[0]
6
6
8
row0
15
0
0
22
0
-15
a[1]
0
0
15
row1
0
11
3
0
0
0
a[2]
0
3
22
row2
0
0
0
-6
0
0
a[3]
0
5
-15
row3
0
0
0
0
0
0
a[4]
1
1
11
row4
91
0
0
0
0
0
a[5]
1
2
3
row5
0
0
28
0
0
0
a[6]
2
3
-6
a[7]
4
0
91
a[8]
5
2
28
21
structure Sparse_Matrix is
稀疏矩陣
的ADT
objects: a set of triples, <row, column, value>, where row and column are integers
and form a unique combination, and value comes from the set item.
functions:
for all a,b
Sparse_Matrix, x
item, I, j, max_col, max_row
Sparse_Matrix Create(max_row, max_col)
::=
index
return a Sparse_Matrix that
can hold up to max_items =
max_row × max_col and
whose maximum row size is
max_row and whose
maximum column size is
max_col.
Sparse_Matrix Transpose(a)
Sparse_Matrix Add(a,b) ::=
::=
return the matrix produced by
interchanging the row and column value of
every triple.
if the dimensions of a and b are the same return
the matrix produced by adding corresponding
items, namely those with identical row and
Sparse_Matrix Multiply(a,b)
column values else return error.
::= if number of columns in a equals number
of rows in b return the matrix d produced
by multiplying a by b according to the
formula: d[i][j]=Σ (a[i][k] × b[k][j])
where d(i,j)is the (i,j)th element else return
error.
end Sparse_Matrix
稀疏矩陣抽象資料型態 (續)
轉置矩陣是將矩陣的行與列互換。也就是將
矩陣中的每個元素a[i][j]變成轉置矩陣中的
元素b[j][i]
row
col
value
row
col
value
a[0]
6
6
8
a[0]
6
6
8
a[1]
0
0
15
a[1]
0
0
15
a[2]
0
3
22
a[2]
0
4
91
a[3]
0
5
-15
a[3]
1
1
11
a[4]
1
1
11
a[4]
2
1
3
a[5]
1
2
3
a[5]
2
5
28
a[6]
2
3
-6
a[6]
3
0
22
a[7]
4
0
91
a[7]
3
2
-6
a[8]
5
2
28
a[8]
5
0
-15
23
void transpose(term a[], term b[])
/* b is set to the transpose of a */
{
int n, i, j, currentb;
n = a[0].value; /* total number of elements */
b[0].row = a[0].col /* rows in b = columns in a */
b[0].col = a[0].row /* columns in b = rows in a*/
b[0].value=n;
if (n>0) { /*non zero matrix*/
currentb=1;
for(I=0; I<a[0].col;I++) /*transpose by the columns in a*/
for(j=1;j<=n;j++) /*find elements from the current column*/
if(a[j].col = = i){ /*element is in current column, add it to b*/
b[currentb].row = a[j].col;
b[currentb].col = a[j].row;
b[currentb].value = a[j].value;
currentb++; }
}
}
上三角和下三角表示法
若一矩陣的對角線以下的元素均為零時,亦
即aij=0,i>j,則稱此矩陣為上三角形矩陣
(upper triangular matrix)
若一矩陣的對角線以上的元素均為零時,亦
即aij=0,i<j,則稱此矩陣為上三角形矩陣
(lower triangular matrix)
a11
a12
a13
a14
a11
0
0
0
0
a22
a23
a24
a21
a22
0
0
0
0
a33
a34
a31
a32
a33
0
0
0
0
a44
a41
a42
a43
a44
25
上三角和下三角表示法 (續)
一個n*n個的上下三角形矩陣共有[n(n+1)]/2個
元素,依序對映至D(1: [n(n+1)]/2)
以列為主(上三角形矩陣):一個n*n的上三角形矩陣
對映至D陣列時,當aij=D(k),則k = n(i-1)-[i(i-1)]/2+j
a11
a12
a13
a14
...
a22
a23
D(1) D(2) D(3) D(4) ... D(n+1) D(n+2)
a24
D(n+3)
...
aij
...
ann
...
D(k)
...
D([n(n+1)]/2)
以列為主(下三角形矩陣):一個n*n的下三角形矩陣
對映至D陣列時,當aij=D(k),則k = [i(i-1)]/2+j
a11
a21
a22
a31
a32
...
aij
...
ann
D(1) D(2) D(3) D(4) D(5) ... D(k) ... D([n(n+1)]/2)
26
上三角和下三角表示法 (續)
以行為主(上三角形矩陣):一個n*n的上三角形矩陣
對映至D陣列時,當aij=D(k),則k = [j(j-1)]/2+I
a11
a12
a22
a13
...
D(1) D(2) D(3) D(4) ...
aij
...
ann
D(k) ... D([n(n+1)]/2)
以行為主(下三角形矩陣):一個n*n的下三角形矩陣
對映至D陣列時,當aij=D(k),則k = n(j-1)-[j(j-1)]/2+ji
a11
a21
a31
a41
...
aij
...
ann
D(1) D(2) D(3) D(4) ... D(k) ... D([n(n+1)]/2)
27