Settlement
advertisement

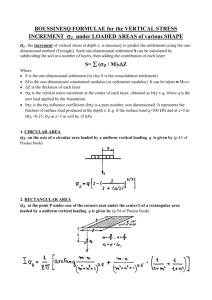
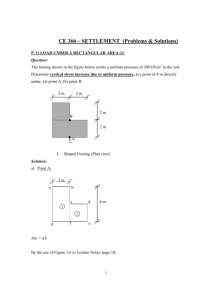
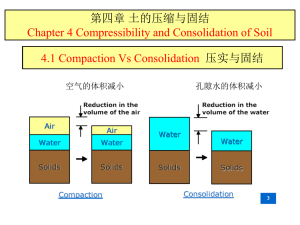
6. Settlement of Shallow Footings CIV4249: Foundation Engineering Monash University Oedometer Test Particular Sample Measurements: General Derived Relationship: • (change of) Height • Applied Load • Void Ratio • Applied Stress h height height vs time plots ho typically take measurements at 15s, 30s, 1m, 2m, 3m, 5m, 10m, 15m, 30m, 1h, 2h, 3h, 6h, 12h, 24h, 36h, 48h, 60h ….etc. elastic primary consolidation secondary compression typically repeat for 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400, 800 and 1600 KPa log time Void ratio = f(h) e 1.00 e = 0.8 1 2.65 Relative Volume Specific Gravity 1+e 1.917 h = 1.9 cm dia = 6.0 cm W = 103.0 g Elastic Settlement By definition fully reversible, no energy loss, instantaneous Water flow is not fully reversible, results in energy loss, and time depends on permeability Clay • Instantaneous component • Occurs prior to expulsion of water • Undrained parameters Sand • Instantaneous component • Expulsion of water cannot be separated • Drained parameters • Not truly elastic Elastic parameters - clay • • • • • Eu Soft clay Firm clay Stiff Clay V stiff / hard clay Eu/cu most clays • • • • 2000 - 5000 kPa 5000 - 10000 kPa 10000 - 25000 kPa 25000 - 60000 kPa • 200 - 300 nu • All clays • 0.5 (no vol. change) Elastic parameters - sand • • • • Ed Loose sand Medium sand Dense sand V dense sand • • • • 10000 - 17000 kPa 17500 - 25000 kPa 25000 - 50000 kPa 50000 - 85000 kPa nd • Loose sand • Dense sand • 0.1 to 0.3 • 0.3 to 0.4 note volume change! Elastic Settlement Q s H E E ez r = H s/E = H.ez Generalized stress and strain field r= 0 ez .dz Distribution of Stress Q • Boussinesq solution e.g. sz = Q Is z2 R sz Is is stress influence factor Is = 3 1 2p [1+(r/z)2]5/2 y r sr sq z Uniformly loaded circular area load, q dr By integration of Boussinesq solution over complete area: sz = q [1- dq a 1 ] = q.Is [1+(a/z)2]3/2 r z sz Stresses under rectangular area L • Solution after Newmark for stresses under the corner of a uniformly loaded flexible rectangular area: • Define m = B/z and n = L/z • Solution by charts or numerically sz = q.Is Is = 1 4p B sz z 2+n2+1)1/2 2mn(m 2mn(m2+n2+1)1/2 . m2+n2+2 -1 + tan m2+n2-m2n2+1 m2+n2+1 m2+n2-m2n2+1 Total stress change 0 0 .0 5 0 .1 0 .1 5 0 .2 0 1 2 3 z/B 4 5 L /B = 1 L /B = 2 6 L /B = 1 0 7 8 0 .2 5 Is Computation of settlement Q 1. Determine vertical strains: 2. Integrate strains: ez = 1 [sz - n ( sr + sq )] E ez = Q .(1+n).cos3y.(3cos2y-2n) 2pz2E r= 0 r= ez .dz Q (1-n2 ) prE R y z sz r sr sq Settlement of a circular area load, q dr Centre : r= 2q(1-n2).a dq a r E Edge : z r = 4q(1-n2).a pE sz Settlement at the corner of a flexible rectangular areaL Schleicher’s solution r = q.B 1 - n2 E Ir sz z m = L/B Ir = 1 m ln p B 1+ m2 + 1 m + ln m+ m2 + 1 0.26 Is A rea covered w ith uniform norm al load, q 0.24 0.22 nz m = 3 .0 m = 2 .5 m = 2 .0 m = 1 .8 m = 1 .6 m = 1 .2 m = 1 .4 m = 1 .0 x 0.20 mz y z m = 0 .9 sz = q.I 0.18 m = oc m = 0 .8 s m = 0 .7 z 0.16 0.14 m = 0 .6 N ote: m and n are interchangeable m = 0 .5 0.12 m = 0 .4 0.10 m = 0 .3 0.08 m = 0 .2 0.06 0.04 m = 0 .1 0.02 0 0.01 m = 0 .0 2 3 4 5 0.1 2 3 4 5 1.0 2 3 45 V E R T IC A L S T R E S S B E LO W A C O R N E R O F A U N IF O R M LY LO AD E D F LE X IB LE R E C TA N G U LA R A R E A . 10 Settlement at the centre of a flexible rectangular area L L/2 B B/2 rcentre = 4q.B 2 1 - n2 E Ir Superposition for any other point under the footing Settlement under a finite layer Steinbrenner method rcorner = q.B 1 - n2 E Ir q X B H E Y “Rigid” Ir = F1 + 1-2n 1-n F2 Va lu es o f F 1 ( 0 0 .1 0 .2 0.3 0 .4 ) and F 2 ( 0 .5 ) 0 .6 0 .7 0 .8 L /B = 1 D epth factor d = H /B 2 L /B = 2 F1 4 L /B = 5 F2 6 L /B = 5 L /B = 1 0 8 L /B = oo L /B = 2 L /B = 1 L /B = 1 0 L /B = oo 10 Influe nce va lue s for se ttle m e nt be ne a th the corne r of a uniform ly loa de d re cta ngle on a n e la stic la ye r (D e pth D ) ove rlying a rigid ba se Superposition using Steinbrenner method L B Multi-layer systems q H1 r = r(H1,E1) + r(H1+H2,E2) - r(H1,E2) B E1 E2 H2 “Rigid” Primary Consolidation • A phenomenon which occurs in both sands and clays • Can only be isolated as a separate phenomenon in clays • Expulsion of water from soils accompanied by increase in effective stress and strength • Amount can be reasonably estimated in lab, but rate is often poorly estimated in lab • Only partially recoverable Total stress change 0 0 .0 5 0 .1 0 .1 5 0 .2 0 1 2 3 z/B 4 5 L /B = 1 L /B = 2 6 L /B = 1 0 7 8 0 .2 5 Is Pore pressure and effective stress changes Ds = Du + Ds At t = 0 : Ds = Du At t = : Ds = Ds sf si Stress non-linearity qnet z pc sf Cr H Cc H r = S 1+eo log s + 1+ec log p i c Soil non-linearity Cr 1 .2 1 .1 1 0 .9 e 0 .8 0 .7 C la y 0 .6 si 0 .5 0 .4 10 pc 100 sf Cc 1000 sv Coeff volume compressibility r = Smv.Ds.DH 1 .2 1 .1 1 C la y 0 .9 e 0 .8 0 .7 0 .6 (1+eo).mv 0 .5 0 .4 0 200 400 600 800 1000 sv Rate of Consolidation h h= =HH/ 2 T = cv ti / H2 U = 90% : T = 0.848 Flow Coefficient of Consolidation • Coefficient of consolidation, cv (m2/yr) • Notoriously underestimated from laboratory tests • Determine time required for (90% of) primary consolidation • Why? Secondary Compression • Creep phenomenon • No pore pressure change • Commences at completion of primary consolidation • ca/Cc 0.05 ca = De log (t2 / t1) r= caH (1+ep) log (t2/t1) Flexible vs Rigid F stress deflection rcentre F stres s deflection 0.8 rcentre RF = 0.8 Depth Correction 1 D e p th F a c to r 0 .9 z 0 .8 0 .7 0 .6 0 .5 0 2 .5 5 7 .5 10 z/B B Total Settlement rtot = RF x DF ( relas + rpr.con + rsec ) Field Settlement for Clays (Bjerrum, 1962) 1.2 S ettlem en t coefficien t Values on curves are D B 1.0 0.25 0.25 0.8 B 0.5 4 1.0 0.6 C lay layer 0.5 D 4 1.0 0.4 C ircle Po re - p ressu re co efficien t S trip N orm ally consolidated O ver-consolidated Very sensitive clays 0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 Differential Settlements Guiding values • Isolated foundations on clay • Isolated foundations on sand < 65 mm <40 mm Structural damage to buildings 1/150 (Considerable cracking in brick and panel walls) For the above max settlement values flexible structure <1/300 rigid structure <1/500 Settlement in Sand via CPT Results (Schmertmann, 1970) layer n r C 1C 2 D s layer 1 Iz Dz E s 0 C 1 1 0 .5 Ds t C 2 1 0 . 2 log 10 0 .1 t is in years