5. Modulation
advertisement

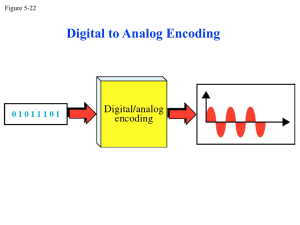
Modulation • Conversion of digital information to analog signals – Example: Telephone lines are band-limited (300-3300Hz) • Modem = modulator/demodulator • Characteristics of defining sine waves: – Amplitude – Frequency – Phase Winter 2005 ECE Change one or more of them to send information ECE 766 Computer Interfacing and Protocols 05 - 1 Modulation • Modulation Techniques – Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) – Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) – Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) • Aspects of Modulation – Bit rate vs. Baud rate Bit rate ≥ Baud rate – Carrier Signal Winter 2005 ECE ECE 766 Computer Interfacing and Protocols 05 - 2 Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) • Basic technique (like AM) change the amplitude of the signal to transfer logical values Amplitude 0 1 0 1 Time 1 baud 1 baud 1 baud 1 baud 1 second • On-Off Keying (OOK) • Highly susceptible to noise • Inefficient Winter 2005 ECE ECE 766 Computer Interfacing and Protocols 05 - 3 Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) • Bandwidth requirement Amplitude Minimum Bandwidth = Nbaud Frequency fc-(Nbaud/2) fc fc+(Nbaud/2) • BW = (1+d) x Nbaud • d ≥ 0 related to the condition of the line Winter 2005 ECE ECE 766 Computer Interfacing and Protocols 05 - 4 Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) • Represent each logical value with another frequency (like FM) Amplitude 0 1 0 1 Time 1 baud 1 baud 1 baud 1 baud 1 second • Not susceptible to noise as much as ASK • Limiting factor: Physical capabilities of the carrier Winter 2005 ECE ECE 766 Computer Interfacing and Protocols 05 - 5 Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) • Bandwidth requirement Amplitude BW=fc1--fc0+Nbaud fc1--fc0 Nbaud/2 Nbaud/2 Frequency fc0 fc1 • How about duplex communication? Winter 2005 ECE ECE 766 Computer Interfacing and Protocols 05 - 6 Phase Shift Keying (PSK) • Use different phased signals to represent binary values Reference – 0 = in phase with reference – 1 = out of phase with reference Amplitude 0 1 0 1 Time 1 baud • Not practical Winter 2005 ECE 1 baud 1 baud 1 baud 1 second ECE 766 Computer Interfacing and Protocols 05 - 7 Phase Shift Keying (PSK) • Differential PSK – 0 = same phase as last signal element – 1 = 180º shift from last signal element Amplitude 0 1 1 0 Time 1 baud 1 baud 1 baud 1 baud 1 second • Constellation Diagram: Winter 2005 ECE 1 ECE 766 Computer Interfacing and Protocols 0 05 - 8 Phase Shift Keying (PSK) • Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (Q-PSK): Do not only use 180º shift 010 01 011 10 001 00 100 11 000 111 101 110 4-PSK (Q-PSK) 8-PSK • Min. BW requirement: same as ASK! • Self clocking (most cases) Winter 2005 ECE ECE 766 Computer Interfacing and Protocols 05 - 9 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) • Combine ASK and PSK such that each signal corresponds to multiple bits 3 amplitudes 12 phases • More phases than amplitudes • Minimum bandwidth requirement same as ASK or PSK Winter 2005 ECE ECE 766 Computer Interfacing and Protocols 05 - 10