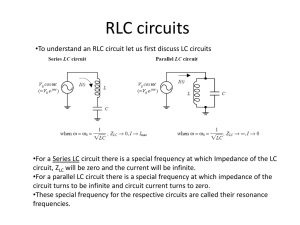
1.3. The Source-Free Series RLC Circuits
advertisement
Yrd. Doç. Dr. Sibel ÇİMEN 26.09.2011 Books Course Book : 1) Fundamentals of Electric Circuits, by Charles K. Alexander and Matthew N. O. Sadiku, McGraw Hill; 3rd edition (2007) Reference Books: 1) Electric Circuits, by James W. Nilsson and Susan Riedel, Prentice Hall; 8th edition (2007) 2) Schaum's Outline of Electric Circuits, by Mahmood Nahvi and Joseph Edminister, McGraw-Hill; 4th edition (2002) 3) Introduction to Electric Circuits, by Richard C. Dorf and James A. Svoboda, Wiley, 7th edition (2006) 4) Schaum's Outline of Basic Circuit Analysis, by John O'Malley and John O'Malley, McGraw-Hill; 2nd edition (1992) Course Outline 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Second Order DC Circuits (Fund. of Electric Circuits, CH 8) Sinusoids and Phasors (Fund. of Electric Circuits, CH 9) Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis (Fund. of Electric Circuits, CH 10) AC Power Analysis (Fund. of Electric Circuits, CH 11) Frequency Response (Fund. of Electric Circuits, CH 14) Laplace Transform (Fund. of Electric Circuits, CH 15 1.1. Introduction 1.2. Finding Initial and Final Values Keep in mind; Capacitor voltage always continuous… Inductor current always continuous… EXAMPLE 1.1. The switch in Figure has been closed for a long time. İt is open at t=0. Find; a) 𝑖(0+ ), 𝑣(0+ ) b) 𝑑𝑖((0+ )/dt, 𝑑𝑣((0+ )/dt, c) 𝑖(∞) , 𝑣(∞) EXAMPLE 1.2. In figure calculate; a) 𝑖𝑙 (0+ ), 𝑣𝑐 (0+ ), 𝑣𝑅 (0+ ) b) 𝑑𝑖𝐿 ((0+ )/dt, 𝑑𝑣𝑐 ((0+ )/dt c) 𝑖𝐿 ∞ , 𝑣𝑐 ∞ , 𝑣𝑅 (∞) 1.3. The Source-Free Series RLC Circuits (1.a) (1.b) 1.3. The Source-Free Series RLC Circuits Applying KVL around the loop; (2) To eliminate the integral, we differentiate with respect to t and rearrange terms:…. (3) 1.3. The Source-Free Series RLC Circuits with initial values equation (2)… (4) or Bobinin uçlarından akan akımın exp. Karakteristiği olduğunu biliyoruz… equation (3) becomes… or i 0 1.3. The Source-Free Series RLC Circuits (5) Known as characteristic equation İt’s roots; Where; 1.3. The Source-Free Series RLC Circuits 𝜔0 : resonant frequency or undamped natural frequency (rad/s) ∝: neper frequency or damping factor (Np/s) İn terms of 𝜔0 𝑎𝑛𝑑 ∝ equation (5) gets… (6) The two values of s in Eq. (5) indicate that there are two possible solutions in Eq. (6); that is, Natural response of series RLC; 1.3. The Source-Free Series RLC Circuits There are three types of solutions; Overdamped Case (∝> 𝝎𝟎 ) İn this situation; 𝑠1 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑠2 negative and real 1.3. The Source-Free Series RLC Circuits Critically Damped Case (∝= 𝝎𝟎 ) 1.3. The Source-Free Series RLC Circuits Under Damped Case (∝< 𝝎𝟎 ) EXAMPLE 1.3. R=40 Ω, L=4H and C=1/4 F. Calculate the characteristic roots of the circuit. Is the natural response overdamped, underdamped, or critically damped? EXAMPLE 1.4. Find i(t) in the circuit. Assume that the circuit has reached steady state at t=0− .