Arthroscopic Shoulder Repair
advertisement

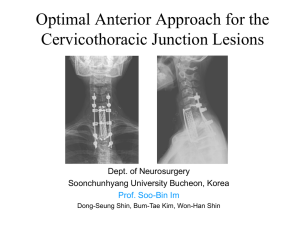
ARTHROSCOPIC BANKART REPAIR T. Andrew Israel, MD Luther Midelfort Orthopaedic & Sports Medicine Center ARTHROSCOPIC BANKART REPAIR • • • • • • • Historical Considerations Current Understandings Surgical Goals Advantages of Arthroscopic vs Open Selection Criteria-preop & intraop Surgical Technique Results HISTORICAL CONSIDERATIONS • Traditionally, open Bankart gold standard with recurrence <5% • Arthroscopic repair initially presented with great enthusiasm by developers but results could not be duplicated • Limited understanding of pathology • Poor patient selection • Technically demanding techniques CURRENT UNDERSTANDINGS • Firm appreciation spectrum of instability and range of pathology • Better teaching of basic arthrosopic techniques • Appreciation of the value of arthroscopy as outpatient surgical technique • Improved technical skills SURGICAL GOALS • Anatomic reconstruction • Reconstruction which approximates an open repair • Ability to manage Bankart lesion and capsular laxity • Immediate strength of repair ADVANTAGES OF ARTHROSCOPIC VS OPEN • • • • • Faster(for some surgeons) Less pain for patient Better cosmesis Better ROM(not shown by some studies) Ability to manage comorbid pathologySLAP, OA, RCT • Less expensive than open repair PREOPERATIVE SELECTION CRITERIA • Traumatic instability(subluxation or dislocation) • Minimal bony lesion(s) • Discrete Bankart lesion • No generalized ligamentous laxity INTRAOPERATIVE SELECTION CRITERIA OPTIMAL FACTORS • • • • Discrete Bankart lesion Robust capsuloligamentous tissue No Bony Bankart lesion No significant loss of articular surface(glenoid or humeral head) INTRAOPERATIVE SELECTION CRITERTA MITIGATING FACTORS • Capsular laxity • ALPSA(Anterior Labral Periosteal Sleeve Avulsion Injury) • Bony Bankart lesion SURGICAL TECHNIQUE • • • • • • • • Position Portal placement Identify pathology Mobilize capsulolabral tissue Glenoid preparation Anchor placement Suture retrieval Knot tying POSITION • Lateral decubitus • Allows for traction • Improved exposure to glenohumeral joint PORTAL PLACEMENT • • • • • Standard posterior portal Antero-superior scope portal Antero-inferior working portal Avoid crowding of anterior portals Clear cannulas allow visualization of sutures and anchors IDENTIFY PATHOLOGY • • • • • Bankart lesion Quality of capsulolabral tissue Concomitant SLAP lesion Rotator cuff injuries Injury to articular surfaces MOBILIZE CAPSULOLABRAL TISSUE • Arthroscopic elevators • Mitek VAPR • Strip off capsulolabral sleeve to muscle of subscapularis GLENOID PREPARATION • • • • Decorticate juxta-articular scapular neck Curette Rasp Shaver ANCHOR PLACEMENT • • • • • Place first anchor as low as possible At or on the articular cartilage margin Metal or biodegradable Prefer minimum of 3 anchors Pass sutures and tie knots before next anchor placement SUTURE RETRIEVAL • Many options • Devices which perforate capsule and retrieve the suture • Devices which shuttle the suture through the tissue • Prefer suture relay technique as it reduces trauma to suture & allows for easier shift from inferior to superior KNOT TYING • Perfect knots • Perfect knots • Flawlessly perfect knots RESULTS Gartsman, JBJS, 2000 • • • • • • 53 arthroscopic Bankart repairs Mean age 32 yrs 44 males & 9 females 33 month follow-up 34/38 athletes return to sport 4/53 recurrent instability(7.5%) CASE PRESENTATION CASE J.H. • 24 male RHD plumber • Traumatic left anterior shoulder dislocation @ age 15 during football • Rx nonoperatively with sling, PT, etc. • Recurrent dislocations during recreational softball @ age 23 and 24 PHYSICAL EXAM • • • • AROM 175/175, 65/75, T12/T10 5/5 power abduction & external rotation 2+ anterior/inferior laxity with endpoint Positive Jobe’s anterior apprehension/relocation test • Negative sulcus sign SHOULDER ANATOMY SURGERY SUMMARY • Arthroscopic techniques here to stay • Pt expectations & economic pressures driving application of these techniques • % performed arthroscopically will increase over time(more resident & fellow education) • Techniques & implants/devices will improve over time