Essential Learning Review
advertisement

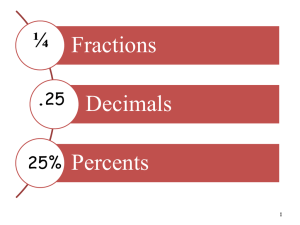
Essential Learning Review Essential Learning Review Topics are correlated to the 5th grade textbook. Please use the pdf links provided on the school website. Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Essential Learning Review Grade 6 Essential Learning These skills should be mastered by students entering grade 6. Mastery of essential learning from previous grade levels continues to be expected. All previous grades plus… Number Sense and Operations Basic fraction knowledge (Chapter 7 Lessons 1-12 p.394-423) Numerator, denominator Simplifying Improper fraction to mixed number and vice versa Equivalent fractions Rounding whole numbers and decimals up to the thousandths place (Chapter 1 Lesson 3 p.8-11; Lesson 8 p.26-27) Add and subtract decimals (Chapter 1 Lessons 12-13 p.38-41) Add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers with like denominators (no regrouping) (Chapter 8 Lessons 1 and 5 p.460-461, 472-473) Understand the relationship between fractions and decimals (Chapter 7 Lessons 13-14 p.426-433) one-tenth is 1 10 and 0.1 Essential Learning Review Geometry and Measurement Basic geometry facts (Chapter 6 Lessons 1-6 p.328-351) Types of angles and triangles Differences between types of quadrilaterals Use formulas to find area, perimeter and volume with proper labels Perimeter – linear (Chapter 9 Lesson 5 p.540-541) Area – square units (Chapter 9 Lessons 7-10 p.548-557) Volume – cubed units (Chapter 10 Lesson 5 p.610-613) Graphing ordered pairs in quadrant one (Chapter 12 Lesson 9 p.724-727) Know the difference between coordinates and axes (Chapter 3 Lesson 14 p.174-175) Convert units in the customary system (Chapter 9 Lesson 1 p.528-531) Essential Learning Review Patterns and Algebra Understand the meaning of a variable (Chapter 2 Lesson 12 p.100-103) Evaluate algebraic expressions (Chapter 2 Lesson 12 p.100-103) Value of a + 7 or 8a if a = 9 Solve algebraic equations using mental math (Chapter 2 Lesson 15 p.108-109) X+3=9 Essential Learning Review Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability Find mean, median, mode and range (Chapter 5 Lesson 6 p.282-285) Create a bar and line graph with proper scale, interval, axis labels, title (Chapter 5 Lessons 2-4 p.262-269) Find the probability of simple everyday events written as fractions (Chapter 5 Lesson 12 p.302-305) Chance with a spinner, coin, number cube Example: chances of winning a boardwalk game Essential Learning Review Problem Solving Solve two step word problems using various strategies Make an organized list (Chapter 2 Lesson 6 p.8081) Work backwards (Chapter 8 Lesson 9 p.484-487) Guess and check (Chapter 4 Lesson 3 p.210-211) Make a table (Chapter 11 Lesson 5 p.660-661) Draw a picture (Chapter 9 Lesson 11 p.558-559) Solve a simpler problem (Chapter 6 Lesson 7 p.352-354) Decide if answers are reasonable (Chapter 1 Lesson 14 p.42-45) Essential Learning Review Place Value and Rounding • Numbers to the right of the decimal point end in “ths” • Read the number before the decimal; read decimal point as “and”; read the number after the decimal; finish with the place value…one million, three hundred forty two thousand, three hundred sixty five and one thousand four hundred twenty seven tenthousandths Essential Learning Review Place Value and Rounding • To round – identify the place you are rounding; every digit in front of it stays the same; look at the place value to the right; 0-4 your number stays the same; 5-9 your number increases by 1; all digits to the right become zero • Round to the hundredths 1, 342, 365.1427 1, 342, 365.1_27 1, 342, 365.1400 Essential Learning Review Place Value and Rounding • Link to practice games http://www.gamequarium.com/pla cevalue2.html Essential Learning Review Fractions Basic Fraction Knowledge http://www.jamit.com.au/htmlFolder/FRAC1001.html#examples Essential Learning Review Fractions Simplifying Fractions • Divide the numerator and denominator by the same number – If you divide by the GCF you are done in one step – You know you can stop dividing when there is no number other than 1 that goes into the numerator and denominator Equivalent Fractions • Multiply or divide the numerator and denominator by the same number Essential Learning Review Fractions Links to Simplifying and Equivalent Fraction Games http://www.funbrain.com/fract/index.html http://www.jamit.com.au/htmlFolder/app1002.html http://classroom.jc-schools.net/basic/math-fract.html Essential Learning Review Fractions Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers • Numerator ÷ denominator – This becomes your whole number • What is your remainder? – This becomes your new numerator • Your denominator stays the same Example: 8 5 1 5 8 5 3 8 5 1 3 5 Essential Learning Review Fractions Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions • Whole number x denominator + numerator – This becomes your new numerator • Your denominator stays the same Example: 1 3 5 1x5 3 8 1 3 5 8 5 http://www.jamit.com.au/htmlFolder/app1003.html Essential Learning Review Fractions Adding and Subtracting Fractions • Add or subtract the numerators • Your denominator stays the same • Simplify your answer Example: video example Essential Learning Review Fractions Adding and Subtracting Mixed Numbers • Add or subtract the numerators • Add or subtract the whole • Your denominator stays the same • Simplify your answer Example: watch an example Essential Learning Review Decimals Fraction versus decimals • For every fraction there is a decimal with the same name! Example: 1 10 Write a decimal that has a 1 in the tenths place. 0.1 Essential Learning Review Decimals Fraction versus decimals • For every decimal there is a fraction with the same name! Example: 0.03 Write a fraction that reads 3 hundredths. 3 100 Essential Learning Review Decimals Fraction versus decimals • It’s very important that the denominator of your fraction is 10, 100, 1000 (or any power of 10) because these match your decimal place values. Example: Change your denominator to a 2 power of 10 (multiply 5 5 x 2 = 10). Then multiply your numerator by the same number. 2x2 5x2 4 10 Equivalent decimal is 0.4 Essential Learning Review Decimals Adding and subtracting decimals • Line up place values and decimal point. • Input zeros in empty spaces. • Bring decimal point down. • Add or subtract like normal. Decimal rules Watch how it’s done Practice with decimal football Essential Learning Review Geometry Basic Facts • Point – a definite location in space • Line – goes on “infinitely” in both directions • Line segment – part of a line • Ray – has one endpoint and goes on infinitely in one direction • Parallel lines – will never intersect • Perpendicular lines – intersect to form right angles ┼ Check out the proper symbols for these terms Essential Learning Review Geometry Types of Angles Acute Obtuse Right Straight Types of Triangles Click here for descriptions Take a practice quiz here Click here to learn about the 6 types of triangles Essential Learning Review Geometry Types of Quadrilaterals Click here for descriptions Click here to sort quadrilaterals Essential Learning Review Geometry Volume, Area and Perimeter NJASK reference sheet Area – The amount of space a figure covers (square units) Perimeter – The distance around a figure (linear units) Volume – The amount of space inside a 3 dimensional solid figure (cubed units) Essential Learning Review Geometry Area and Perimeter Examples Click here for examples Essential Learning Review Geometry Graphing in the first quadrant (5, 3) X-coordinate X-Axis (tells you how many spaces to move right) Y-coordinate Y-Axis (tells you how many spaces to move up) Essential Learning Review Geometry Graphing in the first quadrant (8, 4) Start at zero Move 8 spaces right Move 4 spaces up Put a dot at the intersection Essential Learning Review Geometry Graphing in the first quadrant Practice worksheet The four quadrants Essential Learning Review Geometry Converting in the Customary System • We use this system in the United States. • There are measurements of length, capacity and mass. Click here for flash cards and games There are also conversions on the NJASK reference sheet. Essential Learning Review Patterns and Algebra Variable Expressions • Letter or symbol that takes the place of a number • A mathematical phrase including at least one operation • No equal sign Examples of variables: X, a, Examples: X+5, 3y, 5b-7 Essential Learning Review Patterns and Algebra Equations • A mathematical sentence containing an equal sign Example: P+3=9 Evaluating Expressions • You must be given the value of the variable to find the solution Example: x=9 x+5 plug in 9 where the x is 9+5 = 14 Essential Learning Review Patterns and Algebra Solving Equations • To find the solution you must figure out what value of the variable will make the sentence true Example: P+3=9 P must equal 6 because 6 + 3 = 9 Evaluating Expressions Practice worksheet Try some of these to practice equations Essential Learning Review Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability Mean, Median, Mode and Range • Mean – the average – Add all the numbers together and divide by how many numbers there are • Median – the middle number – Line the numbers up from least to greatest and find the number in the middle – If there are 2 numbers in the middle – find the mean of those two numbers Essential Learning Review Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability Mean, Median, Mode and Range • Mode – the number that occurs most often – There may be no modes – There may be more than one mode • Range – the difference between the highest and lowest numbers – Subtract the highest number minus the lowest number Lots of worksheets Essential Learning Review Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability Bar Graph Line Graph All you need to know about making a bar graph So many line graph examples Essential Learning Review Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability Bar and Line Graphs Key Words and Points to Remember • Scale • Interval • X and y axes • All bars should be equally spaced and the same width • DO NOT connect the bars Essential Learning Review Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability Probability What is the probability of spinning an even number? P(even) There are 8 numbers and 4 are even so the probability is 4 1 8 2 Essential Learning Review Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability Probability The chance of something happening is your numerator. The total chances possible is your denominator. even #’s 4 1 total #’s 8 2 Essential Learning Review Problem Solving Solve two step word problems using various strategies Make an organized list (Chapter 2 Lesson 6 p.80-81) Work backwards (Chapter 8 Lesson 9 p.484-487) Guess and check (Chapter 4 Lesson 3 p.210-211) Make a table (Chapter 11 Lesson 5 p.660-661) Draw a picture (Chapter 9 Lesson 11 p.558-559) Solve a simpler problem (Chapter 6 Lesson 7 p.352-354) Decide if answers are reasonable (Chapter 1 Lesson 14 p.42-45) FOR THE ABOVE PROBLEM SOLVING TOPICS PLEASE REFER TO THE ONLINE 5TH GRADE TEXT BOOK FOR PRACTICE PROBLEMS AND EXAMPLES.