HDAC Inhibition of SelSA Compounds

Katherine Tai
Mentor: Mohaiza Dashwood
Advisor: Rod Dashwood
Department of Environmental & Molecular Toxicology
Linus Pauling Institute
To determine the anticancer effects of compounds SelSA-1 and SelSA-2 in cancer cells HCT 116 (colon cancer) and A431 (skin cancer) in vitro.
http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/genes_and_genomes/acetylation.html
Acetylated histones are usually associated with transcriptionally active chromatin
Histones are acetylated by Histone
Acetyltransferases (HATs)
Deacetylated histones are usually associated with inactive chromatin
Histones are deacetylated by Histone
Deacetylases (HDACs)
4 classes of HDACs:
• Class I: HDAC1, 2, 3, 8
• Class II: HDAC4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10
• Class III: Sir2(yeast), SirT1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
• Class IV: HDAC11
Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition has been shown to elicit anticancer effects in several tumor cells by inhibition of cell growth (Desai et al, 2009)
HDAC inhibitors can induce p21 (WAF1) expression, a regulator of p53's tumor suppressor activity. (Richon etal, 2000)
HDAC inhibitors are currently used for anti-cancer chemotherapy (Desai et al, 2009)
Hydroxamic Acids
Short-Chain Fatty Acids
Cyclic Tetrapeptides/epoxides
Aminobenzamides
Electrophilic ketones
• Vorinostat or suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) is a member of a larger class of compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases (HDAC).
• Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI) have a broad spectrum of epigenetic activities.
• Vorinostat is marketed under the name Zolinza for the treatment of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) when the disease persists, gets worse, or comes back during or after treatment with other medicines. (Merck & Co., 2006)
O
H
N
NH
OH
O
Organoselenium compounds have been shown to be HDAC inhibitors and reduce growth of colon and prostate cancer cells (Nian et al, 2009)
Two selenium analogs of SAHA have been reported as potent HDAC inhibitors (Desai et al, 2009)
O
H
N
O
SAHA
H
N
O
NH
OH
Se Se
Selenium Dimer
(SelSA-1)
O
H
N
SeCN
O
Selenocyanide (SelSA-2)
H
N
Test SAHA derivatives SelSA-1 and SelSA-2 for their anti-cancer activity on cancer cell lines in vitro:
HCT116 (colon carcinoma)
A431 (skin carcinoma)
Test SelSA-1 and -2 for their effect on HDAC activity and histone acetylation.
Test for cellular effects i.e. morphology, growth, cell cycle and cell death on cancer cells.
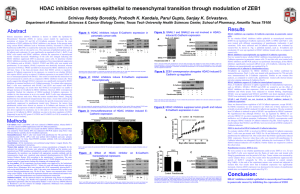
The method requires two steps, both performed on the same microtiter plate.
First, the HDAC fluorogenic substrate, which comprises an acetylated lysine side chain, is incubated with a sample containing HDAC activity (e.g., HeLa nuclear extract).
Deacetylation of the substrate sensitizes the substrate, so that, in the second step, treatment with the Lysine Developer produces a fluorophore.
The fluorophore can be analyzed using a fluorescence plate reader (Ex 360 nm/Em 460 nm).
A standard curve of deactylated substrate is run in parallel.
HDAC activity in Hela Nuclear extract
1600
1400
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
0,2 2 20
Concentration (nM)
200
SAHA
HDAC activity in Hela Nuclear extract
2000
1500
1000
500
0
SELSA-1
0,2 2 20 200
Concentration (nM)
HDAC activity in Hela Nuclear extract
2000
1500
1000
500
0
0,2 2 20
Concentration (nM)
200
SELSA-2
IC50 concentrations were used.
Cancer cells were treated with SelSA-1, SelSA-2, and SAHA at 3, 6 and 24 hrs.
Cells were lysed and lysates collected.
Protein concentration in lysates was determined by
BCA
Western blotting of equal amounts of protein was done on 4-12% Tris-Glycine pre-cast gels.
HisH3
(9-10-10)
HisH3
Acetylated
(9-10-10)
HisH3
Acetylated
K9
(9-10-10
HisH4
(9-10-10)
HisH4
Acetylated
(9-10-10)
Relative 1.07 1.10 1.17 1.25 1.30 1.02 1.06 1.30 1.32 1.07 1.28 1.37 1.26 1.00
Densitometry
HisH4
Acetylated
K12
(9-10-10
Relative
Densitometry
0.95 0.80 1.18 1.60 1.58 0.97 1.31 1.54 1.29 1.25 1.45 1.48 1.55 1.00
α-Tubulin
Acetylated
α-Tubulin
β-Actin
(8-9-10)
HDAC1
(8-9-10)
β-Actin
(8-3-10)
HDAC2
(8-3-10)
HDAC8
(8-3-10)
3H 6H 24H
Treatments:
None SelsA-1 SelsA-1 SelsA-2 SelsA-2 SAHA
2.5μM 5μM 2.5μM 5μM 5μM
β-Actin
(9-16-10)
HDAC3
(9-16-10)
3H 6H 24H
β-Actin
(8-3-10)
HDAC10
(8-3-10)
Treatments:
None SelsA-1 SelsA-1 SelsA-2 SelsA-2 SAHA
2.5μM 5μM 2.5μM 5μM 5μM
β-Actin
(8-3-10)
HDAC11
(8-3-10)
3H 6H 24H
Treatments:
None SelsA-1 SelsA-1 SelsA-2 SelsA-2 SAHA
2.5μM 5μM 2.5μM 5μM 5μM
β-Actin
(4-21-10)
HDAC1
(4-21-10)
HDAC2
(4-21-10)
3H
HDAC3
(6-21-10)
HDAC8
(5-25-10)
6H 24H
Treatments:
None SelsA-1 SelsA-1 SelsA-2 SelsA-2 SAHA
1μM 5μM 1μM 5μM 5μM
β-Actin
(5-25-10)
HDAC7
(5-25-10)
β-Actin
(6-21-10)
HDAC10
(6-21-10)
3H 6H 24H
Treatments:
None SelsA-1 SelsA-1 SelsA-2 SelsA-2 SAHA
1μM 5μM 1μM 5μM 5μM
DMSO SAHA
All Compounds tested at 1μM for 72 hours
SELSA-1 SELSA-2
All Compounds tested at 1μM for 72 hours
Cell Counting Kit-8 is a nonradioactive, sensitive colorimetric assay for the determination of the number of viable cells in cell proliferation and cytotoxicity assays.
Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50): the half maximal (50%) inhibitory concentration (IC) of a substance measuring the effectiveness of a compound in inhibiting biological or biochemical function.
CCK8: WST-8 is reduced by dehydrogenases to give a formazan product. The amount of formazan dye generated, which is soluble in the cell culture medium, is proportional to number of living cells.
2,50
2,00
1,50
1,00
0,50
0,00
0,01 0,1 1
Concentration (uM)
10 100
SAHA
SELSA-1
SELSA-2
VEHICLE (DMSO)
Compound IC
SAHA
50
(uM)
0.8
SELSA-1
SELSA-2
0.6
0.9
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
SelsA-1
SelsA-2
SAHA
No Treatment
DMSO (0.1%)
No
T re a tm e n t
0.1
M
0.25
M
0.5
M
1.0
M
2.5
M
5.0
M
Treatment
7.5
M
10
M
DM
S
O
IC50
• SelSA-1: 1.5 μM
• SelSA-2: 1.75 μM
• SAHA: 5 μM
Treatment increases apoptotic sub-G1 phase
SelSA-1 and SelSA-2 inhibit HDAC activity and induce histone acetylation
These compounds were found to be moderately more potent than SAHA in the activity assay
These compounds inhibit cell growth and cause cell death in colon and skin cancer cells
SelSA-1 and SelSA-2 are important SAHA derivatives which need to be further tested in animal models
HHMI Program
Kevin Ahern
Dashwood Lab
Dr. Roderick Dashwood
Mohaiza Dashwood
Praveen Rajendran
Rong Wang
Hui Nian
Pennsylvania State Hershey College of
Medicine