Thigh & Popliteal fossa
advertisement

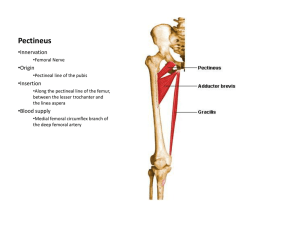
1 The femoral region (thigh)lies between the gluteal, abdominal, and perineal regions proximally and the knee region distally: anteriorly separated from the abdominal wall by the inguinal ligament posteriorly separated from the gluteal region by the gluteal fold superficially by the inferior margins of the gluteus maximus & quadratus femoris on deeper planes Structures enter and leave the top of the thigh by 3 routes: Posteriorly continuous with the gluteal region sciatic nerve Anteriorly abdominal cavity via aperture between inguinal ligament & pelvic bone Medially thigh & pelvic cavity communicates via obturator canal Vessels and nerves passing between the thigh and leg pass through the popliteal fossa posterior to the knee joint. Superficial Fascia of the Thigh Attached to the deep fascia below the inguinal ligament. Deep Fascia of the Thigh (Fascia Lata) Encloses the thigh like a trouser leg. Saphenous opening A gap in the deep fascia in front of the thigh just below the inguinal ligament. Great saphenous vein via hiatus saphenus drains into femoral vein. Filled with loose connective tissue called the cribriform fascia. 3 fascial septa pass from the inner aspect of the deep fascial sheath of the thigh to the linea aspera of the femur. Anterior compartment of thigh Femoral nerve muscles extend the leg at the knee joint. Medial compartment of thigh Obturator nerve muscles adduct the thigh at the hip joint. Posterior compartment of thigh Sciatic nerve muscles extend the thigh at the hip joint & flex the leg at the knee joint. Sartorius Quadriceps femoris Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus medialis Vastus intermedius Insertion base of patella indirectly via patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity femoral nerve Origin Anterior inferior Origin iliac spine superior ASIS&&ilium superior part acetabulum ofto notch inferior to it Insertion Superior part of medial surface of tibia In addition, the terminal ends of the psoas major and iliacus muscles pass into the upper part of the anterior compartment from sites of origin on the posterior abdominal wall. Iliacus+psoas major Ilıopsoas Extends leg at knee joint. Rectus femoris also steadies hip joint & helps iliopsoas flex thigh. Flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates thigh at hip joint. Flexes leg at knee joint (medially rotating leg when knee is flexed). Extension of leg at knee joint Quadriceps femoris Flexion of thigh at hip joint Rectus femoris Sartorius Abduction of thigh at hip joint Sartorius Lateral rotation of thigh at hip joint Sartorius 1.Gracilis 2. Pectineus 3. Adductor longus 4. Adductor brevis 5. Adductor magnus 6.Obturator externus Adductor longus Adductor brevis Adductor magnus Adductor brevis Adductor magnus “adductor part” Adductor magnus “hamstrings part” Obturator externus Adducts thigh; flexes leg; helps rotate leg medially A gap between the aponeurotic distal attachment of the adductor part of the adductor magnus & tendinous distal attachment of the hamstring part. Transmits femoral artery & vein from the adductor canal in the thigh to the popliteal fossa. Located lateral and superior to the adductor tubercle of the femur. Biceps femoris Short head Biceps femoris Long head Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Proximal attachment to ischial tuberosity deep to the gluteus maximus. Distal attachment to the bones of the leg. Thus act on two joints, producing extension @ hip joint & flexion @ knee joint. Innervation by tibial division of the sciatic nerve. Femoral artery largest & main artery of lower limb Obturator artery Inferior gluteal artery Inferior gluteal artery Obturator artery Femoral artery Distal continuation of external iliac artery. Passes under the inguinal ligament. Enters the femoral triangle midpoint of the inguinal ligament (midway between ASIS & pubic tubercle). Continues down the thigh in the adductor canal. Becomes popliteal artery behind the knee. 1. Superficial circumflex iliac artery 2. Superficial epigastric artery 3. Superficial external pudendal artery 4. Deep external pudendal artery 5. Profunda femoris artery Large and important branch Arises from the lateral side of the femoral artery below the inguinal ligament 6. Descending genicular artery Superficial & deep veins Great saphenous vein Largest superficial vein in the thigh Originates from a venous arch on the dorsal aspect of the foot. Ascends along the medial side of the lower limb. Passes through the saphenous ring. To connect with the femoral vein in the femoral triangle. Femoral vein Continuation of the popliteal vein proximal to the adductor hiatus. Enters the femoral sheath Ends posterior to the inguinal ligament, becomes external iliac vein Profunda Femoris Vein drains into the femoral vein. Obturator Vein drains into the internal iliac vein. 3 major nerves in the thigh, each associated with one of the 3 compartments: Femoral nerve anterior compartment of thigh Obturator nerve medial compartment of thigh Sciatic nerve posterior compartment of thigh o Largest branch of the lumbar plexus. o Enters the thigh lateral to the femoral artery and the femoral sheath, behind the inguinal ligament. o In the femoral triangle lies on the lateral side of the femoral artery o Enters the medial compartment of thigh through the obturator canal. o Supplies most of the adductor muscles and skin on the medial aspect of the thigh. o Descends in the midline of the thigh. o Ends by dividing into the tibial and common peroneal nerves. o Innervates all muscles in the posterior compartment of thigh and then its branches continue into the leg and foot. Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh branch of the lumbar plexus (L2& 3) Medial cutaneous nerve of the thigh branch of the femoral nerve Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh branch of the femoral nerve Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh branch of the sacral plexus Superiorly inguinal ligament Medially lateral border of adductor longus Laterally sartorius Contents; from lateral to medial o o o o o Femoral nerve Femoral sheath Femoral artery Femoral vein Deep inguinal lymph nodes A funnel-shaped fascial tube Passes deep to the inguinal ligament Encloses proximal parts of the femoral vessels and creates the femoral canal medial to them. Formed by an inferior prolongation of transversalis & iliopsoas fascia Subdivided into three smaller compartments Lateral compartment for the femoral artery. Intermediate compartment for the femoral vein. Medial compartment constitutes the femoral canal Smallest of the 3 compartments of the femoral sheath Lies between the medial edge of the femoral sheath and the femoral vein. Upper opening of the femoral canal formed by the small opening at its abdominal end. Boundaries Laterally vertical septum between femoral canal & femoral vein. Posteriorly superior ramus of the pubis covered by the pectineus muscle and its fascia. Medially lacunar ligament Anteriorly medial part of the inguinal ligament. Femoral sheath blends with the tunica adventitia of blood vessels. a potentially weak area in the abdomen The part of the femoral sheath that forms the medially located femoral canal is not. femoral hernia A protrusion of peritoneum forced down the femoral canal, pushing the femoral septum before it Intermuscular cleft in the middle 1/3 of the thigh beneath the sartorius muscle Extends from the apex of the femoral triangle to the adductor hiatus Contains o terminal part of the femoral artery o femoral vein (lies behind the artery) o deep lymph vessels o saphenous nerve o nerve to the vastus medialis o terminal part of the obturator nerve Boundaries Anteriorly and laterally vastus medialis Posteriorly adductors longus & magnus Medially sartorius, roof of the canal o An area of transition between the thigh and leg o Major route by which structures pass from one region to the other. o Formed between muscles in the posterior compartments of thigh and leg. Superolaterally Biceps femoris Superomedially Semimembranosus Inferolaterally and inferomedially Gastrocnemius Posteriorly Skin & popliteal fascia (roof) 1) Termination of the small saphenous vein 2) Popliteal arteries and veins and their branches and tributaries 3) Tibial and common fibular nerves 4) Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh 5) Popliteal lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels The sciatic nerve usually ends at the superior angle of the popliteal fossa by dividing into tibial nerve & common fibular nerve tibial nerve ,medial and larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve, descends vertically through the popliteal fossa and exits deep to the margin of plantaris muscle to enter the posterior compartment of leg. common fibular nerve , lateral, smaller terminal branch of the sciatic nerve, exits by following the medial border of the biceps femoris tendon over the lower lateral margin of the popliteal fossa, and continues to the lateral side of the leg where it swings around the neck of the fibula and enters the lateral compartment of leg Continuation of the femoral artery Begins as the femoral artery passes through the adductor hiatus. Ends lateral to the midline of the leg by dividing into anterior & posterior tibial arteries. Popliteal vein is superficial to and travels with the popliteal artery. (formation by ant. & post. tibial veins), becomes femoral vein.