Shanu_21Feb2013
advertisement

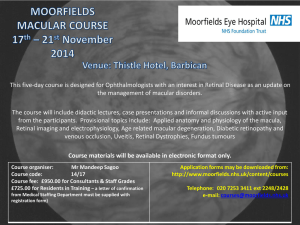
Volume 2, Issue 1, (January 2013) Overview • • • • • • • Objectives Background: Eye, Retina and Müller cells Methods Aim Results Conclusion Objectives revisited Objectives 1. What are retinal Müller cells? 2. What is the role /function of Müller cells in the retina? 3. Why RCS rats are well established retinal degeneration model? 4. What are clinical advantages and disadvantages of neural stem cell therapy? 5. What is Visual acuity? 6. What is OKR? 7. What is luminance threshold? 8. What are neurotrophic factors? 9. What experiments you would propose in addition to experiments performed in the article? 10. What are alternatives approaches besides use of small molecule for stem cell therapy? The Eye Vitreous Optic nerve Cornea Pupil Lens Retina Iris Ciliary Body Choroid Sclera • Retina: Innermost photosensitive layer which contains specialized cells which convert photons of light into nerve impulses which are relayed to the brain. Retina: Divided into 10 Layers Young, B. et al. Wheater’s Functional Histology, 5th edition. (2006) Müller cell GCL INL ONL Function • • • • • • Structural and metabolic support Trophic/Growth factors Water balance Glutamate cycling Potassium balance Progenitor cells Aim • Whether neural stem cell (NSC) derived from human embryonic stem cells (hESC) by small molecules can preserve vision following grafting into the Royal College Surgeon (RCS) rats; a model for retinal degeneration. Methods • • • • • NSCs NSC-Green Fluorescent Protein Experimental Groups Subretinal Injection Intravitreal Injection Functional Evaluation • Optokinetic Response (OKR) • Luminance Thresholds (LT) • Histology Antibodies Used in This Study Figure 1 : Functional evaluation of NSC, sham-injected, and untreated animals. Figure 2: Photoreceptor preservation and general retinal lamination Figure 3 :Confocal images showing the distribution of NSCs-GFP and NSCs Figure 4 :The distribution of NSCs and photoreceptor preservation Figure 5: Confocal images showed NSCs preserved photoreceptors and limited secondary modifications Figure 6: CNTF and GS Conclusions • NSCs derived from hESC by small molecules can survive and preserve vision for long term following subretinal transplantation in the RCS rats. • These cells migrate extensively in the subretinal space and inner retina. • There is no evidence of tumor formation or unwanted changes after grafting into the eyes. Objectives 1. What are retinal Müller cells? 2. What is the role /function of Müller cells in the retina? 3. Why RCS rats are well established retinal degeneration model? 4. What are clinical advantages and disadvantages of neural stem cell therapy? 5. What is Visual acuity? 6. What is OKR? 7. What is luminance threshold? 8. What are neurotrophic factors? 9. What experiments you would propose in addition to experiments performed in the article? 10. What are alternatives approaches besides use of small molecule for stem cell therapy?