PPT
advertisement

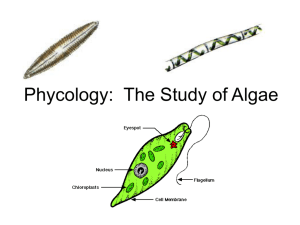
Principles of Biology By Frank H. Osborne, Ph. D. Lab 5 - Green Plant I Green Plants A. The part above the ground is the shoot. 1. The shoot has a stem. 2. Leaves are attached to the stem. 3. The point of attachment is called a node. 4. The part of the stem between the two nodes is called an internode. 5. Cotyledons from the seed used to be attached at the node below the first pair of leaves. Bean Plant germination Seed Leaves Cotyledons Growing Bean Plant Apical Meristem Trifoliate Leaf Second Internode First Internode Cotyledon Attachment Scar Growing Bean Plants Green Plants B. Bean Plant Leaves 1. The first pair of leaves. a. The first pair of leaves used to be part of the embryo in the seed. b. The embryonic leaves of the bean are heart-shaped. Green Plants B. Bean Plant Leaves 2. Other leaves of the bean plant. a. Leaves, other than the embryonic leaves are formed by the shoot tip meristem. b. These leaves are trifoliate and have three leaflets. Pigments of Leaves A. Leaves of green plants contain pigments. 1. Carotene a. Carotene is yellow. b. Carotene is very soluble in organic solvents but not very soluble in water. Pigments of Leaves A. Leaves of green plants contain pigments. 2. Xanthophyll a. Xanthophyll is grey to yellow in color. b. It is equally soluble in water and organic solvents. Pigments of Leaves A. Leaves of green plants contain pigments. 3. Chlorophyll a a. Chlorophyll a is dark blue-green. b. Chlorophyll a is more soluble in water than it is in organic solvents. Pigments of Leaves A. Leaves of green plants contain pigments. 4. Chlorophyll b a. Chlorophyll b is light yellow-green color. b. Chlorophyll b is more soluble in water than it is in organic solvents. B. Principles of Chromatography 1. Special paper is used. a. The paper has water in it between the fibers (aqueous phase) b. A spot of concentrated pigments is put at the bottom of the paper. 2. The paper is placed in solvent. a. The solvent is the organic phase. b. The organic phase (solvent) travels up the paper and carries the pigments with it. 2. The paper is placed in solvent. a. The solvent is the organic phase. b. The organic phase (solvent) travels up the paper and carries the pigments with it. 3. Pigments travel at different rates depending on their solubilities. a. Carotene travels at the fastest rate because it is most soluble in organic solvent. b. Xanthophyll travels at an intermediate rate because it is equally soluble in both water and organic solvent. c. Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b travel at a slow rate because they are more soluble in water. d. The rate of travel is called the ratio of fronts which is abbreviated as Rf. Calculations A. Mark the spot with a pencil. B. Form the spot. C. Run the chromatogram. D. Mark the top and bottom of each band. E. Measure the center of each band and mark it with a dot. F. Make a data table containing the distance of each band from the spot. G. Make another table for calculating the Rf values. Measuring the Chromatogram Measuring the Chromatogram Measuring the Chromatogram Measuring the Chromatogram Measuring the Chromatogram Measuring the Chromatogram Measuring the Chromatogram Distances of Bands from Spot Band Distance of Band from Spot (cm) Chlorophyll b Chlorophyll a Xanthophyll Carotene Front 1.2 cm 3.1 cm 7.2 cm 11.9 cm 12.2 cm Calculation of Rf Values Band Chlorophyll b Chlorophyll a Xanthophyll Carotene Calculation 1.2 cm/12.2 cm 3.1 cm/12.2 cm 7.2 cm/12.2 cm 11.9 cm/12.2 cm Rf 0.10 0.25 0.59 0.98 The End Lab 5 Green Plant I