TM
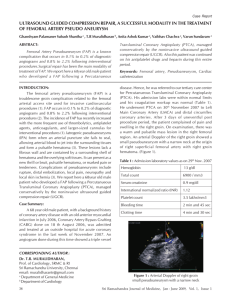
FemoStop
Femoral Compression System
for Ultrasound-Guided Compression Repair (UGCR)
of Femoral Pseudoaneurysm
Module Contents
2
Pseudoaneurysm
Proven to Reduce Complications
Treatment of Pseudoaneurysm
Early Treatment
Principle of Compression Repair
FemoStop Positioning
Applying pressure
Factors Affecting Success
Summary
Pseudoaneurysm
False aneurysm
Extravascular cavity, pseudoaneurysm sac
Presence of flow
Not contained by vessel wall
Pseudoaneurysm sac
Communicating
(feeding) tract
3
Proven to Reduce Complications¹,²
FemoStop reduces vascular
complications following
sheath removal
FemoStop helps prevent
femoral artery
pseudoaneurysm
1.
2.
4
Sridhar K, Fischman D, Goldberg S, et al. Peripheral vascular
complications after intracoronary stent placement: prevention by use
of a pneumatic vascular compression device. Cathet Cardiovasc
Diagn. 1996:39(3):224-229.
Amin F, Yousufuddin M, Stables R, et al. Femoral haemostasis after
transcatheter therapeutic intervention: a prospective randomised
study of the angio-seal device vs. the femostop device. Intl J of
Cardiol. 2000;76(2-3):235-40.
Treatment of Pseudoaneurysm
Treatment by ultrasound-guided compression repair of
femoral artery pseudoaneurysms is an Indication for Use
in the U.S.
5
Early Treatment
By using FemoStop,
compression can be
initiated early on the ward,
while waiting for duplex
ultrasonogram
6
Principle of Compression Repair
Pseudoaneurysm sac
PRESSURE
Communicating
(feeding) tract
7
PRESSURE
Using FemoStop for UGCR
1. Premedication
2. Baseline blood pressure, distal pulses
3. Ultrasound
4. Demarcate compression site
5. Position FemoStop
6. 20 min. compression; distal pulses
7. Release pressure
8. Ultrasound
9. Repeat steps 6-8 if necessary
10. Light compression and bed rest
11. Ultrasound
*
8
FemoStop Positioning
Vein
Pseudoaneurysm
Artery
9
FemoStop Positioning
Sterile tape may be used to demarcate the compression
site as determined by ultrasound
10
FemoStop Positioning
Apply until ultrasound is available:
Pressure on arterial puncture (not skin incision).
PRESSURE
Skin incision
Skin
Artery
Arterial sheath
11
Arterial puncture
Applying Pressure
Apply enough pressure to minimize arterial blood flow
but:
Do not obliterate flow in the artery itself
Do not compress the vein, if possible
Do not make compression unbearable for the patient
(i.e., 20 mmHg below the patient’s systolic blood
pressure)
12
Applying Pressure
PRESSURE
Pseudoaneurysm sac
13
PRESSURE
Patient’s arterial lumen
Pressure Duration
Compression time
Up to 300 minutes (in cycles
of 20 minutes)
Mean compression time
approximately 40 minutes
14
Pressure Duration
Short compression cycles
(20 min*):
Prevent vessel thrombosis
Prevent nerve injury
Prevent skin abrasion/necrosis
*Chatterjee J, et al. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 1999;47:304-9.
15
Factors Affecting Success
Ability to compress
Anticoagulation status
Pseudoaneurysm size
PRESSURE
Patient’s arterial lumen
16
Factors Affecting Success
Ability to compress
Anticoagulation status
Pseudoaneurysm size
One or more compartments
Age of the pseudoaneurysm (epithelialization of the tract
and more fibrous capsule)
Neck width
Short feeding tract <10 mm
17
Summary
FemoStop:
Helps prevent pseudoaneurysms in the first place
UGCR method is relatively easy
Makes UGCR a NON-labor-intensive method of
treatment
A ”first line” treatment to help prevent further
development of a bleeding complication
18
Rx Only
Please review the Instructions for Use prior to using these devices for a complete listing of indications,
contraindications, warnings, precautions, potential adverse events and directions for use.
Product referenced is approved for CE Mark.
FemoStop is designed, developed and manufactured by St. Jude Medical Systems AB. FemoStop,
RADI, ST. JUDE MEDICAL, the nine-squares symbol and MORE CONTROL. LESS RISK. are
registered and unregistered trademarks and service marks of St. Jude Medical, Inc. and its related
companies. ©2011 St. Jude Medical, Inc. All rights reserved.
IPN 1691-11
19