RULES OF BOOLEAN ALGEBRA - Govt. PG College Una (HP)
advertisement
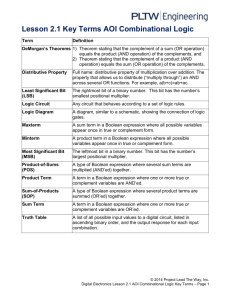
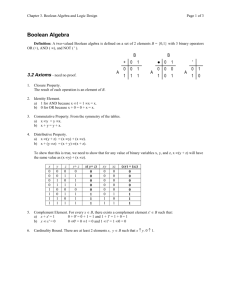
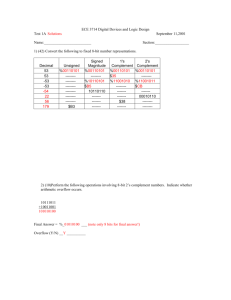
RULES OF BOOLEAN ALGEBRA BASIC RULES OF BOOLEAN ALGERBA Sr. No. Theorem 1. 0’=1 1’=0 2. A+0=A 3. A+1=1 4. A+A=A 5. A+A’=1 6. (A’)’=A 7. A+AB=A 8. A+A’B=A+B 9. (A+B)’=(A)’.(B)’ 10. (A.B)’=(A)’+(B)’ 11. (A+B).(A+C)= A+BC 12. A.1=A A.0=0 13. A.A=A A.(A)’=0 DE MORGAN’S THEOREMS It states, that the complement of any expression can be obtained by replacing each variable and element with its complement and changing OR operators (+) with AND operators(.) and AND operator (.) with OR operators (+). These theorems can be expressed as follows: (A+B)’=(A)’.(B)’ First De Morgan’s Theorem. (A.B)’=(A)’+(B)’ Second De Morgan’s Theorem. De Morgan’s theorems can also applicable to expressions in which there are more than two variables. THREE STEPS OF SIMPLIFICATION (DEMORGANIZATION) 1. Complement each of the individual variables. 2. Change all the OR’s (+) to AND (.) and AND’s(.) to OR’s(+). 3. Complement the whole Boolean function. EXAMPLES 1 Demorganize the following expression: AB’ + A’B’C +AC Step No. 1: Complement each of the individual variables Means : AB’ + A’B’C + AC A’B’’ + A’’B’’C’ + A’C’ Step No. 2: Change all the OR’s (+) to AND (.) and AND’s(.) to OR’s(+) EXAMPLES 1 Means: A’B’’ + A’’B’’C’ + A’C’ A’B + ABC’ + A’C’ A’B + ABC’ + A’C’ (A’+B ).(A+B+C’).(A’+C’) Step No. 3: Complement the whole Boolean function Means: (A’+B ).(A+B+C’).(A’+C’) ((A’+B ).(A+B+C’).(A’+C’))’ TRUTH TABLE FOR THIS EXAMPLE 1. Before Demorganization. AB’ + A’B’C +AC A B C AB’ A’B’C AC R=AB’ + A’B’C + AC 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 TRUTH TABLE FOR THIS EXAMPLE 2. After Demorganization. ((A’+B ).(A+B+C’).(A’+C’))’ A B C A’+B A+B+C’ A’+C’ R=(A’+B).(A+B+C’).(A’+C’) R’ 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 TRUTH TABLE FOR THIS EXAMPLE Now Compare the results of the expression before and after Demorganization R=AB’ + A’B’C + AC R=(A’+B).(A+B+C’).(A’+C’))’ 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 Before Demorganization After Demorganization The Results are identical in both the tables. EXAMPLES 1 Step No. 1 (A+B’).(A+B+C’).(AB) (A’+B’’).(A’+B’+C’’).(A’B’) Step No. 2 (A’+B’’).(A’+B’+C’’).(A’B’) A’.B+A’.B’.C+A’+B’ Step No.3 A’.B+A’.B’.C+A’+B’ (A’.B+A’.B’.C+A’+B’)’ TRUTH TABLE FOR THIS EXAMPLE 1. Before Demorganization. (A+B’).(A+B+C’).(AB) A B C A+B’ (A+B+C’) (AB) R=(A+B’).(A+B+C’).(AB) 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 TRUTH TABLE FOR THIS EXAMPLE 2. After Demorganization. (A’.B+A’.B’.C+A’+B’)’ A B C A’.B A’.B’.C A’+B’ R=A’.B+A’.B’.C+A’+B’ R’ 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 TRUTH TABLE FOR THIS EXAMPLE Now Compare the results of the expression before and after Demorganization R=(A+B’).(A+B+C’).(AB) R=(A’.B+A’.B’.C+A’+B’)’ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 Before Demorganization After Demorganization The Results are identical in both the tables.