Your Amazing Brain:
advertisement

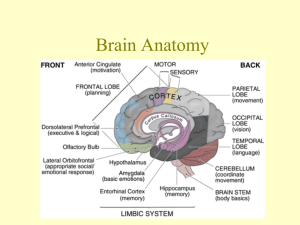
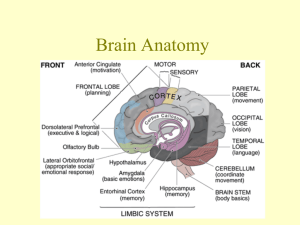
Your Amazing Brain: The Inside Tour Did You Know…? Your brain contains 100 billion neurons and 60 trillion synapses (cortex) Did You Know…? Your brain contains 100 billion neurons and 60 trillion synapses (cortex) The average adult brain weighs about 1.4 kg (3 lbs) Did You Know…? Your brain contains 100 billion neurons and 60 trillion synapses (cortex) The average adult brain weighs about 1.4 kg (3 lbs) Your brain makes up about 2% of body weight yet takes 20% of the body’s blood supply Did You Know…? Your brain contains 100 billion neurons and 60 trillion synapses (cortex) The average adult brain weighs about 1.4 kg (3 lbs) Your brain makes up about 2% of body weight yet takes 20% of the body’s blood supply Brain does not fully mature until age 25-30 years The Key Players: Frontal Lobe: reasoning, judgment, higher order thinking (NOT fully developed until 25-30 yrs) Temporal Lobe: hearing, speech Parietal Lobe: pain, pressure, touch, speech Occipital Lobe: vision The Major Parts: thalamus meninges (3 layers) corpus collosum skull hypothalamus pons cerebellum cerebrum pituitary gland medulla oblongata spinal cord What the Parts Do: Parts Functions Cerebrum (cortex) Voluntary activities, motor control, speech, vision, thinking, pain Corpus Collosum Thalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary Gland Pons Medulla Oblongata What the Parts Do: Parts Functions Cerebrum (cortex) Voluntary activities, motor control, speech, vision, thinking, pain Corpus Callosum Connects right and left hemispheres of cortex Thalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary Gland Pons Medulla Oblongata What the Parts Do: Parts Functions Cerebrum (cortex) Voluntary activities, motor control, speech, vision, thinking, pain Corpus Callosum Connects right and left hemispheres of cortex Thalamus Sends information to cortex about sensation, spatial awareness, sleep-wake cycles and consciousness Hypothalamus Pituitary Gland Pons Medulla Oblongata What the Parts Do: Parts Functions Cerebrum (cortex) Voluntary activities, motor control, speech, vision, thinking, pain Corpus Callosum Connects right and left hemispheres of cortex Thalamus Sends information to cortex about sensation, spatial awareness, sleep-wake cycles and consciousness Hypothalamus Controls pituitary gland, controls body temperature, thirst, hunger Pituitary Gland Pons Medulla Oblongata What the Parts Do: Parts Functions Cerebrum (cortex) Voluntary activities, motor control, speech, vision, thinking, pain Corpus Callosum Connects right and left hemispheres of cortex Thalamus Sends information to cortex about sensation, spatial awareness, sleep-wake cycles and consciousness Hypothalamus Controls pituitary gland, controls body temperature, thirst, hunger Pituitary Gland Secretes hormones that control the entire body A.K.A: The Master Gland Pons Medulla Oblongata What the Parts Do: Parts Functions Cerebrum (cortex) Voluntary activities, motor control, speech, vision, thinking, pain Corpus Callosum Connects right and left hemispheres of cortex Thalamus Sends information to cortex about sensation, spatial awareness, sleep-wake cycles and consciousness Hypothalamus Controls pituitary gland, controls body temperature, thirst, hunger Pituitary Gland Secretes hormones that control the entire body A.K.A: The Master Gland Pons Communicates between cortex and cerebellum, contains many cranial nerves that control face Medulla Oblongata What the Parts Do: Parts Functions Cerebrum (cortex) Voluntary activities, motor control, speech, vision, thinking, pain Corpus Callosum Connects right and left hemispheres of cortex Thalamus Sends information to cortex about sensation, spatial awareness, sleep-wake cycles and consciousness Hypothalamus Controls pituitary gland, controls body temperature, thirst, hunger Pituitary Gland Secretes hormones that control the entire body A.K.A: The Master Gland Pons Communicates between cortex and cerebellum, contains many cranial nerves that control face Medulla Oblongata Controls functions vital to life such as breathing and heartbeat The Inside View: What the Parts Do Continued: Parts Functions Cerebellum Balance and movement co-ordination Meninges Skull (cranium) Cranial nerves What the Parts Do Continued: Parts Functions Cerebellum Balance and movement co-ordination Meninges Protection of the brain 3 layers (dura, arachnoid, pia) Cerebrospinal fluid in between dura and arachnoid) Skull (cranium) Cranial nerves What the Parts Do Continued: Parts Functions Cerebellum Balance and movement co-ordination Meninges Protection of the brain 3 layers (dura, arachnoid, pia) Cerebrospinal fluid in between dura and arachnoid) Skull (cranium) Protection and support of brain Cranial nerves What the Parts Do Continued: Parts Functions Cerebellum Balance and movement co-ordination Meninges Protection of the brain 3 layers (dura, arachnoid, pia) Cerebrospinal fluid in between dura and arachnoid) Skull (cranium) Protection and support of brain Cranial nerves Bundles of nerves that exit from base of brain 12 cranial nerves Control of facial muscles, tongue, hearing, vision, smell Vagus nerve controls viscera (some internal organs) The View from Below: Optic chiasma The Brain’s Blood Supply: When Things Go Wrong: Stroke Concussion Depression When Things Go Wrong: Stroke • Cause: blood clot (embolus) or ruptured blood vessel (aneurysm) • Symptoms: weakness, trouble speaking, paralysis, severe headache, vision problems • Treatment: TPA to bust clot (must be within 3 hrs), surgery if aneurysm, therapy to minimize deficits • Prevention: control high blood pressure, healthy lifestyle When Things Go Wrong: Concussion • Brain makes contact with the cranium (skull) When Things Go Wrong: Concussion •Brain makes contact with the cranium (skull) •Injury not visible on MRI/CT When Things Go Wrong: Concussion • Brain makes contact with the cranium (skull) • Injury not visible on MRI/CT • Causes: blow to head, sudden deceleration When Things Go Wrong: Concussion • Brain makes contact with the cranium (skull) • Injury not visible on MRI/CT • Causes: blow to head, sudden deceleration • Symptoms: headache, confusion, dizziness, vision trouble, vomiting, slurred speech, loss of consciousness When Things Go Wrong: Concussion • Brain makes contact with the cranium (skull) • Injury not visible on MRI/CT • Causes: blow to head, sudden deceleration • Symptoms: headache, confusion, dizziness, vision trouble, vomiting, slurred speech, loss of consciousness When Things Go Wrong: Concussion Continued: • Treatment: Need to see a doctor ASAP, then rest, gradual return to activity (only if symptom free!) on Dr.’s advice • Prevention: Wear proper “brain bucket” for activity (A.K.A-helmet), proper training When Things Go Wrong: Depression •Persistent feelings of sadness, worthlessness, helplessness, self-blame When Things Go Wrong: Depression • Persistent feelings of sadness, worthlessness, helplessness, selfblame • Causes: complex, biochemical imbalance, may occur after stress or loss When Things Go Wrong: Depression • Persistent feelings of sadness, worthlessness, helplessness, self-blame • Causes: complex, biochemical imbalance, may occur after stress or loss • Symptoms: behaviour changes, physical complaints, eating more or less, sleep disturbances, thoughts of suicide When Things Go Wrong: Depression Continued: • Treatment: counseling, exercise, antidepressants • Under diagnosed • Perceived stigma in society still exists The End!