The peritoneum & its reflections
advertisement

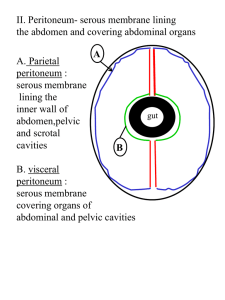
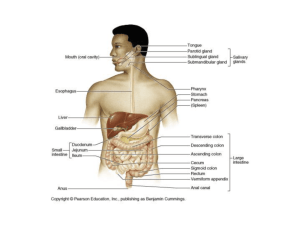
The peritoneum & its reflections J.C. BYIRINGIRO MD, MCS (ECSA), MMED Peritoneum 2 KINDS ELABORATES EXUDATE Parietal (P) Visceral (V) Leucocytes Ease movements of viscera WALL OFF INFECTION & LOCALIZE IT STORE FAT SENSITIVE Visceral - Stretch Parietal - Pain, T0, touch & pressure Peritoneum Peritoneum & viscera during development STOMACH Rapid enlargement Displacement & its rotation by liver to Left DUODENUM Rotates Right Mesentery merges with dorsal mesentery Peritoneum & viscera Formation of retroperitoneal gut Development of mesenteries & peritoneal sacs in Transv.Sect. Development of mesenteries & peritoneal sacs in Longit. Section Peritoneal formations The peritoneal cavity houses a great length of gut, most of which is covered with peritoneum. Extensive continuities are required between the parietal and visceral peritoneum to convey the necessary neurovascular structures from the body wall to the viscera. The parietal and visceral peritoneum lining the peritoneal cavity have a much greater surface area than the skin; therefore, the peritoneum must be highly convoluted. Definitions - ligs, omenta & mes PERITONEAL LIGAMENTSS = 2 folds of peritoneum connecting viscera to abdominal wall OMENTUM = 2 folds of peritoneum connecting stomach to another viscus e.g. greater & lesser omenta MESENTERY = 2 folds of peritoneum connecting intestines to post abdominal wall in adults. For children it is post and anterior Subdivisions of the Peritoneal Cavity Greater and lesser peritoneal sacs The transverse mesocolon (mesentery of the transverse colon) divides the abdominal cavity into: Supracolic compartment, containing the stomach, liver, and spleen, and an Infracolic compartment, containing the small intestine and ascending and descending colon. Subdivisions of the Peritoneal Cavity Ctn’d. The infracolic compartment is divided into right and left infracolic spaces by the mesentery of the small intestine. Free communication occurs between the supracolic and the infracolic compartments through the paracolic gutters.