Introduction to Hear..

Introduction to
Cortical Auditory Evoked
Potentials (CAEP)
Manufactured by Frye Electronics
Many thanks to the researchers at NAL who put together much of the information of this presentation.
From Sydney to Portland
Clinical Uses of HEARLab ACA
Verifying the effectiveness of hearing aid fittings on infants and adults or older children with disabilities in addition to hearing loss
Estimating audiometric thresholds in adults who may not cooperate in conventional hearing test (worker’s compensation)
Testing infants and children with auditory neuropathy
First: How does HEARLab work?
Sound stimulus Generates neural activity
Measured by electrodes Analyzed by HEARLab
What is an Auditory Evoked
Potential?
The human brain generates random electrical activity continually
We can record this electrical activity using electrodes on the scalp (EEG)
Sound stimulates neural activity in the brain that we can extract from the total EEG
The electrical activity generated from exposure to sound is called an Auditory
Evoked Potential (AEP)
Auditory Evoked Potentials
Auditory
Brainstem
Response
(ABR)
Cortical Auditory Evoked
Potential (CAEP)
From: Katz, J (Ed.) Handbook of Clinical Audiology 4 th Ed (Chpt 22)
Cortical Response
Baer, 2003
Auditory Brainstem Response
Electrode Placement
From: Hall, J.W. (1992) Handbook of Auditory Evoked Potentials
Obligatory CAEPs: Adult responses from several sites
From:Vaughan, H.G., Ritter, W. (1970) The sources of auditory evoked responses recorded from the human scalp. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology.
Vol 28.
Test Stimuli
ABR
Broadband clicks (1 ms)
Frequency-specific pips (1 ms)
HEARLab CAEP
Speech stimuli - /m/ /g/ /t/ (30 ms)
Highly frequency-specific tone bursts (30 ms)
ABR vs Audiometer Stimuli
ABR click
Audiometer tone
ABR pip
From: Abramovich (1990) ERA in Clinical Practice .
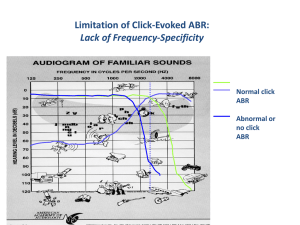
ABRs Unsuitable for Aided
Testing
ABR test occurs 1-5 ms after stimulus
Digital hearing aids have digital processing delay (2-15 ms)
Hearing aids respond poorly to ABR clicks
CAEP Better Solution for Aided
Testing
Test occurs 50-300 ms after stimulus
Stimulus uses speech stimulus (30 ms)
Frequency emphasis speech sounds
/m/ - Low frequency emphasis
/g/ - Mid frequency emphasis
/t/ - High frequency emphasis
HEARLab “Speech” Stimuli
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
/m/
/g/
/t/
Frequency (Hz)
Unlike ABR, latency of the CAEP test (50-200 ms) allows the use of longer test stimuli better suited for use with hearing aids
Auditory Neuropathy
Outer hair cells within the cochlea are functional, but sound information is not transmitted to the auditory nerve and brain properly.
Diagnosis:
Positive Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE)
Negative ABR
Some Auditory Neuropathy patients have relatively normal hearing levels. Others may have severe hearing losses
CAEP can be used to assess audibility of highlyfrequency specific tones.
Subj: normal hearing adult
Stim: /g/
No. of responses: 100 (and replicated)
2.5
µV
30 dB SL
20 dB SL
10 dB SL
-100 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 ms
Infant CAEPs with Maturity
From: Steinschneider, M., et al., (1992) Event
–related potentials in developmental
Neuropsychology. In Handbook of Neuropsychology Vol 6 Elsevier Science
HEARLab Example of CAEP
Infant Response
Adult Response
Traditional Problems with
CAEP
Unlike ABR, CAEP waveforms vary from individual to individual
Requires experience interpreting CAEP traces for clients of different ages to decide whether the sounds are likely audible to the patient
Solution!
Statistical Analysis using Multivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA) with Hotellings T 2
As the HEARLab test runs, an ongoing statistical analysis of the results are performed. If the results are < 0.05, there is a high probability a response is present.
NAL Research shows
Hotellings T 2 works!
Study done comparing a group of experts on
CAEP to the Hotellings analysis
Results shows that Hotellings is at least equal to, if not more able, than the
“composite” examiner to differentiate a CAEP from random noise at sensation levels of 10 dB or more
Example of HEARLab Test
Test Controls
Most recent epoch
Average
Statistics
Residual Noise
Clinical Use of HEARLab ACA
Aided testing with speech sounds (infants, mentally disabled)
Frequency-specific threshold estimation
(multiply disabled, worker’s compensation, auditory neuropathy)
Customer base:
Hospitals
Nursing homes
Hearing aid clinics
Early Hearing Intervention programs
Screening ABR/OAE
Diagnostic ABR
RECD/Simulated Real-ear
NEW!!!
HEARLab ACA