1 - WordPress.com
advertisement

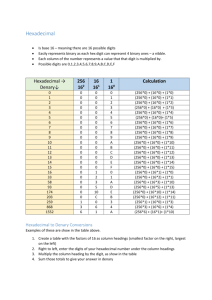
Lesson Objectives • Understand the hexadecimal numbering system • Convert numbers between hexadecimal and denary, and vice versa • ALL students be able to count in hex from 1 to 16 • MOST students will convert hex numbers into denary • SOME students will convert numbers between hex, denary and binary • You already know about base 10 (Decimal/Denary) x10 x10 x10 1000 100 10 1 1 2 3 4 • And you’ve just learnt about base 2 (Binary) x2 x2 x2 8 4 2 1 1 0 1 1 Why do we need binary numbers? • Because computers work on the principle of 2 states, that something is either ON/TRUE or OFF/FALSE. • This can only be done with base 2 (binary) • If it was done with decimal/base 10 there would be 10 different states! The problem with binary… • There is one big problem with binary…numbers can become VERY long! • In order to make it easier for a human programmers to work with binary numbers, they use the hexadecimal system (like a binary shortcut) Hexadecimal x16 x16 x16 4096 256 16 1 0 1 2 3 As we move left, the column headings increase by a factor of sixteen This number is: 1 x 256 + 2 x 16 + 3 x 1 = 291 It’s still two hundred and ninety-one, it’s just written down differently How can there be sixteen possible digits in each column, when there are only ten digits? http://www.advanced-ict.info/interactive/hexadecimal.html Hexadecimal • Hexadecimal uses the digits 0-9 and the letters A-F to represent the denary numbers 0-15 Den Hex Den Hex 0 0 8 8 1 1 9 9 2 2 10 A 3 3 11 B 4 4 12 C 5 5 13 D 6 6 14 E 7 7 15 F Notice how 0 is classed as a digit, so there are 16 numbers in total from 0 to 15 Making bigger numbers • You do it in exactly the same way 16 1 Den 1 0 1x16 16 1 1 1x16 + 1x1 17 1 A 1x16 + 1xA(10) 26 A 0 A(10)x16 160 2 B 2x16 + 1xB(11) 43 Where is it used? • When have you seen numbers being represented as letters? • Hex is often used for 32-bit colour values, especially on web pages • FF00EE99 instead of 111111110000000011101110100110 01. • http://www.advancedict.info/interactive/colours.h tml 255 • Denary – 255 • Binary – 11111111 • Hexadecimal – FF • Large binary numbers are hard to remember • Programmers use hexadecimal values because: – each digit represents exactly 4 binary digits; – hexadecimal is a useful shorthand for binary numbers; – hexadecimal still uses a multiple of 2, making conversion easier whilst being easy to understand; – converting between denary and binary is relatively complex; – hexadecimal is much easier to remember and recognise than binary; – this saves effort and reduces the chances of making a mistake. You convert denary to hex in the same was as binary 16 2 1 D Convert the denary number 45 into a hex number Step 1: How many times does 16 go into 45? 45 / 16 = 2 (with 13 remaining) Step 2: How many times does 13 go into 1? 13! 13 in hex is D Let’s do another one 16 C 1 7 Convert the denary number 199 into a hex number Step 1: How many times does 16 go into 199? 199 / 16 = 12 (with 7 remaining) Step 2: 12 in hex is C Step 2: How many times does 7 go into 1? 7! 7 in hex is 7! Lesson task: • Complete the denary to hex conversions in your workbook. • Extension: If you complete, have a go at the cross word task in your booklet. Hex to binary • To convert from hexadecimal to binary treat each digit separately. It may be easier to go via denary to get a binary number. Hex Denary Binary 1 1 D B 13 11 0 1 1 0 1 1 • So DB in hexadecimal is 11011011 in binary.