The pelvis
and
perineum
Introduction
• pelvis — bony pelvis
pelvic walls
pelvic diaphragm
pelvic organs
blood vessels and nerves
• The bony pelvis:
--- hip bones,
--- sacrum
--- coccyx
--- their connections
(joints, ligaments
and pubic symphysis)
• divisions:
--- greater pelvis
--- lesser pelvis
oblique plane:
Promontory of sacrum
Arcuate line
Pecten pubis
Pubic tubercle
Pubic crest
Superior border of
pubic symphysis
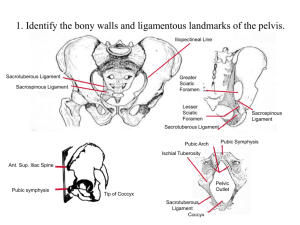
• The pelvic walls:
Post.--- sacrum, coccyx
piriformis
Ant.--- pubes, pubic symphysis
Lat.--- ilium,
body of the pubis, ischium
ligaments
obturator internus
• The floor of pelvis:
--- pelvic diaphragm
levator ani
coccygenus
deep fasciae
--- urogenital diaphragm
muscles
deep fasciae
• The pelvic organs
---The urinary bladder
---The rectum
---The pelvic part of ureter
---The prostate
---The pelvic part of ductus deferens
---The seminal vesicle
---The ejaculatory duct
---The uterus
---The ovaries
---The uterine tubes
--- The vagina
Ⅱ.The urinary
bladder
1. Position,
shape and relatons
It rests against
pubis. When it
empty, is pyramid
has a apex, body
and fundus.
2. The interior of the bladder
urinary trigone—
ureteric orifices and
internal urethral
orifice
position
boundaries
clinical notes
to be susceptical
to tuberlosis and tumor.
---The rectum:
1. Position and relations
2. The shape of the rectum
--- 12~16cm in length
--- 2 parts: pelvic part
(ampulla of rectum)
anal canal
--- 2 curves in sagittal plane:
sacral flexure
perineal flexure
--- 3 curves in coronal plane:
3. The internal features of the rectum
--- 3 transverse folds
--- 6~10 anal columns
--- anal valves
--- anal sinuses
--- dentate line
• ectoderm and entoderm
• there are differents in
epithelial lining, blood and
nerve supply and
lymphatic drainage
--- anal pecten
4.The blood vessels , lymphatic drainage
and nerves
--- Arteries: superior rectal a.
inferior rectal a.
anal a.
--- veins:
internal rectal venous plexus
external rectal venous plexus
--- lymphatic drainage:
inferior mesenteric lymph nodes
internal iliac lymph nodes
superficial inguinal lymph nodes
--- The uterus:
1. Position :
•
between the urinary bladder and rectum
• Anteflection:
bent forward between the body
and neck
• Anteversion:
bent forward between the uterus
and vagina
2. relations:
ant.--- ant. Abdominal wall,
urinary bladder, intestine
post.--- rectouterine pouch,
rectum
inf.--- vagina
lat.--- uterine tube, ovary,
broad lig., blood vessels
sup.--- intestine
3. The shape:
• pear-shaped
• anterior and posterior surfaces
• lateral borders
• fundus,
• body
• neck: supravaginal part
vaginal part
• isthmus
4. The ligaments:
• broad lig. of uterus:
• mesometrium
• mesosalpinx
• mesovarium suspensory lig. of ovary
cardinal lig. of uterus
round ligament of uterus
uterosacral lig.
5. Blood vessels:
• The uterine artery---from the internal iliac a.
• crosses above (or in front of) the ureter lateral to the
neck of uterus about 2cm
6. The lymphatic drainage:
• Fundus and upper part --- lumbar lymph nodes
• along the round lig. --superficial inguinal lymph
nodes
• lower part and neck--internal and external iliac
lymph nodes
7. The nerves
Introduction
The Perineum —
• boundaries
• divisions
• anal region
• urogenital regions in male and female
• boundaries:
--- same boundaries as the outlet of pelvis:
inferior border of the pubic symphysis,
inferior rami of the pubes,
the rami of ischia
ischial tuberosities
sacrotuberous ligaments
2. divisions:
--- anal region: anal canal
--- urogenital region:
urethra (male)
urethra, vagina (female)
3. Pelvic diaphragm:
--- levator ani
--- coccygeus
--- superior fascia of pelvic diaphragm
--- inferior fascia of pelvic diaphragm
4. The ischioanal fossa (ischiorectal fossa):
med.--- levator ani, sphincter ani externus, inferior fascia of pelvic
diaphragm
lat.--- ischial tuberosity, sacrotuberous lig., and the fascia of
obturator internus