Sheep Brain Dissection
advertisement

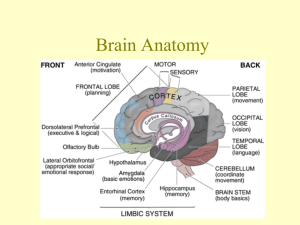
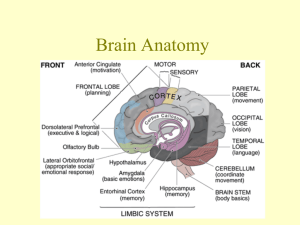
BA BA BA!!! Sheep Brain Dissection By: Katelyn Stickley & Andi Cribari ______________________ Leathery Strongest meninx Surrounds and Protects the brain 2 layered sheet of fibrous connective tissue Dura Mater Leathery Strongest meninx Surrounds and Protects the brain 2 layered sheet of fibrous connective tissue _______________________ Supported on the brain stem and is bulk of the brain Superior grey matter that interprets sensory inputs and responds to it. Helps with emotional and intellectual processing Dorsal View Cerebrum Supported on the brain stem and is bulk of the brain Grey matter that interprets sensory inputs and responds to it. Helps with emotional and intellectual processing Dorsal View ________________________ Second largest portion of brain Behind medulla and pons and below occipital lobes of cerebrum Processes info from cerebral motor cortex and from visual and equilibrium pathways Results in proper balance posture and smooth coordinated skeletal muscle movement Cerebellum Second largest portion of brain Behind medulla and pons and below occipital lobes of cerebrum Processes info from cerebral motor cortex and from visual and equilibrium pathways Results in proper balance posture and smooth coordinated skeletal muscle movement _______________________ Positioned between the cerebrum and spinal cord From superior to inferior, regions are : Maintains cerebral cortical alertness and filters out repetitive stimulI Its motor nuclei helps regulate skeletal and viscera; muscle activity Ventral View Brain Stem Positioned between the cerebrum and spinal cord From superior to inferior, regions are midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata Maintains cerebral cortical alertness and filters out repetitive stimulI Its motor nuclei helps regulate skeletal and viscera; muscle activity Ventral View _____________________ Conduction pathway between higher and lower brain centers Relays info from cerebrum to cerebellum Helps control respiratory rate and depth Pons Conduction pathway between higher and lower brain centers Relays info from cerebrum to cerebellum Helps control respiratory rate and depth ________________________ Conduction pathway between higher brain centers and spinal cord Controls heart rate, blood vessel diameter respiratory rate vomiting, coughing etc. Medulla Oblongata Conduction pathway between higher brain centers and spinal cord Controls heart rate, blood vessel diameter respiratory rate vomiting, coughing etc. _____________________ Intellect and Reason as well as part of emotional control center and home to personality Involved in motor function, problem solving, spontaneity, memory, language, initiation, judgment, impulse control, and social and sexual behavior. There are important asymmetrical differences in the frontal lobes. The left frontal lobe is involved in controlling language related movement, whereas the right frontal lobe plays a role in non-verbal abilities although both lobes are involved in nearly all behavior Frontal Lobe Intellect and Reason as well as part of emotional control center and home to personality Involved in motor function, problem solving, spontaneity, memory, language, initiation, judgment, impulse control, and social and sexual behavior. There are important asymmetrical differences in the frontal lobes. The left frontal lobe is involved in controlling language related movement, whereas the right frontal lobe plays a role in non-verbal abilities although both lobes are involved in nearly all behavior ______________________ The temporal lobes are home to the auditory cortex and more, quite a bit with language. Language can be affected by temporal lobe damage. Left temporal lesions disturb recognition of words. Right temporal damage can cause a loss of inhibition of talking. The temporal lobes are highly associated with memory skills. Temporal Lobe The temporal lobes are home to the auditory cortex and more, quite a bit with language. Language can be affected by temporal lobe damage. Left temporal lesions disturb recognition of words. Right temporal damage can cause a loss of inhibition of talking. The temporal lobes are highly associated with memory skills. ___________________ The occipital lobes are the center of our visual perception system. The occipital lobe is involved with the brain's ability to recognize objects. It is responsible for our vision. Occipital Lobe The occipital lobes are the center of our visual perception system. The occipital lobe is involved with the brain's ability to recognize objects. It is responsible for our vision. _______________________ The parietal lobes are found behind the frontal lobes, above the temporal lobes, and at the top back of the brain. Primary Somatosensory Cortex is in this lobe. They are connected with the processing of nerve impulses related to the senses, such as touch, pain, taste, pressure, and temperature. They also have language functions. Parietal Lobe The parietal lobes are found behind the frontal lobes, above the temporal lobes, and at the top back of the brain. Primary Somatosensory cortex in this lobe. They are connected with the processing of nerve impulses related to the senses, such as touch, pain, taste, pressure, and temperature. They also have language functions. _________________________ Composed of delicate connective tissue, richly invested with tiny blood vessels Meninx that clings tightly to brain Pia Mater Composed of delicate connective tissue, richly invested with tiny blood vessels Meninx that clings tightly to brain How is it going? If you are using this PowerPoint to study, let me know. Print out just the first title slide and write, “Thanks Andi and Katelyn for the great work” and let me know how helpful this was, scale 1-4 (little to lots). You must present this to me at the beginning of the period on Monday for your treat. Mr. Davis _____________________ Also called the primary motor area or, most commonly, the motor strip is immediately anterior to the central sulcus. It controls the voluntary movements of skeletal muscles; cell bodies of the pyramidal tract are found on this gyrus. Pre-Central Gyrus Also called the primary motor area or, most commonly, the motor strip is immediately anterior to the central sulcus. It controls the voluntary movements of skeletal muscles; cell bodies of the pyramidal tract are found on this gyrus. _____________________ Also called the primary sensory area or the sensory strip is immediately posterior to the central sulcus Receives sensory feedback from joints and tendons in the body and is organized in the same manner as the motor strip Post-Central Gyrus Also called the primary sensory area or the sensory strip is immediately posterior to the central sulcus Receives sensory feedback from joints and tendons in the body and is organized in the same manner as the motor strip _____________________ Chief integration center for autonomic nervous system Regulates body temp, food intake, water balance thirst, and biological/circadian rythems and drives Regulates hormonal output of anterior pituitary gland and is an endocrine organ Part of limbic system, helps initiate physical responses to emotions. Hypothalamus Chief integration center for autonomic nervous system Regulates body temp, food intake, water balance thirst, and biological/circadian rythems and drives Regulates hormonal output of anterior pituitary gland and is an endocrine organ Part of limbic system, helps initiate physical responses to emotions. ____________________ Bilateral egg shaped nuclei, conduction of sensory impulses to cerebral cortex for interpretation, Relays impulses to and from cerebral motor cortex and lower motor centers including cerebellum. “Traffic Cop of Brain” Also involved in memory processing Thalamus Bilateral egg shaped nuclei, conduction of sensory impulses to cerebral cortex for interpretation, Relays impulses to and from cerebral motor cortex and lower motor centers including cerebellum. “Traffic Cop of Brain” Also involved in memory processing ______________________ Largest commissure, lies superior to lateral ventricle, deep within longitudinal fissure. WHITE MATTER!!! The function is to connect the left and right side of brain The two hemispheres are physically separate and their only connection is through the corpus callosum, a thick white band of nerves deep within the brain It allows the two hemispheres to communicate and coordinate their activities. Corpus Callosum Largest commissure, lies superior to lateral ventricle, deep within longitudinal fissure. WHITE MATTER!!! The function is to connect the left and right side of brain The two hemispheres are physically separate and their only connection is through the corpus callosum, a thick white band of nerves deep within the brain It allows the two hemispheres to communicate and coordinate their activities. ____________________ Conduction pathways between higher and lower brain centers Superior and inferior colliculi, are visual and auditory reflex Midbrain Conduction pathways between higher and lower brain centers Superior and inferior colliculi, are visual and auditory reflex Internal Views Sagittal View _____________________ Mediates emotional response also involved in memory process Limbic System Also Diencephalon is here. Mediates emotional response also involved in memory process ______________________ Deep to the cortical grey matter is responsible for communication between cerebral areas and between cerebral cortex and lower CNS centers, consists largely of myelinated fibers bundled into large tracts White Matter Deep to the cortical grey matter is responsible for communication between cerebral areas and between cerebral cortex and lower CNS centers, consists largely of myelinated fibers bundled into large tracts _______________________ Contains mostly nerve cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers, also acts as a route sensory or motor stimulus to interneurons of the CNS in order to create a response to the stimulus through chemical synapse activity. These structures (cortex, deep nuclei) process information originating in the sensory organs or in other areas of these regions. This information is conveyed via specialized nerve cell extensions (long axons), which form the bulk of the cerebral, cerebellar, and spinal white matter. Grey Matter Contains mostly nerve cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers, also acts as a route sensory or motor stimulus to interneurons of the CNS in order to create a response to the stimulus through chemical synapse activity. Grey matter structures (cortex, deep nuclei) process information originating in the sensory organs or in other gray matter regions. This information is conveyed via specialized nerve cell extensions (long axons), which form the bulk of the cerebral, cerebellar, and spinal white matter. ________________________ Deep groove which separates the two hemispheres of the brain. It separates the cerebral hemispheres in the frontal and occipital regions, but between these parts of the brain, it extends only as far as the corpus callosum. FISSURE Longitudinal Fissure Deep groove which separates the two hemispheres of the brain. The longitudinal cerebral fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres in the frontal and occipital regions, but between these parts of the brain, the fissure extends only as far as the corpus callosum. FISSURE _______________________ This is a groove (or furrow) in the brain that separates the frontal and parietal lobes of the cerebrum. The frontal lobe is known as the motor cortex and the parietal lobe is known as the sensory cortex. This structure has a 'map' of the human body on each side that corresponds to the other side, when sensory part is stimulated, its associated motor part is right across the sulcus. The Central Sulcus The central sulcus is a deep groove (or furrow) in the brain that separates the frontal and parietal lobes of the cerebrum. The frontal lobe is known as the motor cortex and the parietal lobe is known as the sensory cortex. the central sulcus has a 'map' of the human body on each side that corresponds to the other side, when sensory part is stimulated, its associated motor part is right across the sulcus. _____________________ Elevated ridges of tissue Gyri Elevated ridges of tissue on the surface of the cerebral cortex _________________ Shallow grooves, furroughs Sulci Shallow grooves, furroughs