Kidney Stones

Kidney Stones
Kim Applebee
Alex Kaullen
Definition
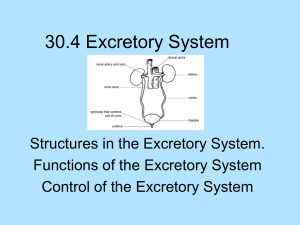
Kidney Stones are small, hard deposits of mineral and acid salts on the inner surfaces of the kidneys
Alternative names include:
Renal Lithiasis
Renal Calculi
Nephrolithiasis (Kidney Stone Disease)
Stones are classified by their location in the urinary system and their composition of crystals.
Statistics
Incidence Rate:
More than 1 million cases annually in US
1 in 272 or 3.6 per 1000 Americans develop stones annually.
80% of stones under 2mm in size
90% of stones pass through the urinary system spontaneously
Generally stone smaller than 6mm are passable
(National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; NIDDK)
(National Kidney and Urologic Disease Information Clearinghouse; NKUDIC)
Kidney Stone Formation
Causes:
Highly concentrated urine, urine stasis
Imbalance of pH in urine
Acidic: Uric and Crystine Stones
Alkaline: Calcium Stones
Gout
Hyperparathyroidism
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
UTI
Medications
Lasix, Topamax, Crixivan http://www.pilotfriend.com/aeromed/medical/images2/25.jpg
Types of Stones
Calcium Oxalate
Most common
Calcium Phosphate
Struvite
More common in woman than men.
Commonly a result of UTI.
Uric Acid
Caused by high protein diet and gout.
Cystine
Fairly uncommon; generally linked to a hereditary disorder.
Case Study
It is a hot summer day, and you are an RN in the emergency department (ED). S.R., an 18-year-old woman, comes to the ED with severe flank and abdominal pain and N/V. S.R. looks very tired, her skin is warm to touch, and she is perspiring. She paces about the room doubled-over and is clutching her abdomen. S.R. tells you that the pain started early this morning and has been pretty steady for the past hours. She gives a history of working outside as a landscaper and takes little time for water breaks. Her past medical history (PMH) includes 3 kidney stone attacks, all during late summer. Exam findings are that her abdomen is soft and w/o tenderness, but her left flank is extremely tender to touch, palpation, and percussion. You place
S.R. in one of the examination rooms and take the following VS
118/98, 90, 20, 99 F. UA shows RBC of 50 to 100 on voided specimen, WBC 0.
What key factors are important to consider?
Signs and Symptoms
What are the key findings?
Severe flank pain
Abdominal pain
Nausea and vomiting
Fatigue
Elevated temperature, BP, and respirations
UA positive for RBC
Objective Data: perspiration, clutching of the abdomen, doubled-over.
Steady Pain
Left flank tendernes
Additional S/S:
Presence of UTI
Fever or Chills
Pain in groin, labia or testicles
Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
Dysuria
Persistent urge to void http://knol.google.com/k/-/-/27ifsyywko3wx/sqc1f9/kidneystonesymptoms.jpg
What additional information should you ask this patient?
Additional Information
Family history
Current medications
Frequency of urination
Do you experience pain while urinating?
What is your typical diet?
How did patient’s kidney stones resolve themselves in the past?
http://erstories.net/wp-content/uploads/2008/10/kidneystone1a.jpg
Identify this patient’s risk factors.
Risk Factors
What are her risk factors?
Past Medical History
Hx of 3 kidney stone attacks
Dehydration/Lack of Fluids
Occupational exposure
Labor Intensive
Outdoors
Weather/Climate
Hot, dry
Additional risk factors:
Family or Personal Hx
Gender (male)
Age (20-55)
Race (Caucasian)
Diet
High sodium
High protein
Food high in oxalate
Vit A/D, grapefruit juice
Sedentary Lifestyle
Obesity
High Blood Pressure http://savethelobsters.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/ist2_4588664_half_empty_glass_of_water_with_clipping_path.jpg
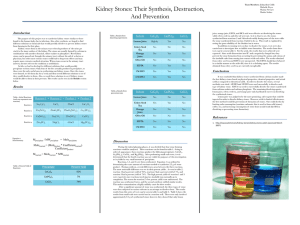
Abnormal Lab Values
BUN
Creatinine
Urine Analysis https://www.clevelandclinic.org/heartcenter/images/guide/tests/lab.gif
http://www.ganfyd.org/images/f/fb/Dipstick_bottle.jpg
Diagnostic Studies
Test and Diagnostics:
Blood Analysis
Urine Analysis
CT Scan
Abdominal x-ray
Ultrasound
Retrograde Pyelogram
Cystoscopy
Intravenous pyelography http://knol.google.com/k/-/-/PYwIQr_i/GXb8Fg/Stone%20CT.jpg
What questions do you need to ask before a patient has an
IV pyelogram?
Answer:
Do you have a history of renal failure?
Contraindicated with renal failure
Have you ever have a reaction to iodine?
Contrast contains iodine
Is there a possibility you could be pregnant?
Are you currently taking any medications?
Metformin may react with contrast
Contrast contains iodine
Check BUN and Creatinine levels prior to IVP
Nursing Diagnosis:
Acute pain r/t obstruction from renal calculi as manifested by patient being doubled-over, pacing around the room, and patient verbalizing pain upon assessment.
Goal: patient will state pain is at a manageable level within 2 hours of admission.
What are Nursing Interventions?
Nursing Goal/Interventions:
Administer pain medication as ordered by physician.
Provide non-pharmaceutical techniques such as imagery and/or meditation to relieve pain.
Patient will determine manageable pain level.
Patient will be asked about any concerns and/or fears that may be associated with pain.
Provide emotional support for the patient.
Reassess patient’s pain levels within 1 hour after administration of pain medications.
Nursing Diagnoses:
Deficient knowledge r/t fluid requirements and dietary restrictions as manifested by reoccurring stones.
Goal: Patient will state methods to prevent future stones by the time patient is D/C. A plan of care will also be created with the patient before patient is D/C to prevent reoccurrence of kidney stones.
Risk for infection r/t kidney stone obstruction of urinary tract causing stasis of urine.
Goal : Patient’s urine will be yellow and clear upon D/C and patient will not have a fever. UA with show no indication of UTI or other infection.
What are Nursing Interventions?
Treatment
Two Focuses of Treatment:
Treatment of acute problems, such as pain, n/v, etc
Identify cause and prevent kidney stones from reoccurring
Acute Treatment:
Pain Medication!!!
Strain urine for stones
Keep Hydrated
Ambulation
Diet Restrictions
Emotional Support
Invasive Procedure (may be necessary) http://www.free-press-release.com/members/members_pic/200906/img/1245774370.jpg
Surgical Procedures
Lithotripsy: used to break into smaller fragments allowing it to pass through the urinary tract.
Extracorporeal Shock-Wave (ESWL)
Percutaneous Ultrasonic
Electrohydraulic
Laser
Surgical Therapy
Nephrolithotomy (Kidney)
Pyelolithotomy (Renal Pelvis)
Ureterolithotomy (Ureter)
Basket Extraction http://www.svhm.org.au/Department_Index/Lithotripsy/images/Kidney-Stones.gif
Prevention
Patient Education
Hydration
Drink 3 liters of fluid per day (14 cups)
Water
Lemonade (citrate decrease stone formation)
Diet
Low sodium
Watch amounts of oxalate
Low protein
Exercise/Increase Activity
Medication http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_-gcaht5yp_0/SdINrCVuqdI/AAAAAAAAAGw/xeEk4-F3z_I/s320/foods+rich+in+oxalate+2.gif
Professional Resources
Renal Disease: A Manual of Patient Care by
Lynn Wenig Kagan, RN, PhD
Differential Diagnosis: Renal and Electrolyte
Disorders by Saulo Klahr, MD
MedLine Plus
www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/kidneystones.html
Journal Article #1
Purpose: Determine effectiveness of an herbal supplement made out of varuna and banana stems, “Herbmed,” on kidney stones
Study: 77 patients participated in a randomized, placebo, double-blinded study that was conducted in India from July 2007 to February 2008. Two groups were formed: Group A with calculi
5-10mm and Group B with calculi >10mm.
Results: Patients relieving the herbal supplement showed a
33% reduction in the size of their kidney stone.
Conclusion: Herbmed is an herbal treatment that may have promising effects in reducing kidney stone size and expulsion.
Journal Article #2
Purpose: To determine the possible effects fructose has on the formation of kidney stones.
Study: The researchers looked at three different cohorts (older woman, younger women, and men) over combined 48 years of follow up. 4902 new symptomatic kidney stones were documented among these three cohorts.
Results: The results from the study showed that there is a positive correlation between the intake of fructose and the development of kidney stones.
Conclusion: Fructose intake can increase insulin resistance which lowers the pH in the urine and increases ones’ risk for the development of uric acid kidney stone. Nurses need to adequately assess the patient’s diet and educate patients on ways to prevent stones.
Journal Article #3
Purpose: The study looked specifically at anxiety associated with treatment, surgery, for kidney stones.
Study: The anxiety of 66 patients was assessed before and after treatment, using three forms of measurement tools: palmar sweat test, visual analogue scale, and Speilberger state anxiety questionnaire. The two groups that were compared were open surgery to minimally/non-invasive treatment.
Results: The results from the study showed no significant change in the questionnaire answers between the three indicators of anxiety.
But, there was a fair reduction in the analogue scores postoperatively in-patients who had open surgery. These same patients also had a lower palmar sweat response. But, pre-operatively patients who going to have open surgery had higher analogue scores.
Conclusion: The two primary causes of anxiety were pain and being under anesthesia. Open surgery treatment resulted in lower levels of anxiety than non-invasive treatments.
Joey has a Kidney Stone….
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BLO5beZY4zc
References
Ackley, B.J., & Ladwig, G.B. (2006). Nursing diagnosis handbook . St. Louis: Mosby, INC..
Asselman, M., & Verkoelen, C. (2008). Fructose intake as a risk factor for kidney stone disease. Kidney
International , 73 (2), 139-140. Retrieved from CINAHL with Full Text database.
Brown, S. (1990). Quantitative measurement of anxiety in patients undergoing surgery for renal calculus disease. Journal of Advanced Nursing , 15 (8), 962-970. Retrieved from CINAHL with Full Text database.
Lewis, S.L., Heitkemper, M.M., Dirksen, S.R., O'Brien, P.G., & Bucher, L. (2007). Medical surgical nursing . St.Louis: Mosby, INC. .
Pagana, K.D., & Pagana, T.J. (2007). Diagnostic and laboratory test reference . St. Louis: Mosby, INC.
Patankar, S., Dobhada, S., Bhansali, M., Khaladkar, S., & Modi, J. (2008). A prospective, randomized, controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of Ayurvedic formulation "varuna and banana stem" in the management of urinary stones. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine , 14 (10),
1287-1290. Retrieved from CINAHL with Full Text database.
(2008, June 16). Kidney Stones . Retrieved from http://www.methodisthealth.com/tmhs/basic.do?channelId=-
1073830932&contentId=1073791018&contentType=HEALTHTOPIC_CONTENT_TYPE
(2009). Kidney Stones . Retrieved from http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/k/kidney_stones/stats.htm
(2009, June 23). Kidney Stones . Retrieved from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/kidneystones/DS00282
(2009, September 30). Kidney Stones . Retrieved from http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/kidneystones.html
(2009, October 8). Kidney Stones in Adults . Retrieved from http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/Kudiseases/pubs/stonesadults/
(2009, October 8). Kidney and Urologic DiseasesSstatistics for the United States . Retrieved from http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/kudiseases/pubs/kustats/