guidelines for suppliers
advertisement

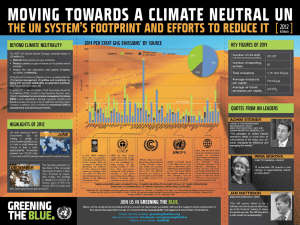
NICSA Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Request Form Instructions for completing the form NICSA Preliminaries • • The greenhouse gas data request form is for Nicsa's subcontractors to provide emissions data for the life cycle of the products they supply so that we can draw up an inventory of greenhouse gas emissions for Abengoa companies. Subcontractors must complete one form for each line or item on the order. NICSA 0. Heading • This section is particularly important and helps those who have to validate the report identify the order and supplies to which it refers. • Accordingly, subcontractors must provide the name of the work or service, the company's name and its location, the Nicsa order number, the estimated duration of the service and the date of issue of the order. 3 NICSA 1. Total GHG Emissions • • This section must be completed after all the calculations necessary for obtaining the total figure for greenhouse gas emissions have been made and it must contain the sum of the emissions that correspond to the following areas. The total GHG emissions associated with the work must be given in equivalent tons of CO2. • The period for reporting the information must also be included. NICSA 1.1 Fuel Consumption • • This section must be completed if the subcontractor uses facilities or machinery that involve combustion processes; otherwise, it should be completed with 'not applicable' (N/A). The form must include the type of fuel used, the quantity of fuel in both liters and kilograms* consumed during the period corresponding to the report and the fuel emission factor. *To convert the quantity of fuel from liters to units of mass, the figure must be multiplied by the density of the fuel. NICSA 1.1 Fuel Consumption • Combustion greenhouse gases include CO2 and, to a lesser extent, CH4 and N2O. The emissions of each gas are calculated as follows: Emission = Activity data x Gas emission factor Fuel consumption x Net calorific value The fuel consumption is the figure shown in section 1.1 (kg) The net calorific value can be obtained from the following sources: – IPCC Guidelines: http://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/index.html (Volume 2, Introduction, Page 19) – Last National Inventory submitted to the Secretariat of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change:http://unfccc.int/national_reports/annex_i_ghg_inventories/national_inventories_submissions/items/4303.php The unit used for the consumption figure (e.g. kg of diesel oil) must be taken into account when obtaining the activity figure in TJ NICSA Example Calculation of Fuel Emissions • We have a consumption of 50 l of diesel oil for a forklift. First of all, the quantity must be converted into kilograms of diesel oil by multiplying the figure by its density. Volume of diesel oil (l) = 50 l x 0.85 kg/l = 42.5 kg of diesel oil. • To calculate the activity figure, we multiply consumption by the net calorific value obtained from the IPCC guidelines: First of all, take the units (TJ/Gg) and convert the kg into Gg: 42.5 kg = 0.0000425 Gg AD (Activity Data) = 0.0000425 Gg x 43 TJ/Gg = = 0.0018275 TJ NICSA Example Calculation of Fuel Emissions • To calculate fuel emissions, we use the figures given in the IPCC Guidelines. In this case, we choose mobile combustion since the combustion takes place in forklifts; and we take the emission factors for CO2, CH4 and N2O for diesel. Combustion emissions = AD (Activity Data) x EF (Emission Factor) CO2 emissions = 0.0018275 TJ x 74100 kg CO2/TJ = = 135.418 kg CO2 CH4 emissions = 0.0018275 TJ x 3.9 kg CH4/TJ = = 0.00713 kg CH4 N2O emissions = 0.0018275 TJ x 3.9 kg N2O/TJ = = 0.00712 kg N2O Total fuel emissions: 135.418 + 0.00713 + 0.00712 = CO2/1000= 0.135 t CO2 13 5.432 kg NICSA 2.3 Electrical or Thermal Energy Consumption • • • • This section must be completed with the total electrical or thermal energy consumption during the work. The emission factor for the electrical or thermal energy used must also be provided. Direct emissions from thermal or electrical energy consumption are calculated by multiplying the energy consumption in kWh by the emission factor. This emission factor can be obtained from: – Directly from the electricity bill. – Energy regulation bodies (in Spain, the CNE) – An average emission factor can be used for each country or region. NICSA 3.2 Information about the Supplies and Consumables Required for the Work • • Subcontractors must give a brief description of the supply or consumable used and the quantity and units in which the figures are given, together with the emission factor for the manufacture of the supply. Emissions for the purchase of supplies and consumables are calculated by multiplying the quantity of product in kg by the supply emission factor. NICSA 3.2 Information about the Supplies and Consumables Required for the Work • The following link points to a database for calculating the life-cycle analysis of various products: http://lca.jrc.ec.europa.eu/lcainfohub/databaseList.vm NICSA 3.2 Information about the Haulage of Supplies Required for the Work • • • In this case, subcontractors must give a description of the supply or consumable that is being transported, indicating the total weight transported (kg), the distance travelled (km), the means of transport used and its emission factor. The following table provides emission factors for the various means of transport. Total emissions for the haulage of supplies are calculated by multiplying the weight of the product or consumables used (in tons) by the kilometers traveled and the emission factor for the means of transport. The final figure is again divided by one thousand to convert it into tons of CO2. NICSA 4. Closing Remarks Finally, all the resulting emissions are added together and included in section 1. It is important to complete the name and position in the company of the person completing the form and the date on which it is completed. Suppliers may encounter difficulties for obtaining information about certain areas. In this case, Nicsa will award the supplier a lower quality index* depending on the quantity and quality of the information provided. At the end of this section, subcontractors must remember to add up all the emissions and include the resulting figure at the top. *Quality index: value associated with each emissions figure for each source and greenhouse gas and with each parameter used to calculate the emissions; it indicates data reliability level. Increasing numerical values for the quality index indicate more reliable data.