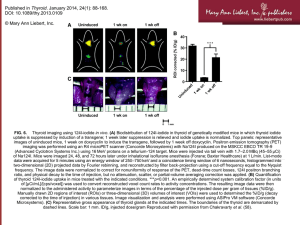
View PowerPoint Presentation of global results
advertisement

International Thyroid Cancer Patient Survey Revised July 2010 Prepared for: Kate Farnell, Thyroid Cancer Alliance Prepared by: Jamie Margerison, Alastair McDougall, Holden Pearmain Research ACTIRA Contents Executive Summary 2. Background & Research Objectives 3. Sample & Methodology 4. Diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer 5. Patient Support at Diagnosis 6. Surgery 7. RAI Treatment 8. Thyrogen V Withdrawal 9. Follow-Up Regime 10. Assessment of Cancer Journey 1. 2 1 Executive Summary Executive Summary (1) The stage of diagnosis was the most difficult time for patients Being diagnosed with cancer (24%) and the resulting anxiety about the future (22%) were the most difficult aspects of the cancer journey for patients Referral to a specialist could be slower than expected 28% of patients had to wait more than 4 weeks before seeing a specialist Establishing the diagnosis could be difficult 18% waited more than 4 weeks from seeing the specialist before receiving a diagnosis 64% of patients required surgery to achieve a diagnosis Information and psychological support at diagnosis were often lacking 77% of respondents were not offered support from a nurse or similar person 93% were not offered psychological support 84% were not given details of a patient support organisation 63% were not given clear written information about their disease and its treatment 4 Executive Summary (2) Repeat neck surgery was a common experience 46% of patients had undergone two or more operations on their neck Post-surgery complications were relatively common 39% of respondents experienced low blood calcium levels and 36% voice problems following surgery Thyroid hormone withdrawal was widely used and often symptomatic 81% of respondents stopped taking all hormone therapy 87% experienced one of more symptoms of hypothyroidism Thyrogen was offered as an option to a minority of patients and was associated with fewer side effects than hormone withdrawal 37% of patients were offered Thyrogen 22% experienced side effects 87% of those who had experienced both Thyrogen and hormone withdrawal preferred Thyrogen 5 Executive Summary (3) RAI treatment was widely used and side effects were common 84% had undergone RAI 80% experienced one or more side effects 41% sought the help of their family doctor around the time of treatment Administration of the first RAI treatment could be delayed 28% of patients had their first treatment more than two months after surgery (median of 3 months in France, Germany and the UK; 4 months in the US and Canada; 6 months in Italy) Outpatient RAI treatment was more common in N. America than in Europe 62% of US patients and 32% of Canadian patients were treated on an outpatient basis, versus 3% in Germany and the UK and 7% in France Access to clinical trials/’off-label’ drugs was more common in the UK than other countries 5% of patients had access in the UK, versus 3% in France, Germany and the US 6 Executive Summary (4) Areas for Improvement: For a minority of patients, speed of referral to a specialist could be improved There was a clear need for better information and psychological support at the time of diagnosis Ensuring that thyroid surgery was only carried out by specialist thyroid cancer surgeons would help reduce the level of post-surgical complications Prolonged calcium supplementation may be reduced by adopting the withdrawal programme protocol currently in place at NCCC Newcastle, UK Offering Thyrogen to more patients would reduce the proportion of patients experiencing side effects from thyroid hormone withdrawal For a minority of patients, delays in receiving RAI after surgery could be addressed Access to clinical trials/’off-label’ drugs could be broadened 7 2 Background & Research Objectives Project Background The Thyroid Cancer Alliance are a group of Thyroid Cancer Patient support organisations from USA, Canada, South America and Europe who have joined together in a number of projects to improve awareness of Thyroid Cancer globally. Their hard work takes many forms, however part of their work includes undertaking a Thyroid Cancer Experience Questionnaire. This questionnaire will be a ground breaking piece of work for the Alliance as it will be the first time a questionnaire of this scale has gone out to so many patients. The aim of this project is for the Alliance to be able to use the presentation at the International Thyroid Cancer Congress, that is to be held in September 2010 in Paris. Due to the very busy schedules of the Alliance members, they are looking to partner with a market research agency to conduct all of the fieldwork, analysis and preparation of the presentation for this very important piece of work. 9 Project Objectives This ground breaking survey will enable the Alliance to learn so much more about the different experiences of Thyroid Cancer across the globe. The questionnaire will focus on four main areas: Assess the life impact of a Thyroid Cancer diagnosis from a wide breadth of patients. [All Thyroid Cancer Types] Identify differences in treatment protocols worldwide Identify areas for improvement Produce an innovative key document for clinicians and patients, present this at an International Thyroid Cancer Conference in Paris 2010 10 3 Research Design: Methodology, Sample and Fieldwork Methodology How? Sample & Recruitment Criteria Quantitative Sample Survey conducted via the Internet (plus face-to-face interviews in the UK) Argentina Using Thyroid Cancer Alliance websites 10-minute interview length Fieldwork conducted in March Canada France Germany UK USA Recruitment Criteria Thyroid Cancer patients 12 4 Diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer Patient Profiles 38% of patients came from the US Argentina 13% 2% Canada 11% 9% France Germany Italy 9 out of 10 patients were female 21% 2% UK 12% 87% 38% US Other Male 5% Female Q2 Are you… Q1 Which country do you live in? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 14 Genetic Profile Just over 1 in 10 patients reported a family history of Thyroid Cancer 7% 13% Papillary (1558) 13% Follicular (209) 13% Mixed (281) Hurthle Cell (40) 12% 8% Medullary (105) 80% Yes No Anaplastic (11) 15% 9% Don't know % with family history by cancer type * Excludes 194 patients with other/don’t know cancers Q3 Do you have a family history of Thyroid Cancer? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 15 Genetic Profile Just over 1 in 10 patients with a family history have had genetic testing Yourself 83% 13% Papillary (196) 7% Follicular (27) 7% 4% Mixed (33) Family member 76% 14% 10% 12% Hurthle Cell (3) 0% Medullary (16) Yes No Don't know 88% Anaplastic (1) 0% % having had genetic testing by cancer type * Excludes 31 patients with other/don’t know cancers Q3a Have you had any genetic testing done for thyroid cancer? Q3b Has one or more of your blood relatives had genetic testing done for thyroid cancer? Base: All with a family history of thyroid cancer (N=307) N.B. Low Bases 16 History of Diagnosis The average age at diagnosis was 38.4 years Patients were diagnosed on average 5.1 years ago 32% 16% 29% 25% 18% 15% 5% 4% 55% 1% Under 19 20-29 30-39 40-49 50-59 60-69 70+ <1year 1-5 years >5 years Patient age at diagnosis (years) Q4 How old were you when you were diagnosed with Thyroid Cancer? Q5 How long is it since your diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 17 Waiting Time to Consultation One third of patients had to wait less than 2 weeks to see a specialist 8% waited more than 3 months to see a specialist 9% I was seen immediately Range (months) Median (months) Canada (42) 5.0 31% Less than 2 weeks France (26) 2 weeks – 4 weeks 30% Over 4 weeks – 3 months 20% 8% More than 3 months Germany (9) 6.5 5.0 UK (31) 4 - 48 4 - 15 Spain (5) US (56) Don’t know 4 - 24 7.0 4 - 36 6.0 4 - 11 6.0 4 - 36 4% * Excludes 12 patients from other countries Q7 How long did you wait to be seen by a thyroid specialist once you were referred? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) Q7a If you had to wait more than 3 months, please N.B. Low Bases would you say exactly how long you waited? Base: All who had to wait more than 3 months (N=181) 18 Initial Consultation An endocrinologist was the first specialist seen for over a third of patients 39% of patients noticed a lump themselves Routine check-up 25% Difficulty swallowing 34% Head & Neck Surgeon 19% Surgeon (general) 19% 15% Imaging test for other reason 12% Nuclear Medicine Specialist 11% Endocrine Surgeon Family member noticed lump 9% Hoarse voice 9% Difficulty breathing Endocrinologist 39% Noticed a lump Oncologist Vascular Surgeon 7% Q6 What led you to see your Doctor initially? Other 6% 2% 1% 9% Q8 Who was the first Thyroid Specialist that you saw when you were suspected of having Thyroid Cancer? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 19 Time to Diagnosis Just over half of patients waited less than 2 weeks before being diagnosed 18% waited more than 4 weeks Range (weeks) Median (weeks) Less than 2 weeks 52% Canada (88) 2 weeks – 4 weeks 25% France (64) Germany (32) 8.0 6.0 5 - 52 5 - 30 5 - 30 18% More than 4 weeks Don’t know 9.0 5% UK (73) 8.0 5 - 60 US (149) 8.0 5 - 64 * Excludes 30 patients from other countries Q11 How long did you wait from seeing your specialist to getting your diagnosis? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) Q11a Please would you say exactly how long you waited? Base: All respondents waiting more than 4 weeks for diagnosis (N=436) 20 Diagnostic Tests 80% of patients reported having had a neck ultrasound 80% Neck Ultrasound 51% Physical Exam Thyroid hormone suppression blood test Other 34% 23% 14% CT/CAT scan PET scan 2% 72% Fine needle aspiration MRI Two-thirds of patients reported having had surgery to gain their diagnosis 64% 6% 3% Yes 20% Q9 Which tests did you have done to evaluate your thyroid lump before you were diagnosed with thyroid cancer? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) No Don't know Q10 Did you have surgery to gain your diagnosis? 21 Communication of Diagnosis Two-thirds of patients were told they had cancer by a thyroid cancer specialist Thyroid Cancer Specialist Two-thirds of patients were given their diagnosis in person 69% Family doctor 11% In person at hospital In person at doctor’s office My doctor’s assistant 1% By a telephone call Nurse 1% By a letter Other 41% Other 15% Q12 Who told you that you had thyroid cancer? 29% 26% 1% 4% Q13 How was the diagnosis given? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 22 Histology Two-thirds of patients reported being diagnosed with papillary thyroid cancer 65% Papillary Mix papillary/ follicular types Follicular Medullary Hurthle Cell Of those with medullary thyroid cancer, a quarter stated it was familial 7% 24% 12% 9% 4% 2% Anaplastic Other Don’t know 69% 3% 5% Q14 What type of thyroid cancer were you diagnosed with? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) Yes No Don't know Q14a Was this a familial/ genetic type? Base: (N=105) 23 5 Patient Support at Diagnosis Support at Diagnosis Three-quarters of patients were not offered additional support from a nurse or other support person 93% stated they were not offered psychological support 1% 6% 3% 20% 77% Yes No 93% Don't know Yes Q15 Were you offered any additional support at the stage of diagnosis from a specialist oncology/cancer nurse or other support person? No Don't know Q17 Were you offered psychological support from a psychologist/ counsellor at the stage of diagnosis? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 25 Information at Diagnosis Over 4 in 5 patients were not given details of a patient support organisation 2% Almost two-thirds of patients were not given clear written information about their disease and its treatment 2% 14% 35% 63% 84% Yes No Don't know Yes Q16 Were you given details of a patient support organisation’s details at the stage of diagnosis? No Don't know Q18 At the time of diagnosis were you given clear written information about your disease and its treatment? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 26 Sources of Information/Support Most patients sought information on their condition from outside sources 9 in 10 sought information from the internet; half said it was the most widely used source Most useful 14% 88% Internet Pamphlets 86% Yes No 7% Patient Support Orgs. 31% 12% Books 30% 5% Family doctor 28% 5% Other patients 28% 8% 26% Family/ friends Complementary therapy Other Q19 Did you seek information/support from outside the hospital clinic at any point after you were diagnosed? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 42% 49% 7% 11% 3% 1% 7% Q19a Please could you say where you sought information or support? Q19b Which of these information sources did you find most beneficial to you personally? Base: All respondents who sought information (N=2,047) 27 6 Surgery Surgery and Complications Just over half of patients had undergone one surgical procedure on their neck 1 39% of patients experienced low blood calcium levels, and 36% experienced voice problems following surgery Low blood calcium levels 54% 39% 36% Voice problems 2 3 38% Numbness 29% Restricted neck/ shoulder movement 5% 27% 11% Vocal cord palsy 4 1% Infection Other 5 1% No complications Q20 How many neck surgeries have you had for thyroid cancer? 3% 17% 27% Q21 Please could you indicate if you experienced any of the following post surgery complications? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 29 Resolution of Complications 42% of patients stated that all their complications had now been resolved Low blood calcium levels had yet to be resolved for one third of patients 32% Low blood calcium levels 29% Numbness 31% Voice problems 31% 42% Restricted neck/ shoulder movement 24% Vocal cord palsy 29% Yes, all have been resolved Yes, most have been resolved No Q22 Have these post surgery complications now been resolved? Base: All who experienced post surgery complications (N=1,743) Infection Other 12% 1% 22% Q22a Which of your post surgery complications have not been resolved yet? Base: All whose post surgery complications had not yet been resolved (N=1,010) 30 7 RAI Treatment Radioactive Iodine Treatment 84% of patients had undergone radioactive iodine treatment. More than half had received one treatment. Papillary (1558) 16% 88% Follicular (209) Mixed (281) 90% Hurthle Cell (40) 89% Medullary (105) 84% 92% 9% Anaplastic (11) 82% % who have had RAI by cancer type Yes No Q23 Have you had radioactive iodine treatment? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) *excludes 194 patients with other/don’t know cancers 57% underwent 1 treatment 27% underwent 2 treatments 9% underwent 3 treatments Remainder underwent 4-15 treatments Q24 How many radioactive iodine treatments have you had? Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (N=2,011) 32 Time to RAI Treatment Almost half of patients had their first RAI treatment 1-2 months after surgery Over a quarter had their first RAI treatment more than 2 months after surgery Range (months) Median (months) One month or less 22% Between one and two months More than two months Canada (131) 48% 28% Don’t know 2% 4.0 3 - 24 France (58) 3.0 3 - 10 Germany (39) 3.0 3 - 60 Italy (24) UK (85) US (218) 6.0 3.0 3 - 24 3 - 24 4.0 3 - 84 *excludes 21 patients from other countries Q25 How long after surgery did you have your first radioactive iodine treatment? Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (N=2,011) Q25a Please would you say how long it was before you had radioactive iodine treatment after your first thyroid cancer surgery? Base: All who waited more than two months (N=576) 33 Preparation for RAI Treatment 81% of patients stopped taking all thyroid hormone replacement therapy Patients stopped taking thyroid hormone replacement for on avg. 4.1 weeks prior to RAI 19% Less than 1 year (271) 65% 1 – 5 years (1140) 81% Yes 78% More than 5 years (600) No Q26 Did you stop taking all thyroid hormone replacement in preparation for your radioactive iodine treatment? 93% % stopping all replacement therapy by time since diagnosis Q26a Please would you say how many weeks you stopped taking all thyroid hormone replacement? Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (N=2,011) 34 Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal 87% of patients experienced one or more symptoms of hypothyroidism when thyroid hormone replacement was stopped 80% Tiredness 61% Inability to concentrate Feeling cold 54% Weight gain 49% Depression 44% Constipation Prolonged headache No symptoms 34% 20% 13% Q27 Did you experience any symptoms of hypothyroidism when you stopped thyroid hormone replacement? Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (N=2,011) 35 Side Effects of RAI Treatment 80% of patients who underwent radioactive iodine treatment experienced one or more side effects Taste disturbance 43% Dry mouth 43% 34% Salivary/ parotid gland swelling /pain 31% Nausea/ vomiting 24% Sore neck Changes in menstrual cycle (women only) 15% Skin problems 15% Stomach pain Dry eyes No side effects 13% 12% 20% Q28 Did you experience any side effects immediately following RAI treatment? Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (N=2,011) 36 Administration of RAI Two-thirds of patients received RAI as an inpatient On average, one third received RAI as an outpatient Overall (1,976) 31% Canada (226) 32% 31% France (177) 7% Germany (425) 3% Italy (37) 0% 69% UK (235) 3% US (772) Inpatient Outpatient 62% *excludes countries with <37 patients Q29 Was your treatment given…? In Argentina (35) 91% of patients received RAI as an outpatient Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (excluding Argentina) 37 RAI Treatment Facilities 62% of patients judged the treatment facilities as good or very good Very Good 30% 32% 29% 6% 3% Very Poor Q30 How did you find the facilities in the room where your treatment was given? Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (N=2,011) 38 Radioactive Iodine Treatment 41% of patients sought the help of their family doctor, with 22% requiring antidepressants and/or sleeping tablets 22% 41% 59% 78% Yes No Q31 Did you seek help from your family doctor physician during the period before and/or after treatment? Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (N=2,011) Yes No Q32 Did you require antidepressants and/ or sleeping tablets during this time? Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (N=2,011) 39 Recovery after RAI Treatment Two-thirds of patients were able to return to normal activities within 3 months 38% Less than 1 month 1-3 months 30% 12% 4-6 months More than 6 months 10% Not returned to normal range of activities Don’t know 8% 2% Q36 How long after radioactive iodine treatment did you feel able to return to your normal range of activities? Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (N=2,011) 40 8 Thyrogen V Withdrawal Treatment with rhTSH (Thyrogen) 37% of patients were offered Thyrogen instead of withdrawal Less than 1 year (271) 41% 37% 1 – 5 years (1,140) 42% 63% More than 5 years (600) Yes 27% No % offered Thyrogen by time since diagnosis Q33 Did your Thyroid Specialist offer rhTSH (Thyrogen) instead of withdrawal from thyroid hormone? Base: All who had radioactive iodine treatment (N=2,011) 42 Treatment with rhTSH (Thyrogen) Over 9 in 10 of those who were offered Thyrogen said that the option was explained to them 9% 91% Yes No Q33a Was the option of rhTSH (Thyrogen) explained to you? Base: All who were offered Thyrogen (N=752) 43 Treatment with rhTSH (Thyrogen) 22% of patients who had Thyrogen experienced side effects 58% reported experiencing fatigue and 53% reported a headache Fatigue 22% 58% Headache 53% 43% Nausea/ vomiting Dizziness 78% Redness, pain, discoloration, hardness Other Yes No Q34 If you had rhTSH (Thyrogen) did you experience any side effects? Base: All who had rhTSH (Thyrogen) (N=995) 33% 10% 24% Q34a Please could you say what these side effects were? Base: All who experienced side effects (N=221) 44 Treatment with rhTSH (Thyrogen) 87% of those who had experienced both Thyrogen and withdrawal preferred Thyrogen 3% 11% 87% Thyrogen Withdrawal Neither Q35 If you have experienced both rhTSH (Thyrogen) and withdrawal, please could you say which you preferred? Base: All who experienced both rhTSH (Thyrogen) and withdrawal (N=915) 45 Treatment with rhTSH (Thyrogen) Just under 1 in 10 patients had to pay for Thyrogen themselves 17% Canada (126) Private Medical Insurance 46% France (93) 0% NHS/ Public Health Insurance Self funded 46% 7% Germany (234) 2% UK (109) 2% US (359) 12% % self-funded by country *excludes 74 patients from other countries Q34b Please could you say who covered the costs for your treatment with Thyrogen? Base: All who received rhTSH (Thyrogen) (N=995) 46 Treatment with rhTSH (Thyrogen) Just under a half of those who paid for Thryogen themselves were placed under financial difficulty 47% 53% Yes No Q34c Did this place you and/ or your family under financial difficulty? Base: All who had to pay for Thyrogen themselves (N=73) 47 9 Follow-Up Regime Current Treatment 84% of patients were currently on T4 replacement T4 (e.g. Levothyroxine, Synthoid) 54% of patients were currently under the care of an endocrinologist 54% Endocrinologist 84% Nuclear Physician Mixed regime of T3 and T4 9% 11% Oncologist Doctor (not a specialist) T3 (e.g. Cytomel) 1% 14% Head and Neck Surgeon 9% 3% Endocrine surgeon 2% Other 6% Other Q37 What is your current replacement hormone regime? 6% Q38 Who is currently responsible for your care? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 49 Treatment Centre A quarter of patients had changed hospitals/centres 24% Moved house 28% Dissatisfied with care 21% Needed more specialised care To access RAI/thyrogen Convenience/closer to home Insurance reasons 76% To stay with same doctor Yes No For operation Other 16% 8% 5% 4% 3% 2% 11% Q38b If you have changed hospitals/centres, please could you indicate the reason for this? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) Base: All who changed hospitals/centres (N=575) 50 Disease Status 57% of patients reported they were currently disease-free Less than 1 year (394) 34% 1 – 5 years (1318) 62% 23% More than 5 years (686) 64% % disease-free by time since diagnosis 57% 20% Papillary (1558) 59% Follicular (209) 58% 62% Mixed (281) Yes No Don't Know Hurthle Cell (40) Medullary (105) Q39 Are you currently disease free? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) Anaplastic (11) 55% 28% 18% % disease-free by cancer type *excludes 194 patients with other/don’t know cancers 51 Disease Status 14% of patients had metastatic disease 14% 15% Observation was the commonest method of management Observation 56% Radioactive Iodine 38% Surgery 36% Radiotherapy 71% Yes No Don't Know Q40 Do you have any metastatic disease outside the neck? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 15% Chemotherapy 5% Palliative Support 4% Other 20% Q40a How is this being managed? Base: All with metastatic disease (N=338) 52 10 Assessment of Cancer Journey Assessment of Cancer Journey Receiving a cancer diagnosis and uncertainty/anxiety about the future were the most difficult aspects for one fifth of patients 24% Receiving a cancer diagnosis Uncertainty/anxiety about the future 22% Side effects of treatment 11% Lack of psychological/ emotional support 8% Negative changes in lifestyle 8% Lack of information 8% Financial/ career worries Effect on relationships 3% 2% Q42 Overall what would you say was the most difficult aspect of your cancer journey? Just under half of patients stated that more information about their disease could have improved their cancer journey More information about disease Introduction to patient support groups Psychological support Clear information about treatment options Introduction to a fellow patient Quicker access to test results Access to a specialist/ oncology nurse Easier access to cancer care teams Other 45% 43% 43% 34% 27% 24% 17% 16% 22% Q43 What, if anything, could your medical team have done to improve this? Base: All respondents (N=2,398) 54