Anatomy - Carolina Raptor Center
advertisement

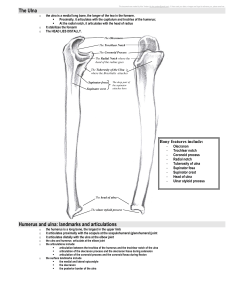
Anatomy – Radiographic and otherwise… Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Lesson Goals Avian-specific anatomy Judge a radiograph for proper positioning and quality Identify boney structures Identify soft tissue structures Recognize common abnormalities Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Feathers Remiges – wing feathers 10 primaries numbered 1 to 10 from the wrist originate from the metacarpal and digit bones 10+ secondaries (variable) numbered 1 to 10 from the wrist originate from the dorsal ulna periosteum Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Feathers <- Primaries Secondaries-> 10 3 1 1 4 Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Feathers Retrices – tail feathers 6 pairs numbered from the center Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Feathers Development In blood – very fragile Preening required for proper growth Bandages can inhibit growth Protect the feathers! Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Patagium 1 2 4 pp – propatagium lp – ligamentum propatagialis h – humerus u - ulna 3 Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Talons 1 2 4 3 Digits are numbered 1 to 4 starting from the hallux and going medially Digits 1 and 2 are the most important Talons are a thin layer of keratin over a boney core\phalange Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Beak Talons are a thin layer of keratin over a boney core\phalange Beak is a thin layer of keratin over a boney core Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute GI tract Hawks have a crop. Owls do not Two-part stomach Proventriculus Ventriculus – grinding stomach but not so much in raptors. Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Respiratory tract Trachea No diaphragm Complete rings – do not use cuffed ET tube. Must move keel to breath. Do not hold to tightly. Syrinx Common place for obstructions Source of voice Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Respiratory tract Air sacs Cervicocephalic Cranial infraorbital sinus – under eye cervical, clavicular, cranial thoracic Caudal caudal thoracic, abdominal Extend into femur, humerus, vertebrae They allow for easy endoscopic examination Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Respiratory tract Birds exchange O2 much more efficient. Two cycles required for air to enter and leave. Fresh air is always entering the lungs (on inspiration and exhalation) Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Eyes Shape AP flattened – parrots, pigeons Conical – hawks Tubular – owls Scleral ossicles No extra-occular muscles Lower lid is more mobile Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Eyes Iris contains striated muscle Complete deccussation of nerve fibers Retina Avascular No tapeturm lucidum Pectin Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Proper positioning - VD Keel should overlay the spine Legs should be pulled downward so that the elbows and stifles do not overlap Wings pulled out symmetrically Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Proper positioning - lateral Acetabullae should overlap Coracoids should overlap Wings pulled back ( requires anesthesia) Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Positioning Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Positioning Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Positioning Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Shoulder joint Complex joint with many bones Humerus Pectoral crest Ventral tubercle Head of humerus Coracoid Scapula Clavicle Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Proximal wing Humerus Ulna Distal condyles Olecranon Secondary feather attachements Notice the curve Radius Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Distal wing Ulna Radius Radial carpal bone Ulnar carpal bone Alula (D1) Major metacarpal Minor metacarpal Phalanges of D2 Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Pelvis Synsacrum Pelvis Illium Ischium Pubis Acetabullum Femur Head and neck Pygostyle Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Proximal leg Femoral condyles Patella and groove Tibiotarsus (not tibia) Fibula Tibiotarsal condyles Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Distal leg Tibiotarsal condyles Tarsometatasus Hallux (1) Metatarsal 1 Digits 2-4 Phalanges Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Soft tissue structures - VD Heart Liver “Hour-glass” Lungs Air sacs Intestines Ventriculus Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Heart-liver “Hour glass” Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Soft tissue structures - lateral Lung Heart Liver Spleen Proventriculus Ventriculus Kidney Acetabullae should overlap Coracoids should overlap Wings pulled back ( requires anesthesia) Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Compared these two What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Pre-op 2 weeks later Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Fracture healing 6 weeks later Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute What do you see? Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute And finally… Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute References Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute Questions? Dave Scott, DVM Carolina Raptor Center P.O. Box 16443 Charlotte, NC 28297 704-875-6521 Medical Environmental Research Learning INstitute