b - Adem KARACA Kişisel Web Sayfası
advertisement

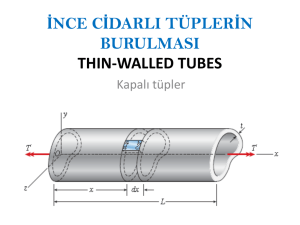
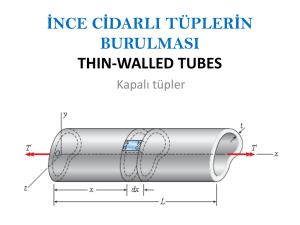
Kesme kuvveti-Kayma gerilmesiKayma akımı-Kayma merkezi Shear Forces-Shear stress Shear flow-Shear center Introduction • Transverse loading applied to a beam results in normal and shearing stresses in transverse sections. • Distribution of normal and shearing stresses satisfies Fx x dA 0 M x y xz z xy dA 0 Fz xz dA 0 M z y x dA Fy xy dA V M y z x dA 0 • When shearing stresses are exerted on the vertical faces of an element, equal stresses must be exerted on the horizontal faces 6-2 • Longitudinal shearing stresses must exist in any member subjected to transverse loading. Shear flow on the Horizontal Face of a Beam Element • Consider prismatic beam • For equilibrium of beam element Fx 0 H C D dA A H M D MC I y dA A • Note, Q y dA A M D MC dM x V x dx • Substituting, VQ x I H VQ q shear flow x I H 6-3 Shear flow on the Horizontal Face of a Beam Element • Shear flow, H VQ q shear flow x I • where Q y dA A first moment of area above y1 I 2 y dA A A' 6-4 second moment of full cross section Shear on the Horizontal Face of a Beam Element • Same result is found for lower area H VQ q x I Q Q 0 q first moment wit h respect to neutral axis 6-5 H H Shear Stress on the Horizontal Face of a Beam Element V xy bz • Shear flow, H VQ q x I • Shear stress is found by dividing the shear flow q with bz. • Shear stress 6-6 q VQ bz Ibz Örnek: Şekildeki yükleme durumu ve kesiti görülen kiriş için; a) C noktasındaki asal gerilmeleri ve doğrultularını bulunuz. b) Kesitteki kayma gerilmesi dağılımını gösteriniz. 20 20 6 kN A B E D 2m C 6 kN 2m G y 2m 40 20 60 Çözüm: KKD - EMD 6 kN A 6 kN 6 kN 2m 6 kN (+) B E D 3m 2m 6 kN (-) 6 kN 12 kNm (+) (+) (+) Ağırlık merkezi ve Atalet momenti 20 6050 20 6010 30 mm y 20 60 20 60 20 20 C G 40 y 20 60 20 603 60 203 2 2 Iz 20 60 50 30 20 60 10 30 12 12 I z 1.36 106 mm 4 Kesme Kuvveti-Kayma Akımı Kayma Merkezi-Kayma Gerilmesi İNCE CİDARLI AÇIK KESİTLERDE KAYMA GERİLMELERİ VE KAYMA MERKEZİ Kesitteki iç kuvvetler: Denge denklemi: Kesme kuvveti: b – b kesitindeki ortalama gerilme: Kayma Gerilmesi: Kayma Akımı: «U» şeklindeki kesitin kayma merkezi Kesitteki Kayma Gerilmesi Değişimi: Kanattaki kesme kuvveti: Kayma merkezi: h 2b 2t1 e 4I z Kanattaki kayma akımı ve kesme kuvveti: ÖRNEK: Şekilde görülen profil P=12 kN’luk bir kesme kuvvetine maruz kaldığına göre: a) Kayma merkezinin yerini bulunuz. b) Kesit çevresi boyunca kayma gerilmesi değişimini gösteriniz. 10 85.5 103 18 MPa ÖRNEK: Şekilde görülen profilin boyutları b=100 mm, h=150 mm ve t=3 mm olup profil P=800 N’luk bir kesme kuvvetine maruz bırakılmaktadır. Buna göre: a) Kayma merkezinin yerini bulunuz. b) Kesit çevresi boyunca kayma gerilmesi dağılımını gösteriniz. b B A e h O’ O t D E Çözüm: b B b=100 mm h=150 mm t=3 mm A e h O’ O t D 1 I 101.5 1533 98.5 147 3 4.22 106 mm 4 12 veya 3 150 2 6 100 150 4.22 106 mm 4 I 12 E I I web 2 I flange 2 1 3 1 3 h I th 2 bt bt 12 12 2 I 1 2 th 6b h 12 AB kolundaki kayma akımını bulmak için s uzunluğundaki bir eleman dikkate alınır. h y 2 ve Ats B Statik momenti: h ht Q y A ts s 2 2 s A y A T .E. Kayma akımı: D VQ V V th q ths s I 2I 2I E h 2 AB kolundaki kesme kuvvetini hesaplamak için A’dan B’ye kadar integral almak gerekir. V th F q ds sds 0 0 2I 2 V t hb F 4I b B b T .E. D s A h y 2 A E O’ noktasına göre moment alınırsa kayma merkezi h M O' 0 V e F h e F V V t hb 2 h e 4I V t h 2b 2 e 4I B şeklinde bulunur. V t h 2b 2 3 150 2100 2 e 4I 4 4.22 106 e 40 mm b A e h O’ O t D E Kesit çevresi boyunca kayma gerilmesi dağılımı A-B ve E-D kesitindeki kayma gerilmesi değişimi h y 2 ve A st Statik momenti: B Kayma gerilmesi denklemi: q VQ Vh s t It 2I sb Vh 800 150 b 100 6 2I 2 4.22 10 D B 1.422 MPa h Q y A st 2 A s max T .E. D y h 2 Kesit çevresi boyunca kayma gerilmesi dağılımı B-D kesitindeki kayma gerilmesi (maksimum kayma gerilmesi) Maksimum kayma gerilmesi T.E. üzerinde meydana gelir. T.Ü. deki alanın statik momenti Statik momenti: Q y1 A1 y2 A2 h2 b t h2 t h4 3 3 30 . 94 10 mm Q h2t b h4 1502 3 100 150 4 Kayma gerilmesi denklemi: V Q 800 30.94 103 It 2 4.22 106 max 2.93 MPa Shearing Stresses in Thin-Walled Members • Consider a segment of a wide-flange beam subjected to the vertical shear V. • The longitudinal shear force on the element is H VQ x I • The corresponding shear stress is H VQ zx xz t x It • Previously found a similar expression for the shearing stress in the web xy VQ It • NOTE: xy 0 xz 0 6 - 29 in the flanges in the web Shearing Stresses in Thin-Walled Members • The variation of shear flow across the section depends only on the variation of the first moment. q t VQ I • For a box beam, q grows smoothly from zero at A to a maximum at C and C’ and then decreases back to zero at E. • The sense of q in the horizontal portions of the section may be deduced from the sense in the vertical portions or the sense of the shear V. 6 - 30 Sample Problem 6.3 Knowing that the vertical shear is 50 kips in a W10x68 rolled-steel beam, determine the horizontal shearing stresses in the top flange at the points a and C. 6 - 31 SOLUTION: • First moment for the shaded area, Q 4.31in 0.770 in 4.815 in Q 15.98 in 3 • The shear stress at a, VQ 50 kips 15.98 in 3 It 394 in 4 0.770 in 2.63 ksi • First moment for the area over point C, Q 9.40 in 0.770 in 4.815 in 4.43 in 0.770 in 2.215 in Q 42.4 in 3 • The shear stress at C, VQ 50 kips 42.4 in 3 It 394 in 4 0.770 in 6.989 ksi - Craig Unsymmetric Loading of Thin-Walled Members • Beam loaded in a vertical plane of symmetry deforms in the symmetry plane without twisting. x My I ave VQ It • Beam without a vertical plane of symmetry bends and twists under loading. x 6 - 40 My I ave VQ It Unsymmetric Loading of Thin-Walled Members • If the shear load is applied such that the beam does not twist, then the shear stress distribution satisfies D B E VQ ave V q ds F q ds q ds F It B A D • F and F’ indicate a couple Fh and the need for the application of a torque as well as the shear load. F h Ve • When the force P is applied at a distance e to the left of the web centerline, the member bends in a vertical plane without twisting. 6 - 41 Example 6.05 Determine the location for the shear center of the channel section with b = 4 in., h = 6 in., and t = 0.15 in. 6 - 42 Example 6.05 • Inertia moment: • b = 4 in., h = 6 in., and t = 0.15 in. I I web 2 I flange 2 1 3 1 3 h I th 2 bt bt 12 12 2 1 2 I th 6b h 12 6 - 43 Solution Fh e I • where b b b VQ V h F q ds ds st ds I I 0 2 0 0 Vthb 2 F 4I • Combining, b 4 in. e h 6 in . 2 2 3b 34 in . 6 - 44 e 1.6 in . Shear stress in flanges • Determine the shear stress distribution for V = 2.5 kips. q VQ t It • Shearing stresses in the flanges, VQ V h Vh st s It It 2 2I Vhb 6 Vb B 1 2 2 12 th 6b h th6b h B 6 2.5 kips 4 in 0.15 in 6 in 6 4 in 6 in B 2.22 ksi Shear stress in web • Determine the shear stress distribution for V = 2.5 kips. q VQ t It • Shearing stress in the web, max VQ V 18 ht 4b h 3V 4b h 1 2 It 2th6b h 12 th 6b h t 32.5 kips 4 4 in 6 in 20.15 in 6 in 6 6 in 6 in 3.06 ksi max max 6 - 46 Örnek: Şekilde kesiti görülen kirişin a) Kayma merkezinin yerini bulunuz. b) Kanatlarda oluşan iç kuvvetleri hesaplayınız. t =6 mm t1 =4 mm t2 =5 mm h1 =60 mm h2 =40 mm t1 t2 P h1 t h2 b b=50 mm P=800 N Çözüm: Denge denklemleri t1 t2 P V1 h1 A V2 x O e h2 max f b e f b F 0 V1 V2 P 0 V1 V2 P M A 0 eP bV2 0 bV2 eP y veya bV1 f P Atalet momentleri Tüm kesitin Atalet momenti 1 Ix 4 603 50 63 5 403 99.567 103 mm 4 12 Başlıkların atalet momentleri t1 1 I 2 5 403 26.667 103 mm 4 12 1 I1 4 603 72 103 mm 4 12 t2 V1 h1 A P V2 O e f b h2 x max Sağ başlıktaki maksimum kayma gerilmesi max V Q2 P h2 h2 P h22 t 2 I x t 2 I x t 2 2 4 8 I x max P h22 800 40 2 1.61 MPa 3 8 I x 8 99.567 10 Sağ başlıktaki kesme kuvveti 2 2 P h22 V2 max h2 t 2 3 3 8 Ix P t 2 h23 I h2 t 2 P 2 I x 12 Ix I2 26.667 103 V2 P 800 214.26 kN 3 Ix 99.567 10 Sol başlıktaki kesme kuvveti I1 72 103 V1 P 800 578.5 kN 3 Ix 99.567 10 Kayma merkezinin yeri: bV2 eP e 13.4 mm V2 214.26 e b 50 P 800 Example: For the channel section, and neglecting stress concentrations, determine the maximum shearing stress caused by a V=800-N vertical shear applied at centroid C of the section, which is located x to the right of the center line of the web BD. A B b=100 mm V h h=150 mm t=3 mm x C x t D E b Solution: B A V C e D x T B V A = E C e D x V B A = E D x A + C e B E C T e D x E x 2100 350 30000 29 mm 2100 3 3 150 1050 1 1 3 I x 3 150 2 100 33 100 3752 4.219 106 mm 4 12 12 75 Q 100 375 75 3 30.94 10 3 mm 3 2 V Q 800 30.94 103 V 1.956 MPa 6 Ix t 4.219 10 3 B B V B A V C D e D D x E h 2b 2t 100 2 150 2.3 e 40 mm 6 4 I x 4 4.219 10 B A O C T T OC V e x V T 40 29800 55.2 10 Nmm 55.2 Nm 3 J 1 1 3 3 3 4 b t 150 2 100 3 3 . 15 10 mm ii 3 3 T 55.2 103 T t 3 52.57 MPa 3 J 3.15 10 e D x E The maximum shearing stress max V T 1.956 52.57 54.526 MPa