Heredity, Gene Regulation, and Development
I. Mendel's Contributions
II. Meiosis and the Chromosomal Theory
III. Allelic, Genic, and Environmental Interactions
IV. Sex Determination and Sex Linkage
V. Linkage
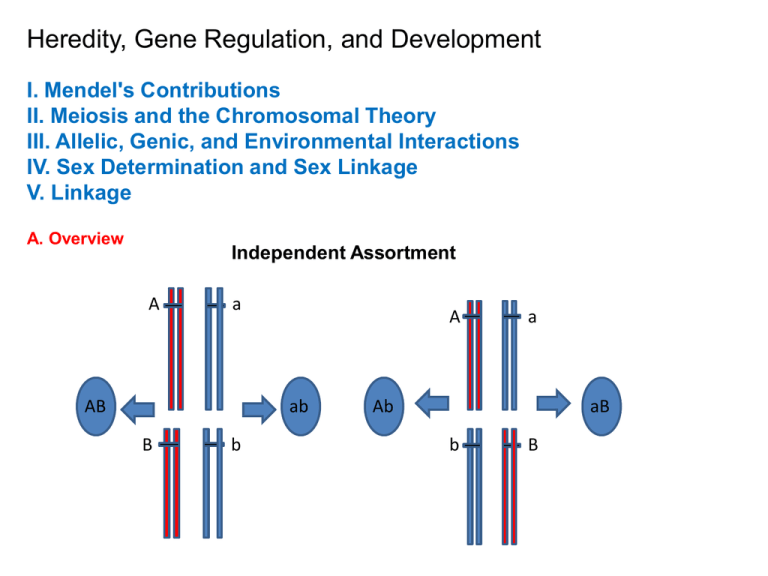
A. Overview
Independent Assortment
A
a
AB
A
ab
B
b
a
Ab
aB
b
B
Independent Assortment
V. Linkage
A
a
A
A. Overview
AB
ab
B
Ab
b
aB
b
Linkage
A
a
AB
ab
B
a
b
B
V. Linkage
Linkage
A. Overview
A
a
AB
ab
B
b
In Prophase I of Meiosis – Crossing-over
A
A a
a
AB
ab
B
b B
Ab
aB
b
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
Test Cross
AABB
aabb
AB
X
AB
ab
ab
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
- if genes are immediate neighbors, they are almost never separated by
crossing over and are ‘always’ inherited together. The pattern mimics that of a single
gene.
AABB
aabb
AB
ab
X
ab
AB
Gametes
AB
ab
ab
F1
AB
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
- if genes are immediate neighbors, they are almost never separated by
crossing over and are ‘always’ inherited together. The pattern mimics that of a single
gene.
ab
ab
F1 x F1
X
ab
AB
Gametes
ab
AB
ab
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
- if genes are immediate neighbors, they are almost never separated by
crossing over and are ‘always’ inherited together. The pattern mimics that of a single
gene.
ab
ab
1:1 ratio A:a
F1 x F1
X
AB
ab
1:1 ratio B:b
1:1 ratio AB:ab
NOT 1:1:1:1
Gametes
ab
AB
ab
Phenotypes
AaBb
AB
aabb
ab
aB ?
Ab ?
C. Incomplete Linkage
a
A
b
B
a
a
b
b
C. Incomplete Linkage
- So, since crossing-over is
rare (in a particular region),
most of the time it WON’T
occur and the homologous
chromosomes will be
passed to gametes with
these genes in their original
combination…these
gametes are the ‘parental
types’ and they should be
the most common types of
gametes produced.
a
A
b
a
B
a
b
A
B
a
b
b
C. Incomplete Linkage
- But during Prophase I,
homologous chromosomes
can exchange pieces of
DNA.
- This “Crossing over”
creates new combinations
of genes…
These are the ‘recombinant
types’
a
A
b
a
B
a
b
A
B
a
B
A
b
a
b
b
C. Incomplete Linkage
As the other parent only
contributed recessive
alleles, the phenotype of the
offspring is determined by
the gamete received from
the heterozygote…
a
A
b
a
a
B
a
b
A
B
b
b
gamete
genotype
phenotype
ab
aabb
ab
ab
AaBb
AB
LOTS of these
a
B
ab
aaBb
aB
A
b
ab
Aabb
Ab
FEW of these
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are linked,
or are assorting independently:
V. Linkage
AaBb x aabb
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are linked, Offspring
or are assorting independently:
AB
- test cross
Number
43
Ab
12
aB
8
ab
37
V. Linkage
AaBb x aabb
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are linked, Offspring
or are assorting independently:
AB
- test cross
- determine expectations under the
hypothesis of independent assortment
Number
43
Ab
12
aB
8
ab
37
The frequency of ‘AB’ should = f(A) x f(B) x N = 55/100 x 51/100 x 100 = 28
The frequency of ‘Ab’ should = f(A) x f(B) x N = 55/100 x 49/100 x 100 = 27
The frequency of ‘aB’ should = f(a) x f(B) x N = 45/100 x 51/100 x 100 = 23
The frequency of ‘ab’ should = f(a) x f(b) x N = 45/100 x 49/100 x 100 = 22
V. Linkage
AaBb x aabb
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are linked, Offspring
or are assorting independently:
AB
- test cross
- determine expectations under the
hypothesis of independent assortment
Number
43
Ab
12
aB
8
ab
37
B
b
A
43
12
a
8
37
Easy with a 2 x 2
contingency table
Col.
Total
Row
Total
V. Linkage
AaBb x aabb
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are linked, Offspring
or are assorting independently:
AB
- test cross
- determine expectations under the
hypothesis of independent assortment
Easy with a 2 x 2
contingency table
Compute Row, Columns,
and Grand Totals
Number
43
Ab
12
aB
8
ab
37
B
b
Row
Total
A
43
12
55
a
8
37
45
Col.
Total
51
49
100
V. Linkage
AaBb x aabb
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are linked, Offspring
or are assorting independently:
AB
- test cross
- determine expectations under the
hypothesis of independent assortment
Easy with a 2 x 2
contingency table
Compute Row, Column,
and Grand Totals
E = (RT x CT)/GT
Number
43
Ab
12
aB
8
ab
37
B
Exp.
b
Row
Total
A
43
28
12
55
a
8
37
45
Col.
Total
51
49
100
V. Linkage
AaBb x aabb
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are linked, Offspring
or are assorting independently:
AB
- test cross
- determine expectations under the
hypothesis of independent assortment
Easy with a 2 x 2
contingency table
Compute Row, Column,
and Grand Totals
E = (RT x CT)/GT
Number
43
Ab
12
aB
8
ab
37
B
Exp.
b
Exp.
Row
Total
A
43
28
12
27
55
a
8
23
37
22
45
Col.
Total
51
49
100
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are
linked, or are assorting independently:
B
Exp.
b
Exp.
Row
Total
A
43
28
12
27
55
a
8
23
37
22
45
Col.
Total
51
49
- Chi-Square Test of Independence
Obs
Exp
(o-e)
(o-e)2/e
AB
43
28
15
8.04
Ab
12
27
-15
8.33
aB
8
23
-15
9.78
ab
37
22
15
10.23
X2 =
36.38
Phenotype
100
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are
linked, or are assorting independently:
2. Detemining the arrangement of
alleles in the F1 individual; which alleles are
paired on each homolog?
AaBb x aabb
Offspring
Number
AB
43
Ab
12
aB
8
ab
37
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are
linked, or are assorting independently:
2. Detemining the arrangement of
alleles in the F1 individual; which alleles are
paired on each homolog?
AaBb x aabb
Offspring
Number
AB
43
Ab
12
aB
8
ab
37
- most abundant types are ‘parental types’
A
B
a
b
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are
linked, or are assorting independently:
A
B
a
b
2. Detemining the arrangement of
alleles in the F1 individual; which alleles are
paired on each homolog?
- most abundant types are ‘parental types’
- least abundant are products of crossing-over:
‘recombinant types’
a
B
A
b
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
1. Determining if the genes are
linked, or are assorting independently:
2. Detemining the arrangement of
alleles in the F1 individual; which alleles are
paired on each homolog?
AaBb x aabb
Offspring
Number
AB
43
Ab
12
aB
8
ab
37
3. Determining the distance between loci:
Add the recombinant types and divide by total
offspring; this is the percentage of recombinant
types. Multiply by 100 (to clear the decimal) and
this is the index of distance, in ‘map units’ or
centiMorgans.
A
B
a
b
20/100 = 0.20 x100 = 20.0 centiMorgans
20 map units
V. Linkage
A.Overview
B.Complete Linkage
C.Incomplete Linkage
D.Summary
- by studying the combined patterns of heredity among linked genes, linkage
maps can be created that show the relative positions of genes on chromosomes.








