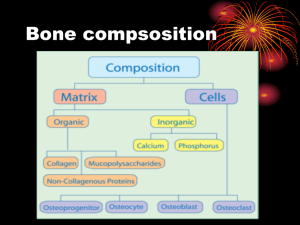
Orthopedic Eponyms - Emory University Department of Pediatrics
advertisement

Pediatric Orthopedic Fractures Dafina Good, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Fellow Emory University School of Medicine Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta Objectives Review unique structural and physiologic differences between children and adult skeletal systems Review fracture patterns unique to children Review the Salter-Harris classification of pediatric physeal fractures Review common presentations and EPONYMS of common pediatric and adult fractures Review Ottawa ankle and knee criteria Epidemiology Orthopedic trauma accounts for 10-15% of ED visits in urban pediatric hospitals It is estimated that over 40% of boys and over 25% of girls will sustain a fracture during childhood Rapid growth of organized sports Skeletal Differences between Children and Adults Presence of Growth Plates (Physis) Presence of Secondary Ossification Centers (Epiphysis) Rapid healing Growth plate injuries constitute up to 25% of all skeletal injuries in children More metabolically active periosteum in children Greater Potential to Remodel More porous and more pliable bones Fracture patterns unique to children Fractures are more common than sprains in young children Ligaments and tendons attaching one bone to another have greater strength than immature bones Normal Bone Anatomy Normal Bone Anatomy Describing Fractures Open vs. Closed Location (shaft, through growth plate etc.) Displacement in mm Shortening in mm Impaction if present Angulation, degree and direction (midshaft-direction of terminal fragment) Salter Harris Classification Neurovascular status Describing Fractures Describing Fractures Salter Harris Classification Fractures Unique to Children Buckle or Torus Fractures Fractures Unique to Children Greenstick Fractures Fractures Unique to Children Greenstick Fractures Fractures Unique to Children Bowing Fractures Fractures unique to children Fractures unique to children Toddler’s Fracture Common Fracture Eponyms Who Named It? From the neck down to the toes! Jefferson Fracture Hangman’s Fracture Teardrop Fracture Chance Fracture Boxer’s Fracture Hand Anatomy Bennett’s Fracture Colle’s Fracture Smith’s Fracture Nightstick Fracture Monteggia Fracture Monteggia Fracture Galeazzi Fracture Supracondylar Fracture Ossification Centers – C-R-I-T-O-E Approximate age of appearance Capitellum - 1 year Radial head - 3 years Internal epicondyle (Medial epicondyle)-5 years Trochlea - 7 years Olecranon - 9 years External epicondyle (Lateral epicondyle)-11 years Proximal Humeral Fracture Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis SCFE’s Klein’s Line Klein’s Line Pelvic Avulsion Fractures Common Locations of Pelvic Avulsion Fractures Spiral Femur Fracture Osgood Slater Disease vs Sinding Larsen-Johansson Patellar Fracture Knee Anatomy Knee Anatomy Ottawa Knee Rules Characteristics of Patients Who Should Undergo Radiography After Knee Trauma Ottawa knee rules Age 55 years or older Tenderness at head of fibula Isolated tenderness of patella Inability to flex knee to 90 degrees Inability to walk four weight-bearing steps immediately after the injury and in the emergency department Pittsburgh decision rules Blunt trauma or a fall as mechanism of injury plus either of the following: Age younger than 12 years or older than 50 years Inability to walk four weight-bearing steps in the emergency department Corner Fracture Bucket Handle Fractures Maisonneuve Fracture Tillaux Fracture Tillaux Fracture CT Scan of Tillaux Fracture Triplane Fracture Triplane Fracture What’s the Difference? Anatomy of the Fifth Metatarsal Ottawa Ankle Rules Reasons to Refer to Orthopedics Open Fractures Unacceptably displaced fractures Fractures with associated neurovascular compromise Significant growth plate or joint injuries Pelvic/Femur fractures (other than minor avulstions) Spinal Fractures Dislocations of major joints other than shoulder/knee Clavicle (distal third) Fractures prone to Nonunion/Malunion Why do we do it? Prevent Growth arrest Prevent malunion or nonunion Restore function as close to physiologic