Vinsia - CCI - Case Western Reserve University
advertisement
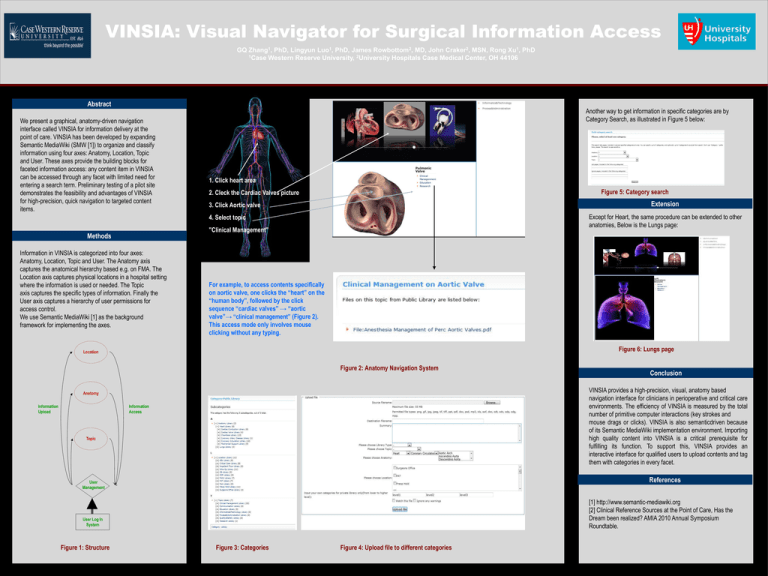
VINSIA: Visual Navigator for Surgical Information Access GQ Zhang1, PhD, Lingyun Luo1, PhD, James Rowbottom2, MD, John Craker2, MSN, Rong Xu1, PhD 1Case Western Reserve University, 2University Hospitals Case Medical Center, OH 44106 Abstract We present a graphical, anatomy-driven navigation interface called VINSIA for information delivery at the point of care. VINSIA has been developed by expanding Semantic MediaWiki (SMW [1]) to organize and classify information using four axes: Anatomy, Location, Topic and User. These axes provide the building blocks for faceted information access: any content item in VINSIA can be accessed through any facet with limited need for entering a search term. Preliminary testing of a pilot site demonstrates the feasibility and advantages of VINSIA for high-precision, quick navigation to targeted content items. Another way to get information in specific categories are by Category Search, as illustrated in Figure 5 below: 1. Click heart area Figure 5: Category search 2. Cleck the Cardiac Valves picture Extension 3. Click Aortic valve Except for Heart, the same procedure can be extended to other anatomies, Below is the Lungs page: 4. Select topic "Clinical Management" Methods Information in VINSIA is categorized into four axes: Anatomy, Location, Topic and User. The Anatomy axis captures the anatomical hierarchy based e.g. on FMA. The Location axis captures physical locations in a hospital setting where the information is used or needed. The Topic axis captures the specific types of information. Finally the User axis captures a hierarchy of user permissions for access control. We use Semantic MediaWiki [1] as the background framework for implementing the axes. For example, to access contents specifically on aortic valve, one clicks the “heart” on the “human body”, followed by the click sequence “cardiac valves” → “aortic valve”→ “clinical management” (Figure 2). This access mode only involves mouse clicking without any typing. Figure 6: Lungs page Location Figure 2: Anatomy Navigation System VINSIA provides a high-precision, visual, anatomy based navigation interface for clinicians in perioperative and critical care environments. The efficiency of VINSIA is measured by the total number of primitive computer interactions (key strokes and mouse drags or clicks). VINSIA is also semanticdriven because of its Semantic MediaWiki implementation environment. Importing high quality content into VINSIA is a critical prerequisite for fulfilling its function. To support this, VINSIA provides an interactive interface for qualified users to upload contents and tag them with categories in every facet. Anatomy Information Upload Information Access Topic References User Management [1] http://www.semantic-mediawiki.org [2] Clinical Reference Sources at the Point of Care, Has the Dream been realized? AMIA 2010 Annual Symposium Roundtable. User Log In System Figure 1: Structure Conclusion Figure 3: Categories Figure 4: Upload file to different categories