m162-12

Wong Wai Ling, Lam Pui Ki
2011-3-22
1
Identification number
clearly identify a person or a thing
Check digit
an extra digit for the purpose of error detection
2
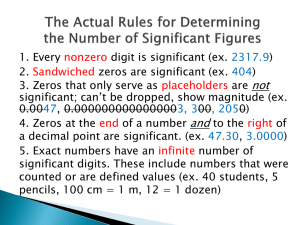
11-digit
sum of the first 10 digits is divided by 9
remainder = check digit
Disadvantages
can’t detect mistake
1) replace 0 by 9
2) numbers interchange
3
4
First letter
identify the country that issues the note
add up the numbers, add each single digit in the sum until a single digit remains
sum = 4+7+9+5 = 25, 2+5 = 7
5
Checksum
single digit obtained previously
refer to the particular country
6
12-digit
1 st : category
2 nd -6 th : manufacturer
7 th -11 th : identify the product
12 th : check digit
sum = 3 (1 st )+ 1 (2 nd )+ 3 (3 rd )+ … + 3 (11 th )+ 1 (12 th )
sum should end with a 0. (e.g. 10,20,30,…)
can detect all single position error and about 89% of other kinds of errors
7
use a variation of the UPC scheme append check digits to the numbers assigned to banks
Each bank has a 8-digit routing number
sum = 7 (1 st )+ 3 (2 nd )+ 9 (3 rd )+ … + 7 (7 th )+ 3 (8 th )
an extra 9 th digit (check digit) = last digit of the sum i.e. sum = 53 → check digit = 3
numbers 7 , 3 , 9 are called weights
can detect most transposition errors
8
13-digit
become worldwide standard
existing UPC numbers are converted to EAN by adding an extra “0” at the beginning
sum = 1 (1 st )+ 3 (2 nd )+ 1 (3 rd )+ … + 1 (11 th )+ 3 (12 th )+ 1 (13 th )
does not affect the check digit compared with UPC
9
Credit cards, libraries, blood banks, etc
Computation
1) add the digits in odd positions
2) double the result
3) add the numbers in odd positions that exceed 4
4) add the remaining digits (even positions)
check digit = the number needed to bring the total result to end with 0
10
detect 100% single position error and 98% common error
11
10-digit e.g. a
1
- a
2 a
3 a
4 a
5
- a
6 a
7 a
8 a
9
- a
10
↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ published publisher identification check digit
country sum = 10a
1
+9a
2 number
+8a
3
+7a
4
+6a
5
+5a
6
+4a
7
+3a
8
+2a
9
+1a
10 is divisible by 11
however, the 10 th digit (check digit) could be 10
solution: use “X” instead of “10”
detect 100% single position error and transposition error
another type: 13-digit, same as EAN
12
The ISBN 0-669-03925-4 is the result of a transposition of two adjacent digits not involving the first or last digit.
Determine the correct ISBN.
13
A series of dark and light spaces that represents characters
Binary code
A system for representing data with two symbols
Bar coding
Method for automated data collection
14
A beam of light passes through the bars and spaces by scanning device
The differences in reflection intensities
Dark bars reflect less; light spaces reflect more
15
most often encountered, first used on grocery items in
1973 translate 12-digit number into bars
12-digit number
two five-digit numbers in between two single-digit
16
12-digit: 0-12345-67890-5
1 st number (0) : kinds of product
next 5 digits (12345): manufacturer number
next 5 digits (67890): product number
last digit (5) : check digit
17
digits are represented by a space divided into 7 modules of equal width
2 long bars with one-module thickness in each end separated by a light space of one-module thickness the modules are named as guard bar patterns
18
separate the manufacturer’s number and the product number not a part of identification number
5 modules: a light space, a long dark bar, a light space, a long dark bar, a light space
19
one-module-thickness light space 0 one-module-thickness dark bar 1 code in the product number can be obtained from the code in the manufacturer’s number, vice versa
20
replace 1 by 0, 0 by 1
Example
0111011 for manufacture’s number
= 1000100 for the product number manufacture’s number : odd number of 1’s product number : even number of 1’s
Determine whether the barcode is scanned from LHS or
RHS
scanning can be done correctly
21
1. Prove that the ISBN detects 100% of the single position errors.
2. The following is an actual identification number and bar code from a roll of wallpaper.
What appears to be wrong with them? Speculate on the reason for the apparent violation of the UPC format.
(write at least two)
22
Extra : Compare the advantages and the disadvantages of the algorithm methods stated in class. Give examples on the purpose of each method.
23
Thank you!
24