Demystifying SEIFA
advertisement
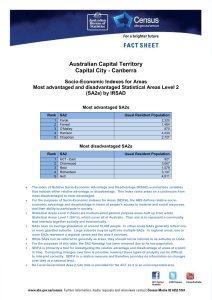
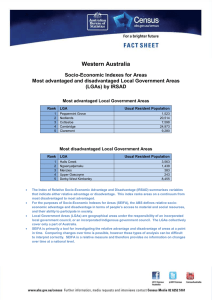
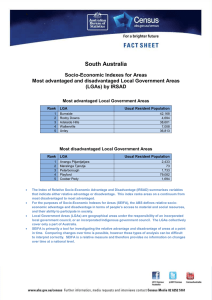
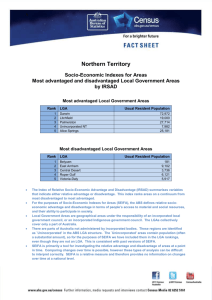
Demystifying SEIFA Jeff Wright Peter Radisich Socio-Economic Indexes For Areas Socio Economic Indexes For Areas Concept of Interest: Relative Advantage and Disadvantage Concept of Interest: Relative Advantage and Disadvantage Broadly define in terms of people’s access to material & social resources, and ability to participate in society No post-school qualifications High Income Unemployed Employed as Professional Concept of Interest: Relative Advantage and Disadvantage Access to Broadband Number of bedrooms One parent families Low Income Needs assistance with core activities No post-school qualifications Employed as Professional High Income Unemployed Concept of Interest: Relative Advantage and Disadvantage Access to Broadband High number of bedrooms One parent families Low Income Needs assistance with core activities No post-school qualifications High Income Unemployed Employed as Professional Concept of Interest: Relative Advantage and Disadvantage INDEX SCORE Access to Broadband High number of bedrooms One parent families Low Income Needs assistance with core activities Socio-Economic Indexes For Areas The four indexes Index of Relative Socio-Economic Disadvantage Index of Relative Socio-Economic Advantage & Disadvantage Index of Economic Resources Index of Education & Occupation Socio-Economic Indexes For Areas • The indexes apply at an area level - Summary of all people living in the area - Note: Socio-economic status of people within an area will vary. Base (smallest) area used: In the past Census Collection Districts (CD) SEIFA 2011 Statistical Area Level 1 (SA1) (average population size = approximately 500) (population size = approximately 300 to 400) SEIFA is also released for larger areas Product from 2006 Targeting areas for business & services Strategic Planning Applications of SEIFA Plus tips on good use Design of sample surveys Social & Economic Research Index of Relative Advantage & Disadvantage: Quintiles by Statistical Local Area, Melbourne, 2006 Index of Relative Socio-Economic Advantage & Disadvantage: Top and bottom deciles, CD Level, Melbourne, 2006 Legend Top Decile (Most Advantaged) Bottom Decile (Most Disadvantaged) 2 Excluded CDs (No Index Score) Using SEIFA for Social Research Index of Economic Resources decile for CD A further example: Proportion of people reporting fair/poor health, by Index of Economic Resources decile (2006) lowest 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 9th highest 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 Proportion of people reporting fair/poor health Source of Health Data: ABS National Health Survey, 2004-05 Say you were standing with one foot in the oven and one foot in an ice bucket. According to the percentage people, you should be perfectly comfortable. Bobby Bragan, 1963 Diversity of socio-economic characteristics within areas An example from Australia: Index of Relative Socio-Economic Disadvantage: Deciles, CD Level, Campbelltown North, 2006 Good Use of SEIFA - Summary Good Use of SEIFA - Key Points • SEIFA is for area level analysis – Interpretation if using for individuals, represents the surrounding area, not the individual! • Interpretation (health analysis) – A greater proportion of people living in the most disadvantaged 10% of CDs report fair/poor health • Ecological fallacy – A greater proportion of the 10% most disadvantaged people report fair/poor health – Why? A person who reports fair/poor health may live in a disadvantaged area, but not be disadvantaged themselves Accessing SEIFA Free of charge on the ABS website Take home messages • Summary measures with many applications • Free of charge • SEIFA 2011 will be released early 2013 Additional Slides For discussion purposes & answering questions SEIFA 2011 – Geography SA1 will be the base level ABS Structures – ASGS SA1 : score SA2 : score + distribution SA3 : score + distribution SA4 : distribution State : distribution Example of Distribution Measure: Non-ABS Structures (constructed using 'best fit' correspondences) SLA : score + distribution LGA : score + distribution SSC : score + distribution POA : score + distribution CED : distribution (not SED) Index of Advantage & Disadvantage high/low income high/low education high/low occupation housing broadband internet disability good for identifying advantaged OR disadvantaged areas Index of Disadvantage low income low education low occupation housing disability Indigenous status poor English good for focusing on disadvantaged areas Index of Economic Resources income housing size/cost tenure type business owners good for focusing on financial aspects of advantage/disadvantage Index of Education & Occupation education occupation employment good for focusing on education/occupation Using SEIFA for Social Research Proportion of total population (all ages) Example: Investigating the relationship between socio-economic status & age 25% 20% 15% % under 15 years 10% % over 64 years 5% 0% Decile of IRSAD IRSAD = Index of Relative Socio-Economic Advantage & Disadvantage (2006) Using SEIFA for Social Research Proportion of adults with ‘high’ or ‘very high’ mental distress, by Index of Relative Advantage and Disadvantage decile Index of Relative Advantage and Disadvantage decile for CD lowest 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 9th highest 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 Proportion of adults with 'high' or 'very high' mental distress Source of Health Data: ABS National Health Survey, 2004-05 Postal Area: 2617 25,476 people State Suburb 3,057 people Statistical Local Area Census Collection District 3,057 people 649 people income high income low income 10 most disadvantaged CDs 11% 31% Australia 24% 17% 10 most advantaged CDs 79% 2% education no qualifications 61% 49% 25% Internet access broadband access no internet access 21% 62% 41% 37% 80% 10% occupation unemployed Labourers Professionals 13% 18% 15% 5% 11% 20% 2% 2% 42% housing high mortgage high rent payments low rent payments household overcrowding "rent social" 16% 11% 51% 9% 27% 19% 18% 16% 3% 5% 77% 87% 1% 0% 0%