Nerve Blocks
Steven Lanski, MD
Assistant Professor Pediatrics and Emergency Medicine
Emory University
What is Pain?
What is Pain?
International Assoc for the Study of Pain:
“an unpleasant sensory and emotional
experience connected with actual or potential
tissue damage…”
afferent impulses from averse stimuli
processing of that information
Factors Involved
Thickness
Myelination
Perception
Components of the Pain System:
Sensation
Afferent fibers
“A” delta fibers: mechanoceptors (pressure)
small, lightly myelinated …”first” pain
rapid, sharp, localized
“C” fibers: polymodal (heat,chemical)
unmyelinated (slower)…”second” pain
delayed, prolonged, dull, poorly localized
Mechanism of Action
Decreases sodium influx across neuronal membranes
Decreases polarization amplitude
No action potential
No impulse
Duration of action
Dependant upon protein binding and blood
supply.
Adverse Reactions
Cardiovascular - hypotension, bradycardia
CNS - excitatory - seizures
Allergic - preservative - methylparaben
esters - tetracaine, benzocaine, procaine, cocaine
amides - lidocaine, bupivacaine, diphenhydramine (1%)
Anxiety
Locations
Facial
Supraorbital and
trochlear
infraorbital
mental
ear
dental
Extremity
digital
radial
median
ulnar
sural
tibial
Supraorbital/Supratrochlear Blocks
Helpful for multiple lacerations of forehead
and anterior scalp
Supraorbital/Supratrochlear Blocks
Landmark - superior orbital rim
Infraorbital Block
Anesthesia to lower eyelid, lateral inferior
nose and lower lip
Infraorbital Block
Landmarks - canine, infraorbital foramen
Mental Nerve Block
Anesthesia to lower lip and partial chin
Mental Nerve Block
Landmark - 2nd bicuspid
Auricular Block
Dental Blocks
Local
Inferior Alveolar - anesthesia to the mandible,
teeth and chin
Inferior Alveolar Block
Landmarks - ramus of the mandible
and coronoid notch
Digital Blocks
Dorsal and palmar digital nerves
Toes (except 1st) single needle insertion
Digital Blocks
Landmarks - bone and web space
Thumb Block
Median Nerve Block
Anesthesia to palm (radial half), 1st-3rd digits
Landmark - proximal flexor crease, radial artery,
flexor carpi radialis and palmaris longus tendons.
Ulnar Nerve Block
Anesthesia to dorsal and palmar aspect of hand
(ulnar half), ulnar half of 4th digit and 5th digit
Landmarks - flexor carpi ulnaris and ulnar artery
- dorso-ulnar aspect wrist (2nd branch)
Radial Nerve Block
Anesthesia to dorsal surface of 1st-3rd digits
and radial portion of hand
Landmark – dorso-radial aspect of wrist
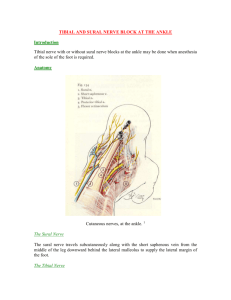
Sural Nerve Block
Anesthesia to heel and lateral half of foot
Landmarks - lateral malleolus, Achilles tendon
Posterior Tibial Block
Anesthesia to the medial aspect of the foot
Landmark - posterior tibial artery, Achilles tendon
and medial malleolus
Penile Block
Landmarks - base of penis
and Buck’s fascia
Conclusion
Choice of agents based on duration required
Beneficial for multiple or extensive injuries in
which conscious sedation will not be
performed
More comfortable than local infiltration in
some sites