VISUAL ACUITY
PRESENTED BY
T.Muthuramalingam
DEFINITION
Is an ability of eye to discriminate two
stimuli separated in space.
Is the resolving power of eye.
PURPOSE
For refraction and prescribing spectacles
For monitoring ocular health
PRINCIPLE
To see an object it must subtend 1min
angle at the nodal point.
That means to produce an image of the
minimum size of 0.004mm
NOTATION
Visual acuity is noted in terms of Snellen’s
fraction.
Near visual acuity is noted in terms of N
notation
V/A = distance at which test is made
distance at which the smallest
letter read subtend angle of 5min.
E.g. the distance between pt and test
object is 6m and he read the letter of size
for 9m for normal person, then V/A=6/9
Print size of the letter is near visual acuity
E.g letter size is 8point the V/A= N8
Equipments for
measurement
V/A is measured by using different charts.
Like snellen’s chart, ETDRS chart,logmar chart
etc
Snellen’s chart is more popular using chart
Equipments:
•
•
•
•
•
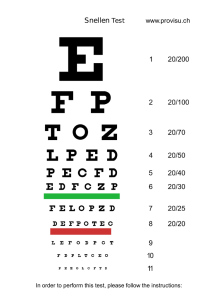
Snellen’s chart
Pointer
Occluder
Pinhole
Near vision chart
Construction of snellen’s
chart
Principle:
Each letter is designed in a
(Fig:)square with sides 5 times
the width of letter strokes.
The breadth of black (red)
strokes and spaces are equal.
The breadth of line and spaces
produce 1° of angle at nodal
point when viewed at certain
distance.
Each letter subtends an angle
of 5° at the nodal point when
seen at a certain distance.
Construction
The first line of the type is so constructed that the
angle is formed at a distance of 60 meters, the
sixth at 9, the seventh at 6,while additional lines
are usually inserted which subtend the same
angle at 5 and 4 meters .
These letters should thus be read by a person with
standard vision at these distance away.
Contd.
Meters
6/6
6/9
6/12
6/18
6/24
6/36
6/60
Feet
20/20
20/30
20/40
20/60
20/80
20/120
20/200
Types of chart and
room setup
Paper chart, projection chart, E-chart, alphabet
chart, picture chart
Room’s length should be 6m as light rays are
parallel for practical purpose.
If it is not possible then required distance is
achieved by using mirror in 3m.(for reflection of
reversed test types)
Illumination should not less then 50lumen/sq.ft
Chart should be more or less at the eye level of
the patient.
Distance visual acuity
This measure the patient’s distance vision by
testing the ability to read distance characters at a
standard distance.
Snellen’s chart is used with different test types.
For literate number chart and alphabet chart and
for illiterate E-chart,broken C-chart are used
The normal V/A is 6/6 in meter or 20/20 in feet
Near visual acuity
It is measured at distance with in arm’s
length usually it is 33to 40cm.
Test material is in the style of book or
newspaper but in series of unrelated words.
The size label ‘N8’indicates that the size of
test font is 8points and distance is
specified.
E.g. N8 at 40cm.
Pinhole acuity
A below – normal visual acuity recording
may be result of refractive error which can
be conformed with pinhole acuity
If use of pinhole improves a patients poor
uncorrected V/A means pt’s has refractive
errors.
If not improved then it is any other problem
other than refractive error.
Procedure of recording
V/A
Contd.
Position the Patients 20 feet( 6 meters ) from an
illuminated snellen’s chart.
Have the patient cover the left eye with an Occluder.
Ask the patient to read the letters from left to right up to
last line.
Note the smallest line in which more then half the
characters are read correctly.
Record the corresponding acuity fraction as well as the
number of letters missed. Ex,6/18 –2
Repeat Steps 2 to 4 with the right covered.
Record the acuity value for each eye separately, with and
without correction.
Contd.
If the subjects cannot read the largest letter he is
asked to walk towards the types.For example if he
sees the top letter at a distance of 2 meters,
then VA =2/60.
If not possible – VA = CF(counts fingers) at 1meter
If not possible – VA = HM(Hand movements).
If not possible – VA = PL(perception of light)
If not recorded - VA = No PL, this is total
blindness.
Vision assessment in
children
Neonates - Follow a light, face object(ask mother)
Optokinetic nystagmus
► 3-6 months
- Fixation and following
► 6-18 months – Preferential looking (keeler card)
► 9-24 months - Cake decoration
► 2-3 years
- Cardiff vanishing card
► 21/2–5 years - picture cards & matching charts
(S.G.card)
► >5 years
- Snellen chart
Types of chart
Keeler Card( fig.1)
Cardiff Card( fig.2)
Sheridan Gardiner test( fig.3)
Cambridge Crowding Card( fig.4)
Picture Chart( fig.5)
Snellen’s Chart( fig.6)
1.
3.
2.
5.
4.
6.
Points to remember
Carefully observed whether the patients is
completely covering the eye with cup of hand or
not
Observed the position of head whether he is
trying to see from side
Tell the patient to sit straight
As V/A plays a vital role in eye examination it
should be recorded carefully.
 0
0