20 METRIC SYSTEM
advertisement
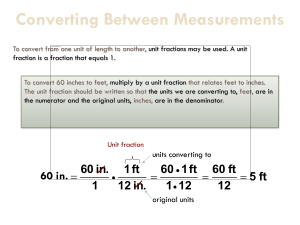
The METRIC SYSTEM & CONVERSIONS MSJC ~ San Jacinto Campus Math Center Workshop Series Janice Levasseur The Metric System • The metric system is an internationally standardized system of units of measurement. • The metric system is based on a base unit and prefixes. Prefixes • • • • • • • Kilo Hecto Deca Deci Centi Milli - 1000 100 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.001 k h da d c m Length • The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter (m) • Metric Units of Length – – – – – – – Kilometer (km) = 1000 m Hectometer (hm) = 100 m Decameter (dam) = 10 m Meter (m) = 1 m Decimeter (dm) = 0.1 m Centimeter (cm) = 0.01 m Millimeter (mm) = 0.001 m Mass • Weight is a measure of how strongly gravity is pulling on an object (decreases as elevation increases) • Mass is the amount of material in an object (doesn’t change) • Note: on Earth, weight and mass are used interchangeably Mass • The basic unit of mass in the metric system is a gram (g) • 1 g = mass of water in a cube that measures 1 cm x 1 cm x 1cm • Metric Units of Mass – – – – – – – Kilogram (kg) = 1000 g Hectogram (hg) = 100 g Decagram (dag) = 10 g Gram (g) = 1 g Decigram (dg) = 0.1 g Centigram (cg) = 0.01 g Milligram (mg) = 0.001 g Capacity • Liquid substances are measured in units of capacity. • The basic unit of mass in the metric system is a liter (L) • 1 L = capacity of a cube that measures 10 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm • Metric Units of Capacity – – – – – – – Kiloliter (kL) = 1000 L Hectoliter (hL) = 100 L Decaliter (daL) = 10 L Liter (L) = 1 L Deciliter (dL) = 0.1 L Centiliter (cL) = 0.01 L Milliliter (mL) = 0.001 L Conversions within the Metric System • To convert units within the metric system, write the prefixes in order from largest to smallest k h da d c m • To convert from a smaller unit to a larger unit, move to the left • To convert from a larger unit to a smaller unit, move to the right Ex: Convert 1600 cm to m • km hm dam m dm cm mm • Move 2 places to the left to get from cm to m • Therefore, move the decimal point in 1600 two places to the left to convert from cm to m 1600 cm = 16.00 m Ex: Convert 2 kL to L • kL hL daL L dL cL mL • Move 3 places to the right to get from kL to L • Therefore, move the decimal point in 2 three places to the right to convert from kL to L 2 KL = 2000 L Ex: Convert 241 g to mg • kg hg dag g dg cg mg • Move 3 places to the right to get from g to mg • Therefore, move the decimal point in 241 three places to the right to convert from g to mg 241 g = 241,000 mg Ex: Convert 3 mL to L • kL hL daL L dL cL mL • Move 3 places to the left to get from mL to L • Therefore, move the decimal point in 3 three places to the left to convert from mL to L 3 mL = 0.003 L Ex: Convert 45 cm to km • km hm dam m dm cm mm • Move 5 places to the left to get from cm to km • Therefore, move the decimal point in 45 five places to the left to convert from cm to km 45 cm = 0.00045 km Ex: Convert 5.4 kg to dg • kg hg dag g dg cg mg • Move 4 places to the right to get from kg to dg • Therefore, move the decimal point in 5.4 four places to the right to convert from kg to dg 5.4 kg = 54000 dg Conversions between the U.S. Customary System and the Metric System • Approximate equivalences between the U.S. Customary System and the Metric System are needed for conversion between systems • Dimensional Analysis will be used to compute the conversion Equivalences • Units of Weight – 1 oz 28.35 g – 1 lb 454 g – 2.2 lb 1 kg • Units of Capacity – 1.06 qt 1 L – 1 gal 3.79 L • Units of Length – – – – 1 in = 2.54 cm 3.28 ft 1 m 1.09 yd 1 m 1 mi 1.61 km Dimensional Analysis • Dimensional Analysis (also called FactorLabel Method or the Unit Factor Method) is a problem-solving method that uses the fact that any number or expression can be multiplied by one without changing its value (Multiplication Property of 1 – the Magic One) • Use the units to dictate the form of the Magic One Ex: Convert 130 lbs to kg (round to the nearest whole number) • Write the original measurement as a unit fraction • Multiply the unit fraction by a magic one – the form of which is dictated by the units – the numerator unit is the unit you want – the denominator unit is the unit you want to eliminate • Write your answer in the specified form (decimal number) Ex: Convert 130 lbs to kg (round to the nearest whole number) 130 lbs 1 1 kg 2 . 2 lbs = 59.0 kg 130 kg 2 .2 Ex: Convert 60 km to mi (round to the nearest whole number) • Write the original measurement as a unit fraction • Multiply the unit fraction by a magic one – the form of which is dictated by the units – the numerator unit is the unit you want – the denominator unit is the unit you want to eliminate • Write your answer in the specified form (decimal number) Ex: Convert 60 km to mi (round to the nearest whole number) 60 km 1 1 mi 1 . 61 km = 37.2 mi = 37 mi 60 mi 1 . 61 Ex: Convert 5.4 kg to lb (round to the nearest tenth place) • Write the original measurement as a unit fraction • Multiply the unit fraction by a magic one – the form of which is dictated by the units – the numerator unit is the unit you want – the denominator unit is the unit you want to eliminate • Write your answer in the specified form (decimal number) Ex: Convert 5.4 kg to lb (round to the nearest tenth place) 5 . 4 kg 2 . 2 lb 11 . 88 lb 1 1 kg 1 = 11.88 lb = 11.9 lb Ex: Convert 45 cm to in (round to the nearest tenth place) • Write the original measurement as a unit fraction • Multiply the unit fraction by a magic one – the form of which is dictated by the units – the numerator unit is the unit you want – the denominator unit is the unit you want to eliminate • Write your answer in the specified form (decimal number) Ex: Convert 45 cm to in (round to the nearest tenth place) 45 cm 1 1 in 2 . 54 cm = 17.71 in = 17.7 in 45 in 2 . 54 Ex: As a practical joke, on the show Candid Camera, a gas station listed their price as $1.79/Liter. People gassing up thought they were getting a great deal, but then were outraged when their total owed came up. WHY? • What do you notice about the listed price? • What should we do? Listed their price as $1.79/Liter. $ 1 . 79 3 . 79 L 1L 1 gal $ 6 . 78 1 gal Ex: The price of a certain medication is $35 per Liter. Find the price per fluid ounce. $ 35 1L 1 qt 1 pt 1 C $ 35 1 L 1 . 06 qt 2 pt 2 C 8 fl oz 33 . 92 fl oz But now what? There isn’t a direct equivalence from Liters to fluid ounces. We can use several equivalences stepping down to fluid ounces Liters Quarts Pints Cups fluid ounces $ 1 . 03 / fl oz