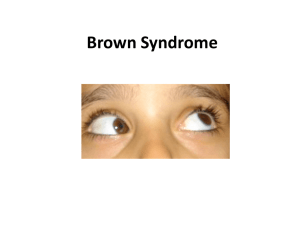
Brown’s Syndrome
Dr Sunayana Bhat
Consultant
Paediatric ophthalmology , Strabismus and Neuro
ophthalmology
Vasan eye care , Mangalore
Ph : 9611102754
chanyn9@gmail.com
Historical Background
• 1950 : Harold W. Brown
Published on an unusual motility disorder, characterized
limited elevation in adduction
• 1970s : Short anterior sheath of the superior oblique tendon
• mid 1970s : A tight or short superior oblique tendon
Pathophysiology
Brown syndrome can be divided into
• Congenital
• Acquired.
• To understand Brown’s syndrome
understand relationships.
• Particularly the relationship between the superior and inferior
oblique.
Normal superior and inferior oblique relationship
in adduction
Dr. G.Vicente
Divergence in upgaze
Brown syndromeDown
OS
shoot in attempted elevation in adduction?
Dr. G.Vicente
Brown Syndrome OS (from above)
Dr. G.Vicente
Congenital
Helveston theory
• Elongation - telescoping
mechanism
• Central tendon fibres
Wright hypothesis
• Computer model
computer simulation of Brown
syndrome, using two specific
models
(1) a short superior oblique
tendon
(2) a stiff superior oblique
tendon (stretched
sensitivity).
Stiff muscle tendon complex
( anomalous ?????)
( type of CFEOM ?????)
Aquired Brown ‘s Syndrome
Peritrochlear scarring and adhesions –
Chronic sinusitis, trauma , blepharoplasty and fat removal, and lichen sclerosus et
atrophicus and morphea
Tendon-trochlear inflammation and edema - Idiopathic inflammatory (pain and click),
trochleitis with superior oblique myositis, acute sinusitis, adult rheumatoid arthritis,
juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, possibly distant trauma
(cardiopulmonary resuscitation [CPR] and long bone fractures), and possibly
postpartum hormonal changes
Superior nasal orbital mass - Glaucoma implant and neoplasm
Tight or inelastic superior oblique muscle - Thyroid disease (inelastic muscle),
peribulbar anesthesia (inelastic tendon), Hurler-Scheie syndrome (inelastic tendon),
and superior oblique tuck (short tendon)
Acquired brown’s
Some statistics …
• 1 in 450 strabismic pts ..
• 35% have a squinting relative
• Laterality , sex predilection in conclusive
History
• Diplopia
▫ Rare : suppression.
• Pain
• Acquired Brown syndrome present with inflammatory signs.
- supranasal orbital pain
- tenderness
- intermittent limitation of elevation in adduction
Hallmark Features
• Elevation limitation in adduction
• Divergence in upgaze
• FDT +VE
Other …
• Downshoot in adduction
• Widening of palpebral fissure on adduction
• Ortho or hypo in primary position
• Head posture ( chin up )
• Audible Click
Pseudo Brown
Congenital
Acquired
• Anomalous inferior orbital
adhesions
• Posterior orbital bands
• Floor fracture
• Retinal band around inferior
oblique muscle
• Inferior temporal adhesions
Differential Diagnosis
• Inferior oblique paralysis
•
•
•
•
DEP
Fracture orbital floor
CFEOM
Grave’s disease
•Hypo in primary >15 PD
•SO Overaction
•Ductions> versions
Brown Syndrome Treatment
Treat the underlying condition.
• Surgery indications
▫ Hypotropia in primary
▫ Anomalous head posture: severe chin up.
Brown Syndrome Tx: SO tenotomy
(for the less shy)
SR
IO
LR
LR
RM
IR
MR
SR
IR
IO
Dr. G.Vicente
For those surgeons who are a little too chicken to
completely cut the SO tendon and cause a SO
palsy…
Chicken suture technique
Brown Syndrome Tx: Chicken suture
Dr. G.Vicente
Or else…….
Try the synthetic … chicken trick
“ silicone expander ”
Silicone expander
Dr. G.Vicente