Why Immunotherapy Fails
advertisement

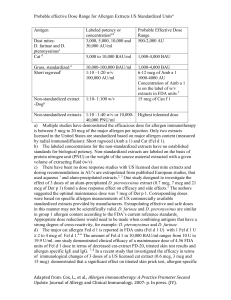
Why immunotherapy fails ? Stephen Durham Imperial College and Royal Brompton Hospital, London UK Declaration • Research funding, consultancy and lecture fees from ALK Abello • Lecture fees from Allergy Therapeutics Why immunotherapy fails ? • • • • • wrong set up wrong patient wrong allergen(s) wrong dose wrong duration Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration Immunotherapy clinic Immunotherapy clinic • Leadership/organisation of allergy clinic • Staff competencies (induction/training) • Clinic facilities – bookings, observation space – storage for vaccines / skin test reagents – safety procedures – rescue equipment • Immunotherapy protocols Alvarez-Cuesta E et al Allergy 2006; 61 Suppl. 82: 1-20 Staff competencies • • • • • • • • • Evaluation of the patients’ condition Entering data in “Immunotherapy Record Form” Injection technique Dose modification Active observation of patients Early recognition of anaphylactic reactions Treatment /monitoring of anaphylactic reactions How to perform scheduled assessments Factors determining whether to continue/stop IT Alvarez-Cuesta E et al Allergy 2006; 61 Suppl. 82: 1-20 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration Selection of patients for immunotherapy • Symptoms induced by allergen • IgE to relevant allergen (SPT/RAST) • Symptoms due to one or few allergens • No contra-indications (severe asthma, beta/blockers, inability to comply with IT) Immunotherapy in adults with birch allergy Arvidsson M, Löwhagen O Rak S J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002;109:777-83 Immunotherapy in children with perennial asthma and multiple allergen sensitivities Franklin Adkinson N et al New Engl J Med 1999; Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration Selection of allergen extracts • Standardisation - in-house reference standards (IHRs) - units of biologic potency - major allergen content (5-20 mcg major Ag) - recombinant allergens • Documented benefit (controlled trials) - efficacy - safety - children and adults - longterm effects J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 319-25 26 centres, n=410 100,000 SQ, 10,000 SQ and placebo Grass pollen immunotherapy: UK immunotherapy study Frew AJ et al, J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 319-25 Rhinoconjunctivitis QoL score 3 p<0.001 2.5 2 1.5 p=0.027 P=0.027 1 p=0.027 P=0.027 0.5 0 Baseline Season 100,000 SQ-U 10,000 SQ-U Baseline/Season Placebo Frew AJ et al, J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 319-25 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 1338-45 Sublingual Grass Tablet Immunotherapy J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 1338-45 Sublingual Grass Tablet Immunotherapy J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 1338-45 Randomised DBPC trial (n=855). 3 doses v placebo • 2,500 SQ-T • 25,000 SQ-T • 75,000 SQ-T Once daily 8 weeks pre-season and continued throughout season Sublingual Grass Tablet Immunotherapy Entire pollen season Peak pollen season 18 P=0.071 P=0.047 16 Percentage 14 12 P=0.46 P=0.19 10 8 6 4 2 0 2,500 SQ-T 25,000 SQ-T 75,000 SQ-T n=136 n=139 n=141 Durham SR et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 802-9 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration - efficacy - tolerance 50.0% P-value medication score Medication score reduction compared to placebo P-value symptom score Symptom score reduction compared to placebo 45.0% 0.50 0.45 40.0% 0.40 35.0% 0.35 30.0% 0.30 25.0% 0.25 20.0% 0.20 15.0% 0.15 10.0% 0.10 5.0% 0.05 0.0% 0.00 0 2 4 6 8 P-value Reduction in rhinoconjunctivitis score compared to placebo 8 Weeks Pre-Seasonal Treatment 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 Pre-seasonal treatment (Weeks) 17% reduction in average seasonal daily rhinoconjunctivitis symptom (p<0.05) 23% reduction in average seasonal daily medication scores ( p<0.05) Calderon MA et al. Allergy 2007 50.0% P-value medication score Medication score reduction compared to placebo P-value symptom score Symptom score reduction compared to placebo 45.0% 0.50 0.45 40.0% 0.40 35.0% 0.35 30.0% 0.30 25.0% 0.25 20.0% 0.20 15.0% 0.15 10.0% 0.10 5.0% 0.05 0.0% 0.00 0 2 4 6 8 P-value Reduction in rhinoconjunctivitis score compared to placebo > 8 Weeks Pre-Seasonal Treatment 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 Pre-seasonal treatment (Weeks) 37% reduction in average seasonal daily rhinoconjunctivitis symptom (p<0.0001) 47% reduction in average seasonal daily medication scores ( p<0.0001) Calderon MA et al. Allergy 2007 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration - efficacy - tolerance (persistent efficacy after withdrawal) 1 Grass pollen IT in adults: 3 years duration induces tolerance 0 0 8 0 6 0 1 9 9 3 1 9 9 4 ( 4 P o l l e n 3 u n t / m 0C o 2 0 1 1 9 9 5 1 0 8 . 4 ) 0 8 0 6 0 4 0 2 0 S y m p t o m s 0 3 1 3 1 7 2 1 1 4 M I T I 7T A 2 8 29 2 6 6 3 2 1 Y y4 r 3 6 1 2 0 M y 1 3 2 7 A r / 18 5 2 Y 5 2 1 1 M 2 5 1 2 9 1 2 2 6 A 07 4 2 J Y P I l Ta - c ne ab i o v U 4 1 N E e3 Durham SR et al New Engl J Med 1999;341:468-75 J hy ar y House dust mite IT in children : 3 years duration induces tolerance Des Roches A et al, Allergy 1996; 51 :430-3 Can sublingual immunotherapy induce tolerance? J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008;12:512-518 Phase III – Safety and Efficacy Medication score relative to placebo (mean) On-going and Long-term Study Percentage 100 90 38% 46% 80 p<0.0001 p<0.0001 Year 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 and 2009 70 60 n= 316 50 n=188 Grass Tablet 75,000 SQSQ-T once daily No treatment Placebo No treatment 40 Randomisation 30 20 10 0 n=318 Placebo Grazax 2005 n=163 Grazax 2006 Trial extended to additionally 2 years of treatment followed by a 2-year follow-up (Protocol amendment) Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration - efficacy - tolerance Why immunotherapy fails? • • • • • wrong set up wrong patient wrong allergen(s) wrong dose wrong duration - no efficacy - no tolerance Immunotherapy (high dose Ag) IgE IL-4 Natural exposure (low dose Ag) + IgE APC B cell Allergy Th2 (-) (-) IL-5 Eosinophil Tr Th1 IFNg IL-10 TGF-b IgG IgG4 IgA Robinson DS, Larche ML and Durham SR J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1389-97 Two types of regulatory T cells Natural Thymus Treg CD4+CD25+ T cells Foxp3 transcription factor Adaptive Tr1 Tr1 cells IL-10 Foxp3? Thn Th3 Th3 cells TGF-b Phenotypic Tregs in the nasal mucosa J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; April 17th epub p=0.1 p=0.01 p=0.35 (36.7) + Foxp3 CD4 2 cells/mm + 20 10 0 CD3 CD25 Foxp3 CD3 IL-10 Foxp3 Norm al controls Controls In season Before Placebo After IT hayfever Immunotherapy Out of season Th2 responses prevent tolerance induction? Th2 IL-4 resistor GATA3 negative feedback naive NFAT FOXP3 Treg Amplifier Positive feedback Anti-IL-4 directed therapy to augment tolerance induction against allergens TGF-β, IL-10 TGF-b IL-27 IL-10 IL-35 Mantel P-Y et al, PLOS Biology 2007; 5 (12): e329 Can we predict success or failure of immunotherapy? Change in response Time course of biomarkers during immunotherapy 2 weeks IL-10 production Grass pollen count 0 2 4 6 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 late phase response 40 44 Duration of allergen immunotherapy (weeks) J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121(5):1120-1125 48 52 Time course of changes in IL-10 and Time course of biomarkers during immunotherapy IgG-associated inhibitory activity Change in response Late allergen-induced Skin Response 4 weeks Grass Pollen season 0 2 4 6 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 52 Duration of allergen immunotherapy (weeks) late phase response J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121(5):1120-1125 Change in response IgG4 IgE-FAB inhibition Pollen count 8 weeks 0 2 4 6 8 12 Early skin response 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 Duration of allergen immunotherapy (weeks) 52 Correlation between clinical response (Sx/Rx) IgG4 and IgE-FAB inhibitory activity IgE-FAB IgG4 100 80 r= - 0.6 5 p = 0.02 60 Phl p 5 specific IgG4 (% binding) % Inhibition of allergen/IgE binding to B cells 100 r= 0.0 5 50 p= 0.9 0 40 0 2500 5000 7500 10000 Symptom/Medication score 0 2500 5000 7500 10000 Symptom/Medication score Shamji M et al 2008, unpublished Immunotherapy (high dose Ag) IgE IL-4 Natural exposure (low dose Ag) + IgE APC B cell Allergy Th2 (-) (-) IL-5 Eosinophil Tr Th1 IFNg IL-10 TGF-b IgG IgG4 IgA Robinson DS, Larche ML and Durham SR J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1389-97 Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Imperial College and Royal Brompton Hospital, London, UK M Calderon D R Wilson C Pilette S Radulovic K T Nouri-Aria M R Jacobson J N Francis M Shamji G Paraskavopoulos L Wilcock C Schmidt-Weber S J Till