(COCs) Advanced Slide Set
advertisement

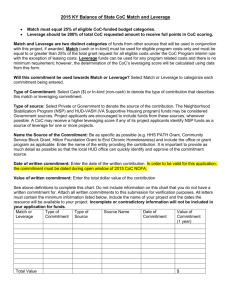
Combined Oral Contraceptive Pills (COCs) Advanced Slide Set Advanced Slide Set, Slide #1 Combined Oral Contraceptives Effectiveness Spermicides Female condom Standard Days Method Male condom Oral contraceptives DMPA IUD (TCu-380A) Pregnancy rate when used correctly and consistently Female sterilization Male sterilization Pregnancy rate as commonly used Implants 0 Source: Trussell, 2011. 5 10 15 20 25 30 Percentage of women pregnant in first year of use Advanced Slide Set, # 2 Protective Effect of COC Use on Ovarian and Endometrial Cancer Lifetime risk of acquiring ovarian or endometrial cancer after 8+ years of COC use Number per 100 women 100 10 Ovarian Cancer Non COC users COC users 8 Endometrial Cancer Non COC users COC users Protection develops after 12 months of use and is present for at least 15 years 6 4 2 3.1 1.7 1.2 0.7 0.6 0.7 0.2 Reduces risk by more than 50% 0.3 0.6 0.2 0.4 0.1 0 United States Costa Rica Source: Petitti and Porterfield, 1992; CASH Study 1987. China Advanced Slide Set, # 3 Understanding Relative Risk Definition Relative Risk = Probability of developing condition X in exposed population Probability of developing condition X in unexposed population Advanced Slide Set, # 4 Understanding Relative Risk Risk Versus Protection Relative Risk Log Scale 10 5 Increased Risk 1 No Effect 0.5 Protective Effect Exposure increases risk of disease No association Exposure decreases risk of disease 0.1 Advanced Slide Set, # 5 Understanding Relative Risk Confidence Interval Relative Risk Log Scale 10 5 A B Increased Risk C No Effect 1 D 0.5 Statistical interpretation: 0.1 A – Significant risk Protective Effect B – Nonsignificant risk C – Nonsignificant protection D – Significant protection Advanced Slide Set, # 6 Relative Risk for Breast Cancer among COC users and Non-users Relative Risk Log Scale 10 Increased Risk 1.0 1.24 1.16 1.07 1.01 [1.15–1.33] [1.08–1.23] [1.02–1.13] [0.96–1.05] No Effect 1 0.1 Protective Effect [95% Confidence Interval] Nonusers Current COC users 1–4 yrs after stopping 5–9 yrs after stopping 10+ yrs after stopping Source: Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer, 1996; Milne, 2005; Silvera, 2005 . Advanced Slide Set, # 7 COC Users and Risk of Blood Clots Estimates of venous thromboembolism per 100,000 woman-years Incidence Relative Risk 4–5 1 Low-dose COCs 12–20 3–4 High-dose COCs 24–50 6–10 Pregnant women 48–60 12 Young women in the general population Pregnancy presents a higher risk of blood clots than do COCs. Source: WHO, 1998; Speroff, 2005. Advanced Slide Set, # 8 COC Users and Risk of Heart Attack Estimated number of heart attacks per million woman-years Characteristic Age 20-24 Age 30-34 Age 40-44 Healthy non-COC user 0.14 1.7 21.3 Healthy COC user 0.34 4.2 53.2 COC user who smokes 1.6 20.4 255 COC user with BP 2.0 25.5 319 Screening for existing risk factors is important. Source: Farley, 1998. Advanced Slide Set, # 9