Physics 101: Lecture 21 Waves

Exam 3
Physics 101: Lecture 21
Waves
Today’s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 11
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 1
Preflight 5
Which concepts did you find the most difficult when preparing for this lecture?
Superposition and interference
Waves and wave motion in general are difficult for me to grasp…
Overtones…
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 2
Waves Overview
Types
Speed
Harmonic
Superposition
Standing
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 3 05
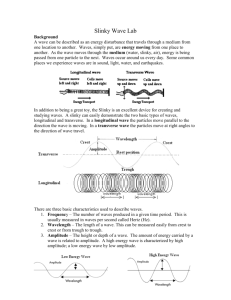
Types of Waves
“Understanding all the different kinds of waves.”
Transverse: The medium oscillates perpendicular to the direction the wave is moving.
Water (more or less)
Slinky demo
“I have a hard time visualizing what a period is.”
Longitudinal: The medium oscillates in the same direction as the wave is moving
Sound
Slinky demo
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 4 8
Slinky Preflight 3
Suppose that a longitudinal wave moves along a
Slinky at a speed of 5 m/s. Does one coil of the slinky move through a distance of five meters in one second?
1. Yes totally guessing here, but I LOVE
SLINKYS!!
2. No correct
5 m/s isn't the distance one coil moves, its how fast the wave moves
34%
5m
66%
0% 20% 40% 60% 80%
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 5 12
Velocity of Waves Act
v
T ension m/L
T ension
A spring and slinky are attached and stretched. Compare the speed of the wave pulse in the slinky with the speed of the wave pulse in the spring.
A) v slinky
> v spring
B) v slinky
= v spring
C) v slinky
< v spring
Slinky stretches more, so it has a smaller mass/length .
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 6 17
Harmonic Waves
y(x,t) = A cos( w t –kx)
“the weird/new symbols get me confused i never know what they represent “
Wavelength: The distance
between identical points on the wave.
Amplitude: The maximum displacement A of a point on the wave.
Angular Frequency w
: w
= 2 p f
Wave Number k: k = 2 p
/
Recall: f = v /
y
Wavelength
Amplitude A x
A
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 7 20
Period and Velocity
Period: The time T for a point on the wave to undergo one complete oscillation.
Speed: The wave moves one wavelength
in one period T so its speed is v =
/ T .
v
T
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 8 22
Harmonic Waves Exercise
+2 y(x,t) = A cos( w t –kx)
Label axis and tic marks if the graph shows a snapshot of the wave y(x,t) = 2 cos(4t –2x) at x=0.
Recall: T = 2 p
/ w
T = 2 p/w
2p/4
1.58
p /4 p / 2 t
-2
3p /4
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 9 25
Preflight 1+2
Suppose a periodic wave moves through some medium. If the period of the wave is increased, what happens to the wavelength of the wave assuming the speed of the wave remains the same?
1. The wavelength increases correct
2. The wavelength remains the same
3. The wavelength decreases
= v T
62%
16%
22%
0% 20% 40% 60% 80%
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 10 26
ACT
The wavelength of microwaves generated by a microwave oven is about 3 cm . At what frequency do these waves cause the water molecules in your burrito to vibrate ?
(a) 1 GHz (b) 10 GHz (c) 100 GHz
1 GHz = 10 9 cycles/sec
The speed of light is c = 3x10 8 m/s
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 11 29
ACT Solution
Recall that v =
f .
f
v
.03m
10 Hz
10GHz
H H
Makes water molecules wiggle
O
1 GHz = 10 9 cycles/sec
The speed of light is c = 3x10 8 m/s
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 12 30
Absorption coefficient of water as a function of frequency.
f = 10 GHz
Visible
“water hole”
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 13 31
Interference and Superposition
When two waves overlap, the amplitudes add.
Constructive: increases amplitude
Destructive : decreases amplitude
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 14 34
Reflection Act
A slinky is connected to a wall at one end. A pulse travels to the right, hits the wall and is reflected back to the left. The reflected wave is
A) Inverted B) Upright
Fixed boundary reflected wave inverted
Free boundary reflected wave upright
I don't understand the picture with free boundary versus fixed boundary
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 15 37
Standing Waves Fixed Endpoints
Fundamental n=1 (2 nodes)
n
= 2L/n
f n
= n v / (2L)
I did not really understand what the point or meaning of the fundamental frequency was.
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 16 44
Standing Waves:
L / 2 f
1
= fundamental frequency
(lowest possible)
A guitar’s E-string has a length of 65 cm and is stretched to a tension of 82N. If it vibrates with a fundamental frequency of 329.63 Hz, what is the mass of the string?
v
T
f = v / tells us v if we know f ( frequency
) and ( wavelength) v =
f
= 2 (0.65 m) (329.63 s
= 428.5 m/s
-1 ) v 2 = T /
= T / v 2 m= T L / v 2
= 82 (0.65) / (428.5) 2
= 2.9 x 10 -4 kg
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 17 48
Wave Types
Summary
Transverse (eg pulse on string, water)
Longitudinal (sound, slinky)
Harmonic
y(x,t) = A cos( w t –kx) or A sin( w t – kx)
Superposition
Just add amplitudes
Reflection (fixed point inverts wave)
Standing Waves (fixed ends)
n
= 2L/n
f n = n v / 2L
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 18 50
Practice Problems
Chapter 11, probs 1, 9, 13, 15, 17, 21, 25,
29, 31, 33, 49, 57, 61, 65 (hard!), 77
(hard!)
Physics 101: Lecture 21, Pg 19